Polina Lobacheva
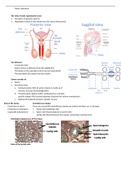
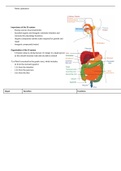
> Right atrium
> right ventricle
> lung circulation
> pulmonary artery (15 mmHg)
> pulmonary capillaries
> picks up O2
> pulmonary venules
> pulmonary veins
> left atrium
> left ventricle
> systemic circulation
> aorta (80 - 110 mmHg)
> systemic arteries and arterioles
> systemic capillaries
> systemic venules / lymphatics
> systemic veins
> inferior / superior vena cava
> right atrium
Blood circulation and blood components:
- Pulmonary circulation pumps blood at a low blood pressure (8-
20mmHg) to the lungs to acquire O2 and eliminate CO2
- The heart pumps blood at 5 - 25 liters per minute from the left
ventricle of the heart at high pressure (80 - 110 mmHg)
- Blood travels through organs via blood vessels:
- Arteries > arterioles > capillaries > venules > veins
- veins and venules provide cells with O2/ nutrients (from
arteries, arterioles and capillaries)and remove H+ and CO2
- lymphatic vessels collect fluid that leaks from capillaries
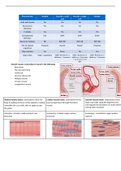
Blood composition: Red blood cells and haemoglobin: blood contains about 2 liters of RBCs = 2 x 10^13
1. 55% of blood volume is plasma (40 ml/kg (2.5- cells
3L): - Measured using a hematocrit as 40 - 50% of blood volume
a. Water, proteins (albumin, fibrinogen), - Biconcave disc shaped
nutrients, hormones - No nuclei, organelles or mitochondria
b. Major role in buffering H+ using proteins and - Flow through capillary single file as rouleaux
HCO3- - Lifespan of a 100 - 120 days
2. Blood plasma osmolarity is 280 - 300 mosmol/l: RBCs contain hemoglobin which has for peptide chains (two alpha and two beta) and
Na+(140), Cl-(105), HCO3- (25), K+(4), glucose (5) for haem groups which combines to four O2 molecules
mmol/l - Hb molecules normally deliver one O2 molecule to a cell
3. 45% of blood volume is cellular: red, white and - Each RBC contains about 280 million Hb molecules
platelets - RBCs deliver about 250 ml of O2 per minute at rest
The lumen is narrower in arteries than in veins but the walls are thicker in arteries. 3 layers:
1. Tunica intima (inner layer): lined by endothelial cells
2. Tunica media (middle layer): smooth muscle layer
, Polina Lobacheva
3. Tunica externa (outer layer): adventitia layer of elastic connective
tissue
Arteries and arterioles:
- Large arteries have good elasticity (aorta): absorbs pressure
generated by cardiac contractions to reduce peak systolic pressure
and ensure better flow
- Large arteries have a narrow lumen but thick muscular walls: dilate or
constrict in a regulated manner to regulate and help direct blood flow
to active organs
- Small arteries/arterioles are small and act as resistance vessels: have
limited elasticity but do contain smooth muscle and regulate blood
pressure and flow through capillaries
Their diameter is regulated by many many mediators released by the
inner lining endothelial cells:
1. Vasodilators (histamine, nitric oxide, prostaglandins, bradykinin and
adenosine)
2. Vasoconstrictors (endothelin, thromboxane, noradrenaline (alpha) adrenaline (a))
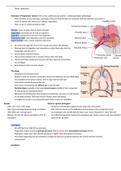
Structure of blood vessels and capillaries:
Vascular resistance and turbulent flow: Capillary endothelium (single cell layer):
- According to Poisseuille’s law vascular resistance and 1. Continuous capillaries are the most common type
therefore blood flow is proportional to the 4th power of 2. Fenestrated capillaries are permeable leaky (renal)
the radius of the vessels: if the radius is reduced by 1/2 3. Discontinuous capillaries from sinusoids in liver/spleen/bone
the flow is reduced to 1/16 - No tunica media or externa
- Turbulent flow is caused by vessel obstruction - Controls fluid movement
(atherosclerosis) - Site of gas diffusion (O2 and CO2)
- Viscosity is proportional today in haematocrit of blood: - Respond to vasoactive growth factors, mediators and cytokines
increase in haematocrit = increase in viscosity - Stimulate blood clotting
- Participate in angiogenesis
> Right atrium
> right ventricle
> lung circulation
> pulmonary artery (15 mmHg)
> pulmonary capillaries
> picks up O2
> pulmonary venules
> pulmonary veins
> left atrium
> left ventricle
> systemic circulation
> aorta (80 - 110 mmHg)
> systemic arteries and arterioles
> systemic capillaries
> systemic venules / lymphatics
> systemic veins
> inferior / superior vena cava
> right atrium
Blood circulation and blood components:
- Pulmonary circulation pumps blood at a low blood pressure (8-
20mmHg) to the lungs to acquire O2 and eliminate CO2
- The heart pumps blood at 5 - 25 liters per minute from the left
ventricle of the heart at high pressure (80 - 110 mmHg)
- Blood travels through organs via blood vessels:
- Arteries > arterioles > capillaries > venules > veins
- veins and venules provide cells with O2/ nutrients (from
arteries, arterioles and capillaries)and remove H+ and CO2
- lymphatic vessels collect fluid that leaks from capillaries
Blood composition: Red blood cells and haemoglobin: blood contains about 2 liters of RBCs = 2 x 10^13
1. 55% of blood volume is plasma (40 ml/kg (2.5- cells
3L): - Measured using a hematocrit as 40 - 50% of blood volume
a. Water, proteins (albumin, fibrinogen), - Biconcave disc shaped
nutrients, hormones - No nuclei, organelles or mitochondria
b. Major role in buffering H+ using proteins and - Flow through capillary single file as rouleaux
HCO3- - Lifespan of a 100 - 120 days
2. Blood plasma osmolarity is 280 - 300 mosmol/l: RBCs contain hemoglobin which has for peptide chains (two alpha and two beta) and
Na+(140), Cl-(105), HCO3- (25), K+(4), glucose (5) for haem groups which combines to four O2 molecules
mmol/l - Hb molecules normally deliver one O2 molecule to a cell
3. 45% of blood volume is cellular: red, white and - Each RBC contains about 280 million Hb molecules
platelets - RBCs deliver about 250 ml of O2 per minute at rest
The lumen is narrower in arteries than in veins but the walls are thicker in arteries. 3 layers:
1. Tunica intima (inner layer): lined by endothelial cells
2. Tunica media (middle layer): smooth muscle layer
, Polina Lobacheva
3. Tunica externa (outer layer): adventitia layer of elastic connective
tissue
Arteries and arterioles:
- Large arteries have good elasticity (aorta): absorbs pressure
generated by cardiac contractions to reduce peak systolic pressure
and ensure better flow
- Large arteries have a narrow lumen but thick muscular walls: dilate or
constrict in a regulated manner to regulate and help direct blood flow
to active organs
- Small arteries/arterioles are small and act as resistance vessels: have
limited elasticity but do contain smooth muscle and regulate blood
pressure and flow through capillaries
Their diameter is regulated by many many mediators released by the
inner lining endothelial cells:
1. Vasodilators (histamine, nitric oxide, prostaglandins, bradykinin and
adenosine)
2. Vasoconstrictors (endothelin, thromboxane, noradrenaline (alpha) adrenaline (a))
Structure of blood vessels and capillaries:
Vascular resistance and turbulent flow: Capillary endothelium (single cell layer):
- According to Poisseuille’s law vascular resistance and 1. Continuous capillaries are the most common type
therefore blood flow is proportional to the 4th power of 2. Fenestrated capillaries are permeable leaky (renal)
the radius of the vessels: if the radius is reduced by 1/2 3. Discontinuous capillaries from sinusoids in liver/spleen/bone
the flow is reduced to 1/16 - No tunica media or externa
- Turbulent flow is caused by vessel obstruction - Controls fluid movement
(atherosclerosis) - Site of gas diffusion (O2 and CO2)
- Viscosity is proportional today in haematocrit of blood: - Respond to vasoactive growth factors, mediators and cytokines
increase in haematocrit = increase in viscosity - Stimulate blood clotting
- Participate in angiogenesis