Manishshaw929
On this page, you find all documents, package deals, and flashcards offered by seller manishshaw929.
- 234
- 0
- 5
Community
- Followers
- Following
239 items

Chemistry class 12th Average_Rate_of_Hydrolysis_Butyl_Chloride
The average rate of hydrolysis of butyl chloride depends on factors such as solvent, temperature, and reaction conditions. In aqueous solutions, butyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis via an SN1 mechanism, forming butanol and hydrochloric acid. The reaction rate is influenced by the stability of the carbocation intermediate, with tertiary butyl chloride reacting faster than primary or secondary forms. In polar protic solvents like water or ethanol, the reaction rate increases due to better solvatio...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
The average rate of hydrolysis of butyl chloride depends on factors such as solvent, temperature, and reaction conditions. In aqueous solutions, butyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis via an SN1 mechanism, forming butanol and hydrochloric acid. The reaction rate is influenced by the stability of the carbocation intermediate, with tertiary butyl chloride reacting faster than primary or secondary forms. In polar protic solvents like water or ethanol, the reaction rate increases due to better solvatio...

Chemistry class 12th Products_of_Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a process where an electric current passes through an electrolyte, causing chemical reactions that break down compounds into their elements or new substances. The products of electrolysis depend on the electrolyte and the electrodes used. In aqueous solutions, the products can be influenced by the reactivity of ions and water. For example, electrolysis of water produces hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode. Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution (brine) yields hydrog...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages •
Electrolysis is a process where an electric current passes through an electrolyte, causing chemical reactions that break down compounds into their elements or new substances. The products of electrolysis depend on the electrolyte and the electrodes used. In aqueous solutions, the products can be influenced by the reactivity of ions and water. For example, electrolysis of water produces hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode. Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution (brine) yields hydrog...

Chemistry class 12th Kohlrausch_Law
Kohlrausch’s Law states that the limiting molar conductivity (Λ₀) of an electrolyte is the sum of the individual contributions of its ions: Λ₀ = λ₀⁺ + λ₀⁻, where λ₀⁺ and λ₀⁻ are the limiting molar conductivities of the cation and anion, respectively. This law is particularly useful for strong electrolytes, whose conductivity varies linearly with the square root of concentration. For weak electrolytes, it helps determine their dissociation constant. It is wide...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
Kohlrausch’s Law states that the limiting molar conductivity (Λ₀) of an electrolyte is the sum of the individual contributions of its ions: Λ₀ = λ₀⁺ + λ₀⁻, where λ₀⁺ and λ₀⁻ are the limiting molar conductivities of the cation and anion, respectively. This law is particularly useful for strong electrolytes, whose conductivity varies linearly with the square root of concentration. For weak electrolytes, it helps determine their dissociation constant. It is wide...

Chemistry class 12th Limiting_Molar_Conductivity_298K.
Limiting molar conductivity (Λ₀) at 298 K is the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution, where ion interactions are negligible. It is determined using Kohlrausch’s Law, which states that Λ₀ is the sum of the individual ion conductivities. For strong electrolytes, Λ₀ is obtained by extrapolating conductivity measurements, while for weak electrolytes, it is calculated using the Ostwald dilution law. Λ₀ is crucial in electrochemistry for understanding ion transport,...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
Limiting molar conductivity (Λ₀) at 298 K is the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution, where ion interactions are negligible. It is determined using Kohlrausch’s Law, which states that Λ₀ is the sum of the individual ion conductivities. For strong electrolytes, Λ₀ is obtained by extrapolating conductivity measurements, while for weak electrolytes, it is calculated using the Ostwald dilution law. Λ₀ is crucial in electrochemistry for understanding ion transport,...

Chemistry class 12th Electrolytic_Cells_and_Electrolysis
Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions through electrolysis. These cells consist of an electrolyte solution and two electrodes: the cathode (where reduction occurs) and the anode (where oxidation occurs). A power source forces electrons to flow, breaking compounds into their elements or forming new substances. Common applications include electroplating, metal refining, and water electrolysis to produce hydrogen and oxygen. Unlike galvanic cells, whic...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages •
Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions through electrolysis. These cells consist of an electrolyte solution and two electrodes: the cathode (where reduction occurs) and the anode (where oxidation occurs). A power source forces electrons to flow, breaking compounds into their elements or forming new substances. Common applications include electroplating, metal refining, and water electrolysis to produce hydrogen and oxygen. Unlike galvanic cells, whic...

Chemistry class 12th Batteries_Class_12_Chemistry
Batteries (Class 12 Chemistry) Batteries are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. They are classified into primary batteries (non-rechargeable) and secondary batteries (rechargeable). Primary batteries, like dry and alkaline cells, are used in remote controls and clocks. Secondary batteries, such as lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, are rechargeable and used in automobiles and electronic devices. Batteries consist of an anode,...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages •
Batteries (Class 12 Chemistry) Batteries are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. They are classified into primary batteries (non-rechargeable) and secondary batteries (rechargeable). Primary batteries, like dry and alkaline cells, are used in remote controls and clocks. Secondary batteries, such as lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries, are rechargeable and used in automobiles and electronic devices. Batteries consist of an anode,...

Chemistry class 12th Primary_Batteries_Class_12_Chemistry
Primary Batteries (Class 12 Chemistry) Primary batteries are non-rechargeable electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through irreversible redox reactions. Common examples include dry cells (Leclanché cell) used in flashlights and alkaline batteries, which offer longer life and stability. These batteries have a limited lifespan and must be discarded after use. They typically consist of an anode (zinc), a cathode (manganese dioxide or other materials), and an...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages •
Primary Batteries (Class 12 Chemistry) Primary batteries are non-rechargeable electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through irreversible redox reactions. Common examples include dry cells (Leclanché cell) used in flashlights and alkaline batteries, which offer longer life and stability. These batteries have a limited lifespan and must be discarded after use. They typically consist of an anode (zinc), a cathode (manganese dioxide or other materials), and an...

Chemistry class 12th Secondary_Batteries_Class_12
Secondary Batteries (Class 12) Secondary batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries, can be recharged and reused multiple times by reversing the chemical reaction through an external electric source. Common examples include lead-acid batteries, used in automobiles, and lithium-ion batteries, widely used in smartphones and electric vehicles. These batteries store energy through redox reactions and offer longer lifespans compared to primary batteries. Their efficiency depends on charge-dis...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 2 pages •
Secondary Batteries (Class 12) Secondary batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries, can be recharged and reused multiple times by reversing the chemical reaction through an external electric source. Common examples include lead-acid batteries, used in automobiles, and lithium-ion batteries, widely used in smartphones and electric vehicles. These batteries store energy through redox reactions and offer longer lifespans compared to primary batteries. Their efficiency depends on charge-dis...
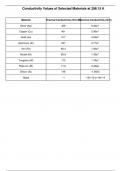
Chemistry class 12th Conductivity_Values_298K
Conductivity Values at 298K At 298K (25°C), conductivity values vary depending on the material and medium. Pure water has a low conductivity of about 0.055 µS/cm, while seawater reaches 50 mS/cm due to dissolved salts. Metals like copper and silver exhibit extremely high conductivities, around 5.8 × 10⁷ S/m and 6.3 × 10⁷ S/m, respectively. Aqueous solutions' conductivity depends on ion concentration; for example, 0.01 M KCl has 1.41 mS/cm. Temperature affects conductivity, typically ...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
Conductivity Values at 298K At 298K (25°C), conductivity values vary depending on the material and medium. Pure water has a low conductivity of about 0.055 µS/cm, while seawater reaches 50 mS/cm due to dissolved salts. Metals like copper and silver exhibit extremely high conductivities, around 5.8 × 10⁷ S/m and 6.3 × 10⁷ S/m, respectively. Aqueous solutions' conductivity depends on ion concentration; for example, 0.01 M KCl has 1.41 mS/cm. Temperature affects conductivity, typically ...

Chemistry class 12th Conductivity measurement
Conductivity measurement determines a material's ability to conduct electrical current, often used in liquids, metals, and semiconductors. It is quantified in Siemens per meter (S/m) and depends on ion concentration in solutions or electron mobility in solids. Common methods include two-electrode, four-electrode, and inductive (toroidal) sensors. Applications range from water quality monitoring and industrial process control to material science and electronic component testing. Factors like tem...
- Book
- Class notes
- • 1 pages •
Conductivity measurement determines a material's ability to conduct electrical current, often used in liquids, metals, and semiconductors. It is quantified in Siemens per meter (S/m) and depends on ion concentration in solutions or electron mobility in solids. Common methods include two-electrode, four-electrode, and inductive (toroidal) sensors. Applications range from water quality monitoring and industrial process control to material science and electronic component testing. Factors like tem...
