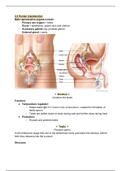
2.4 Human reproduction
Male reproductive organs include:
- Primary sex organs = testis
- Ducts = epididymis, sperm duct and urethra
- Accessory glands (eg: prostate gland)
- External gland = penis
✶ Scrotum ✶
Contains the testis
Function:
● Temperature regulator:
○ Keeps testis @2-3°C below body temperature, needed for formation of
fertile sperm
○ Testis are pulled closer to body during cold and further away during heat
● Protection:
○ Houses and protects testis
✶ Testis ✶
Produce sperm
In the embryonic stage they are in the abdominal cavity just below the kidneys, before
birth they descend into the scrotum
Structure:
, ● Two oval structures that are suspended outside the body in the scrotum
● Made of lobules (compartments) that contain convoluted tubules =
seminiferous tubules (250m in each testis)
● Germinal epithelium lines the tubules
● Between the tubules are groups of endocrine cells, interstitial cells/Leydig
Function:
● Produce:
○ Sperm (male gametes) by germinal layer
○ Testosterone (male hormone) by interstitial cells
✶ Ducts ✶
a. Epididymis
Seminiferous two bills join to form epididymis (highly convoluted tubes that is about 5 m
long)
Function:
● Mature to become motel and fertile
● Store for several months
b. Vas deferens (sperm duct)
Muscular sperm duct that is a continuation of the epididymis. Leaves scrotum, passes
through prostate gland and enters urethra
Function:
● Pushes mature sperm forward by strong peristaltic waves (contraction of muscle
walls) from the epididymis into the urethra aka ejaculation
c. Urethra
Duct at the end of the uro-genital system leading to the exterior
Function:
● Transport of semen and urine (no together)
✶ Prostate gland ✶
Plum-sized gland surrounding urethra at base of bladder
Function:
● Secrete fluid that is the transport of sperm and contains enzymes that makes
them more active. This fluid makes up one-third of seminal fluid (semen)
✶ Cowper’s gland ✶
Two Cowper's glands are found at the base of the penis
,Function:
● Neutralize acidic urine that may still be present in urethra
● Lubricate urethra and external urethral opening to protect sperm from
mechanical damage during ejaculation
✶ Penis ✶
Male external organ
Structure:
● Consists of special spongy tissue (erectile tissue) that runs the length of the
penis.
3 sections:
○ Two are situated on the dorsal side, corpus cavernosum
○ One on the vertical side the, corpus spongiosum
● Primary mechanism that brings about an erection
○ Dilation of dorsal and central arteries supplying blood to the penis
○ More blood fills erectile tissue
○ Chambers cause penis to lengthen and stiffen aka erection
○ Without an erection sperm cannot be transferred to the female vagina
Function:
● Deposit semen with sperm into female vagina during copulation
Distinction of human penis:
● Only mammal that has no erectile bone (baculum) in penis = relies on
engorgement (filling up) with blood to become erect
● Not attached to abdominal wall, hangs free
✶ Seminal Vesicle ✶
● Glands posterior to urinary bladder
● Each has a short duct that joins with ductus deferens at the ampulla to form an
ejaculation duct
, ✶ Semen ✶
Consist of sperm from the testes and seminal fluid from the sperm doctor and
accessory glands
Seminal fluid = viscous, has fructose, proteins and prostaglandins
Ejaculation vs erection
Erection = stiffening of penis
Ejaculation = expulsion of semen
Female reproductive organs include:
- Ovaries
- Accessory organs- fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina
- External genitalia (vulva)
✶ Ovaries ✶
2 almond-shaped organs found in the pelvic capacity, held in position by
ligaments
Structure:
● A germinal epithelium layer surrounds each ovary
● Primary follicles (tiny sac-like structures containing an immature eggs are
embedded in the outer layer) - children born with these follicles
● Primary follicle develops into a mature follicle (Graafian follicle)
● After ovulation, the Graafian follicle forms corpus luteum (yellow body)
Function:
Male reproductive organs include:
- Primary sex organs = testis
- Ducts = epididymis, sperm duct and urethra
- Accessory glands (eg: prostate gland)
- External gland = penis
✶ Scrotum ✶
Contains the testis
Function:
● Temperature regulator:
○ Keeps testis @2-3°C below body temperature, needed for formation of
fertile sperm
○ Testis are pulled closer to body during cold and further away during heat
● Protection:
○ Houses and protects testis
✶ Testis ✶
Produce sperm
In the embryonic stage they are in the abdominal cavity just below the kidneys, before
birth they descend into the scrotum
Structure:
, ● Two oval structures that are suspended outside the body in the scrotum
● Made of lobules (compartments) that contain convoluted tubules =
seminiferous tubules (250m in each testis)
● Germinal epithelium lines the tubules
● Between the tubules are groups of endocrine cells, interstitial cells/Leydig
Function:
● Produce:
○ Sperm (male gametes) by germinal layer
○ Testosterone (male hormone) by interstitial cells
✶ Ducts ✶
a. Epididymis
Seminiferous two bills join to form epididymis (highly convoluted tubes that is about 5 m
long)
Function:
● Mature to become motel and fertile
● Store for several months
b. Vas deferens (sperm duct)
Muscular sperm duct that is a continuation of the epididymis. Leaves scrotum, passes
through prostate gland and enters urethra
Function:
● Pushes mature sperm forward by strong peristaltic waves (contraction of muscle
walls) from the epididymis into the urethra aka ejaculation
c. Urethra
Duct at the end of the uro-genital system leading to the exterior
Function:
● Transport of semen and urine (no together)
✶ Prostate gland ✶
Plum-sized gland surrounding urethra at base of bladder
Function:
● Secrete fluid that is the transport of sperm and contains enzymes that makes
them more active. This fluid makes up one-third of seminal fluid (semen)
✶ Cowper’s gland ✶
Two Cowper's glands are found at the base of the penis
,Function:
● Neutralize acidic urine that may still be present in urethra
● Lubricate urethra and external urethral opening to protect sperm from
mechanical damage during ejaculation
✶ Penis ✶
Male external organ
Structure:
● Consists of special spongy tissue (erectile tissue) that runs the length of the
penis.
3 sections:
○ Two are situated on the dorsal side, corpus cavernosum
○ One on the vertical side the, corpus spongiosum
● Primary mechanism that brings about an erection
○ Dilation of dorsal and central arteries supplying blood to the penis
○ More blood fills erectile tissue
○ Chambers cause penis to lengthen and stiffen aka erection
○ Without an erection sperm cannot be transferred to the female vagina
Function:
● Deposit semen with sperm into female vagina during copulation
Distinction of human penis:
● Only mammal that has no erectile bone (baculum) in penis = relies on
engorgement (filling up) with blood to become erect
● Not attached to abdominal wall, hangs free
✶ Seminal Vesicle ✶
● Glands posterior to urinary bladder
● Each has a short duct that joins with ductus deferens at the ampulla to form an
ejaculation duct
, ✶ Semen ✶
Consist of sperm from the testes and seminal fluid from the sperm doctor and
accessory glands
Seminal fluid = viscous, has fructose, proteins and prostaglandins
Ejaculation vs erection
Erection = stiffening of penis
Ejaculation = expulsion of semen
Female reproductive organs include:
- Ovaries
- Accessory organs- fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina
- External genitalia (vulva)
✶ Ovaries ✶
2 almond-shaped organs found in the pelvic capacity, held in position by
ligaments
Structure:
● A germinal epithelium layer surrounds each ovary
● Primary follicles (tiny sac-like structures containing an immature eggs are
embedded in the outer layer) - children born with these follicles
● Primary follicle develops into a mature follicle (Graafian follicle)
● After ovulation, the Graafian follicle forms corpus luteum (yellow body)
Function: