Pure Mathematics
Quadratics
Domain: The set of possible input values for a function.
Range: The set of possible output values for a function.
Roots: The values of x for which f(x) = 0.
Graphs and transformations
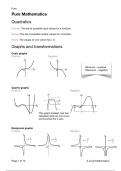
Cubic graphs
Positive Negative
Minimum - positive
Maximum - negative
Quartic graphs
Positive Negative
This graph instead, has two
repeated roots so one curve
just touches the x-axis
Reciprocal graphs
Positive Negative
Page 1 of 12 A Level Mathematics
, Pure
Points of In ection
Curvature: Second derivative/rate of change of the gradient (f’’(x))
Convex function: When f’’(x) > 0
Concave function: When f’’(x) < 0
Point of in ection: When the graph switches from convex to concave (or vice versa) or
when f’’(x) changes sign
Translating graphs
• Translations
• Stretches
• Re ections
Functions and graphs
Mapping
• Functions can only either be one-to-one or many-to-one
Composite functions
• When two or more functions are combined to make a new function
Inverse functions
• The domain of f(x) is the range of f⁻¹(x)
• The range of f(x) is the domain of f⁻¹(x)
Combining transformations
Page 2 of 12 A Level Mathematics
fl
fl fl