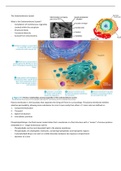
The Endomembrane System
What is the Endomembrane System?
- Compilation of membranous organelles
- Located within the cytoplasm
- Structural divide
- Functional diversity
- Evolved from mitochondria
Plasma membrane: is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane exhibits
selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others. It’s main roles are defined as:
1. Compartmentalisation
2. Transport
3. Signal transduction
4. Intercellular junctions
Phospholipid bilayer: the fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins
embedded in it – Singer & Nicholson (1972)
- Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane
- Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
- A phospholipid bilayer can exist as a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments
- Diameter of 2.5nm
, Membrane Proteins & Functions: Membrane proteins and functions:
- Mosaic – collection/clustering of proteins
- Membrane proteins specific to cell type
- Receptors can often infer cell/organ function
- Key roles in cellular homeostasis
What is the Endomembrane System?
- Compilation of membranous organelles
- Located within the cytoplasm
- Structural divide
- Functional diversity
- Evolved from mitochondria
Plasma membrane: is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane exhibits
selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others. It’s main roles are defined as:
1. Compartmentalisation
2. Transport
3. Signal transduction
4. Intercellular junctions
Phospholipid bilayer: the fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins
embedded in it – Singer & Nicholson (1972)
- Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane
- Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
- A phospholipid bilayer can exist as a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments
- Diameter of 2.5nm
, Membrane Proteins & Functions: Membrane proteins and functions:
- Mosaic – collection/clustering of proteins
- Membrane proteins specific to cell type
- Receptors can often infer cell/organ function
- Key roles in cellular homeostasis