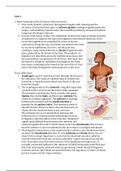
TUMORS OF SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINES
COLONIC POLYPS
Raised outgrowth of COLONIC MUCOSA protruding into lumen.
May be pre-cancerous.
Removal can prevent colon cancer.
POLYPS CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS:
NON-NEOPLASTIC POLYPS:
1. INFLAMMATORY POLYPS.
2. HYPERPLASTIC POLYPS.
3. HAMARTAMATOUS POLYPS.
NEOPLASTIC POLYPS:
1. ADENOMAS/ ADENOMATOUS POLYPS.
2. ADENOCARCINOMA / COLON CANCER.
HYPERPLASTIC POLYPS
Decreased epithelial cell turnover and delayed shedding of surface epithelial cells leading to
pilling up of goblet and absorptive cells.
Usually Benign
Most common type of polyp.
Common in rectosigmoid colon/ left colon.
Normal cellular structure, no dysplasia, no malignant potential.
Less than 5mm in diameter.
Classically have a “saw tooth” or serrated pattern. Morphologic Hallmark
Usually, no special screening required after biopsy.
, INFLAMMATORY POLYPS
Occur because of chronic cycles of injury and healing.
Classic triad: rectal bleeding, mucous discharge, and inflammatory lesions on anterior rectal
wall.
E.g Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome.
Doesn’t increase the risk of malignancy.
HAMARTAMATOUS POLYPS
A hamartoma is a local malformation made up of an abnormal mixture of cells and tissue.
Caused by germline mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes.
2 types:
1. Juvenile polyps
2. Peutz jeghers syndrome
1. JUVENILE POLYPS
Focal malformations of epithelium and lamina propria.
Occur in children < 5 years
Usually, pedunculated.
Solitary lesions are called retention polyps ( no malignant potential ).
JUVENILE POLYPOSIS SYNDROME:
Autosomal dominant disorder, mutations of SMAD 4 gene.
Multiple juvenile polyps ( 50-100 ).
Increased risk of cancer.
Extra intestinal manifestations: Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations.
COLONIC POLYPS
Raised outgrowth of COLONIC MUCOSA protruding into lumen.
May be pre-cancerous.
Removal can prevent colon cancer.
POLYPS CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS:
NON-NEOPLASTIC POLYPS:
1. INFLAMMATORY POLYPS.
2. HYPERPLASTIC POLYPS.
3. HAMARTAMATOUS POLYPS.
NEOPLASTIC POLYPS:
1. ADENOMAS/ ADENOMATOUS POLYPS.
2. ADENOCARCINOMA / COLON CANCER.
HYPERPLASTIC POLYPS
Decreased epithelial cell turnover and delayed shedding of surface epithelial cells leading to
pilling up of goblet and absorptive cells.
Usually Benign
Most common type of polyp.
Common in rectosigmoid colon/ left colon.
Normal cellular structure, no dysplasia, no malignant potential.
Less than 5mm in diameter.
Classically have a “saw tooth” or serrated pattern. Morphologic Hallmark
Usually, no special screening required after biopsy.
, INFLAMMATORY POLYPS
Occur because of chronic cycles of injury and healing.
Classic triad: rectal bleeding, mucous discharge, and inflammatory lesions on anterior rectal
wall.
E.g Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome.
Doesn’t increase the risk of malignancy.
HAMARTAMATOUS POLYPS
A hamartoma is a local malformation made up of an abnormal mixture of cells and tissue.
Caused by germline mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes.
2 types:
1. Juvenile polyps
2. Peutz jeghers syndrome
1. JUVENILE POLYPS
Focal malformations of epithelium and lamina propria.
Occur in children < 5 years
Usually, pedunculated.
Solitary lesions are called retention polyps ( no malignant potential ).
JUVENILE POLYPOSIS SYNDROME:
Autosomal dominant disorder, mutations of SMAD 4 gene.
Multiple juvenile polyps ( 50-100 ).
Increased risk of cancer.
Extra intestinal manifestations: Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations.