Polina Lobacheva
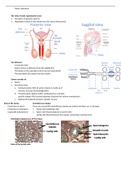
The roles of male reproductive tract:
1. Formation of gametes (sperm)
2. Deposition of these in the female tract (for sexual intercourse)
Vas deferens:
- A muscular tube
- Sperm moves as deferens (from the epididymis)
- Terminates in the ejaculatory duct (near prostate gland)
- The ejaculatory duct opens into the urethra
Semen consists of:
1. Sperm
2. Secretions from:
a. Seminal vesicles: 60% of semen volume is made up of
mucous, fructose and prostaglandins
b. Prostate gland: alkaline buffer, clotting factors, prostate-
specific-antigen (PSA) and prostasomes (required for calcium transduction)
c. Bulbourethral glands (Cowper's gland): mucous
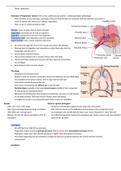
Role of the testes: Seminiferous tubules:
- Production of sperm There are around 800 seminiferous tubules per testicle and there are 2 cell types:
- Production of androgens 1. Sertoli cells (epithelial cells)
(especially testosterone) 2. Sperm cells (found adjacent to sertoli cells)
- Leydig cells (found between the tubules and produce testosterone)
Histological appearance of the testes:
Role of the Sertoli cells:
, Polina Lobacheva
- They line the walls of the seminiferous tubules
- Source of nutrition to sperm
- Phagocytosis of dead sperm
- Formation of the blood-testis barrier
- Production of seminiferous tubule fluid
Determinants of male and female development:
1. Male and female glands are derived from the same embryological tissue: the urogenital ridge
2. This remains undifferentiated until week 6
3. The double genital duct system:
a. Mullerian ducts: capable of developing into female reproductive organs
b. Wolffian ducts: capable of developing into male reproductive organs
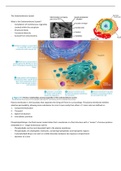
Spermatogenesis: production of mature sperm (continuous)
- Each ejaculate (2-10ml) contains around 100 million sperm per ml
- Occurs in the seminiferous tubules
- Sperm stem cells = spermatogonia, which are located at the periphery
- Developing sperm cells move towards the lumen as they mature
Stages of spermatogenesis: clonal expansion via mitosis
First stage of meiotic division: primary spermatocytes divide into two secondary spermatocytes
The roles of male reproductive tract:
1. Formation of gametes (sperm)
2. Deposition of these in the female tract (for sexual intercourse)
Vas deferens:
- A muscular tube
- Sperm moves as deferens (from the epididymis)
- Terminates in the ejaculatory duct (near prostate gland)
- The ejaculatory duct opens into the urethra
Semen consists of:
1. Sperm
2. Secretions from:
a. Seminal vesicles: 60% of semen volume is made up of
mucous, fructose and prostaglandins
b. Prostate gland: alkaline buffer, clotting factors, prostate-
specific-antigen (PSA) and prostasomes (required for calcium transduction)
c. Bulbourethral glands (Cowper's gland): mucous
Role of the testes: Seminiferous tubules:
- Production of sperm There are around 800 seminiferous tubules per testicle and there are 2 cell types:
- Production of androgens 1. Sertoli cells (epithelial cells)
(especially testosterone) 2. Sperm cells (found adjacent to sertoli cells)
- Leydig cells (found between the tubules and produce testosterone)
Histological appearance of the testes:
Role of the Sertoli cells:
, Polina Lobacheva
- They line the walls of the seminiferous tubules
- Source of nutrition to sperm
- Phagocytosis of dead sperm
- Formation of the blood-testis barrier
- Production of seminiferous tubule fluid
Determinants of male and female development:
1. Male and female glands are derived from the same embryological tissue: the urogenital ridge
2. This remains undifferentiated until week 6
3. The double genital duct system:
a. Mullerian ducts: capable of developing into female reproductive organs
b. Wolffian ducts: capable of developing into male reproductive organs
Spermatogenesis: production of mature sperm (continuous)
- Each ejaculate (2-10ml) contains around 100 million sperm per ml
- Occurs in the seminiferous tubules
- Sperm stem cells = spermatogonia, which are located at the periphery
- Developing sperm cells move towards the lumen as they mature
Stages of spermatogenesis: clonal expansion via mitosis
First stage of meiotic division: primary spermatocytes divide into two secondary spermatocytes