Polina Lobacheva
Importance of the GI system:
- Energy sources (macronutrients)
- Essential organic and inorganic nutrients (vitamins and
minerals) for physiology functions
- Organic compounds (amino acids) required for growth and
repair
- Inorganic compounds (water)
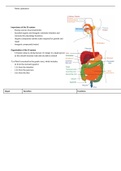
Organisation of the GI system
- 5.5meters long in a living human; it’s longer in a dead person
as the smooth muscles relax and are able to stretch
7L of fluid is secreted by the gastric tract, which includes:
- 2L from the stomach (gastric)
- 1.5L from the intestine
- 1.5L from the pancreas
- 0.5L from the liver
Organ Secretion Functions
, Polina Lobacheva
Mouth and pharynx Salt and water - moisten food Chewing (mastication), swallowing
Salivary glands Mucus - lubrication
Amylase - polysaccharide digestive enzyme
Oesophagus Mucus (lubrication) Move food to stomach (peristaltic waves)
Stomach HCl - solubilisation of particles, kill microbes, activation of Store, mix, dissolve, continue digestion, regulate rele
pepsinogen to pepsin into intestine
Pepsin - protein digestive enzyme
Mucus - lubricate and protect epithelial surface
Pancreas Enzymes - digest CHO, fats and proteins Secretion of enzymes and bicarbonate (neutralises
Bicarbonate - Neutralise HCl entering small intestine acidity from the stomach), non-digestive endocrine
functions
Liver Bile salts - Solubilise water-insoluble fats Secretion of bile and other non-digestive functions
Bicarbonate - neutralise HCl entering small intestine
Organic waste products and trace metals - elimination in faeces
Gallbladder Stores and concentrates bile between meals
Small intestine Enzymes - food digestion Digestion and absorption of most substances
Salt and water - maintain fluidity of luminal contents
Mucus - lubrication
Large intestine Mucus (lubrication) Storage and concentration of undigested matter,
absorption of salt and water, defecation
Structure of the GI tract wall, the 4 major tissue layers (listed from the inside out):
1. Mucosa (inner lining)
a. Epithelial cells which are moistened by secretion
b. Gland cells that secrete digestive juices
c. Endocrine gland cells that secrete GI hormones
Importance of the GI system:
- Energy sources (macronutrients)
- Essential organic and inorganic nutrients (vitamins and
minerals) for physiology functions
- Organic compounds (amino acids) required for growth and
repair
- Inorganic compounds (water)
Organisation of the GI system
- 5.5meters long in a living human; it’s longer in a dead person
as the smooth muscles relax and are able to stretch
7L of fluid is secreted by the gastric tract, which includes:
- 2L from the stomach (gastric)
- 1.5L from the intestine
- 1.5L from the pancreas
- 0.5L from the liver
Organ Secretion Functions
, Polina Lobacheva
Mouth and pharynx Salt and water - moisten food Chewing (mastication), swallowing
Salivary glands Mucus - lubrication
Amylase - polysaccharide digestive enzyme
Oesophagus Mucus (lubrication) Move food to stomach (peristaltic waves)
Stomach HCl - solubilisation of particles, kill microbes, activation of Store, mix, dissolve, continue digestion, regulate rele
pepsinogen to pepsin into intestine
Pepsin - protein digestive enzyme
Mucus - lubricate and protect epithelial surface
Pancreas Enzymes - digest CHO, fats and proteins Secretion of enzymes and bicarbonate (neutralises
Bicarbonate - Neutralise HCl entering small intestine acidity from the stomach), non-digestive endocrine
functions
Liver Bile salts - Solubilise water-insoluble fats Secretion of bile and other non-digestive functions
Bicarbonate - neutralise HCl entering small intestine
Organic waste products and trace metals - elimination in faeces
Gallbladder Stores and concentrates bile between meals
Small intestine Enzymes - food digestion Digestion and absorption of most substances
Salt and water - maintain fluidity of luminal contents
Mucus - lubrication
Large intestine Mucus (lubrication) Storage and concentration of undigested matter,
absorption of salt and water, defecation
Structure of the GI tract wall, the 4 major tissue layers (listed from the inside out):
1. Mucosa (inner lining)
a. Epithelial cells which are moistened by secretion
b. Gland cells that secrete digestive juices
c. Endocrine gland cells that secrete GI hormones