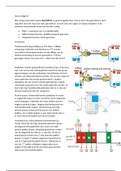
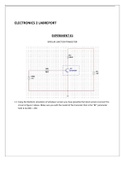
Group Dynamics: Lecture Notes
Ch 1, 2, 16 not in the exam
Lecture 1-Group Membership
Ch 1,3,4
• Behavior is the function of the person and the situation
• Social value orientation predicts:
- Concession making
- Self-sacrifice for partners in relations
- Pro-environmental behavior
- Traffic behavior
- donations
- How people respond to others’ emotions
- Cooperation within and between groups
• Entitativity→ the extent to which a group seems to be a single unified entity- a real
group
1. Similarity
2. Proximity
3. Common fate
• Collective categorization→ belongs to the larger overall group
• Subgroup categorization→ belongs to the smaller group within the large group
• Personal categorization→ everyone for themselves
• Shared group membership→ part of different groups at the same time
- Warm vs cold side→ closer to one group than another group
• Prosocials are more cooperative to ingroup members than to outgroup members
• Individualists are less cooperative regardless of the group membership
• Level of categorization- depends on identification, similarity, proximity and common
fate
Psychology of Group Memberships:
• Social comparison theory→ people rely on others for information about themselves
-Upward social comparison- people who are better→ feelings of jealousy, low self-
esteem
- Downward social comparison→ feelings of content, high self-esteem
• Social Validation motive for comparison→ to be OK or to belong
- Often more important than to gain accurate info
• Ostracism→ being excluded form a group- social exclusion
- Threatens fundamental needs: the need to belong, need for control, need for self-
esteem and the need for meaningful existence
, - Being excluded lights up the same area of the brain as physical pain
- Negative effects of being excluded are very strong in all situations
- Taking pain medicine reduces the -ve effects of exclusion- also money
Economics of Group Membership:
• Social Exchange Theory→ 3 factors- R, CL, CLailt
- R→ relation/group membership- taken in consideration
- CL→ Comparison Level- what can you expect from R
- CLalt→ Comparison level of alternatives- what you expect from alternatives
1. Satisfied + dependent→ stay with R as alternatives are worse and you are happy
2. Dissatisfied and Independent→ break with R as alternatives are better options
3. Satisfied and independent→ possibly break with R- transaction costs?
4. Dissatisfied and dependent→ stay with R -against your will- no choice
Lecture 2: Social Influence
Ch 7 and 5
How and why?
• Social influence is dynamic process and keeps on going
• Social comparison theory→ comparison happens from a social validative reason
• 2 types of influence→ normative influence and informational influence
- Majority often has both normative and informational influence
- Minority only have informational influence
Reactions:
• 4 types of reactions:
- Conversion→ privately and publicly agree
- Compliance→ publicly agree but privately disagree
- Anti-conformity→ privately agree but publicly disagree
- Independence→ privately and publicly disagree
• Compliance→ Asch line experiment
• Conversion→ autokinetic effect – sheriff experiment with the light and whether it
moves or not
• Minority can influence→ green movement, Nazis, civil rights movement
• Conversion theory→Minorities use informational influence- moscovici et al experiment
with the blue or green circle
- Profound changes in attitude which have long lasting effects
- Generalize to new settings over time
- Surprising and captures the attention
, • Dual process theory→ social influence can occur via 2 routes
- Central route→ conversion- through information processing, need for personal
validation and provides accurate knowledge
- Peripheral route→ compliance- shallow information processing, need for social
validation
- Minorities often use central route whereas majorities often use peripheral route
• Anti-conformity→ often seen in teenagers, although they agree they act like they
disagree
• Independence→nicer than anti-conformist
Power of Social Influence
• Dynamic social impact theory→ Social impact = function of strength, immediacy and
number of sources
- Strength of sources- high and low status/power
- Immediacy of sources- closer physically or digitally has stronger impact
- Number of sources- the more people the more impact
- First opinions are more likely to influence you then later opinions
- Personal needs – information vs social validation
• Situational aspects of social impact:
- More conformity if→ important task, public response, size majority (no difference
after >3), ambiguous task, unstable position, group cohesion
• 4 causes of conformity:
- Implicit influence→ when you get influenced without consciously noticing- mirror
neurons help us feel empathy- mimicry increases likings and thus conformity
- Informational influence→ to gain information
- Normative influence→ descriptive norms= what most people do, injunctive norms=
what most people should do
- Interpersonal Influence→ when people encourage/discourage conformity by simply
telling you, e.g. threats
• Cohesion:
- Social cohesion→ you feel as a whole because you like others in the group
- Task cohesion→ you share a commitment on a group- all work towards the same
goal
- Collective cohesion→ we are all in this together
- Emotional cohesion→ group pride and loyal to the group
- Structural cohesion→ defined roles- everyone has a part to play
• Pro of cohesion→ member satisfaction, higher productivity, better coordination
• Con of cohesion→ emotionally demanding (old sergeant syndrome), lower productivity,
pressure to conform
Ch 1, 2, 16 not in the exam
Lecture 1-Group Membership
Ch 1,3,4
• Behavior is the function of the person and the situation
• Social value orientation predicts:
- Concession making
- Self-sacrifice for partners in relations
- Pro-environmental behavior
- Traffic behavior
- donations
- How people respond to others’ emotions
- Cooperation within and between groups
• Entitativity→ the extent to which a group seems to be a single unified entity- a real
group
1. Similarity
2. Proximity
3. Common fate
• Collective categorization→ belongs to the larger overall group
• Subgroup categorization→ belongs to the smaller group within the large group
• Personal categorization→ everyone for themselves
• Shared group membership→ part of different groups at the same time
- Warm vs cold side→ closer to one group than another group
• Prosocials are more cooperative to ingroup members than to outgroup members
• Individualists are less cooperative regardless of the group membership
• Level of categorization- depends on identification, similarity, proximity and common
fate
Psychology of Group Memberships:
• Social comparison theory→ people rely on others for information about themselves
-Upward social comparison- people who are better→ feelings of jealousy, low self-
esteem
- Downward social comparison→ feelings of content, high self-esteem
• Social Validation motive for comparison→ to be OK or to belong
- Often more important than to gain accurate info
• Ostracism→ being excluded form a group- social exclusion
- Threatens fundamental needs: the need to belong, need for control, need for self-
esteem and the need for meaningful existence
, - Being excluded lights up the same area of the brain as physical pain
- Negative effects of being excluded are very strong in all situations
- Taking pain medicine reduces the -ve effects of exclusion- also money
Economics of Group Membership:
• Social Exchange Theory→ 3 factors- R, CL, CLailt
- R→ relation/group membership- taken in consideration
- CL→ Comparison Level- what can you expect from R
- CLalt→ Comparison level of alternatives- what you expect from alternatives
1. Satisfied + dependent→ stay with R as alternatives are worse and you are happy
2. Dissatisfied and Independent→ break with R as alternatives are better options
3. Satisfied and independent→ possibly break with R- transaction costs?
4. Dissatisfied and dependent→ stay with R -against your will- no choice
Lecture 2: Social Influence
Ch 7 and 5
How and why?
• Social influence is dynamic process and keeps on going
• Social comparison theory→ comparison happens from a social validative reason
• 2 types of influence→ normative influence and informational influence
- Majority often has both normative and informational influence
- Minority only have informational influence
Reactions:
• 4 types of reactions:
- Conversion→ privately and publicly agree
- Compliance→ publicly agree but privately disagree
- Anti-conformity→ privately agree but publicly disagree
- Independence→ privately and publicly disagree
• Compliance→ Asch line experiment
• Conversion→ autokinetic effect – sheriff experiment with the light and whether it
moves or not
• Minority can influence→ green movement, Nazis, civil rights movement
• Conversion theory→Minorities use informational influence- moscovici et al experiment
with the blue or green circle
- Profound changes in attitude which have long lasting effects
- Generalize to new settings over time
- Surprising and captures the attention
, • Dual process theory→ social influence can occur via 2 routes
- Central route→ conversion- through information processing, need for personal
validation and provides accurate knowledge
- Peripheral route→ compliance- shallow information processing, need for social
validation
- Minorities often use central route whereas majorities often use peripheral route
• Anti-conformity→ often seen in teenagers, although they agree they act like they
disagree
• Independence→nicer than anti-conformist
Power of Social Influence
• Dynamic social impact theory→ Social impact = function of strength, immediacy and
number of sources
- Strength of sources- high and low status/power
- Immediacy of sources- closer physically or digitally has stronger impact
- Number of sources- the more people the more impact
- First opinions are more likely to influence you then later opinions
- Personal needs – information vs social validation
• Situational aspects of social impact:
- More conformity if→ important task, public response, size majority (no difference
after >3), ambiguous task, unstable position, group cohesion
• 4 causes of conformity:
- Implicit influence→ when you get influenced without consciously noticing- mirror
neurons help us feel empathy- mimicry increases likings and thus conformity
- Informational influence→ to gain information
- Normative influence→ descriptive norms= what most people do, injunctive norms=
what most people should do
- Interpersonal Influence→ when people encourage/discourage conformity by simply
telling you, e.g. threats
• Cohesion:
- Social cohesion→ you feel as a whole because you like others in the group
- Task cohesion→ you share a commitment on a group- all work towards the same
goal
- Collective cohesion→ we are all in this together
- Emotional cohesion→ group pride and loyal to the group
- Structural cohesion→ defined roles- everyone has a part to play
• Pro of cohesion→ member satisfaction, higher productivity, better coordination
• Con of cohesion→ emotionally demanding (old sergeant syndrome), lower productivity,
pressure to conform