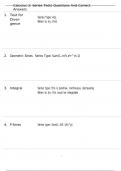
Solutions
channels & pores
Transport systems (p-glycoprotein) (energy pump)
Direct penetration of the membrane (drug molecule must be
lipid soluble
3 ways a drug passes across the membrane
loading dose
use of a higher dose than what is usually used for treatment to
allow the drug to reach the critical concentration sooner
molecules supplied by the body
Physiologic conditions, receptor function is regulated by:
mimic or block the action of the body's own regulatory
molecules
All that drugs can do at receptors is :
alter the rate of per existing processes.
Because drug action limited to mimicking or blocking the body's
own regulatory molecules, drugs cannot give cells new
functions. Rather, drugs can only?
agonist
activates drug/cell
antagonist
,blocks neurotransmitter
selectivity
the extent to which a receptor binds with a particular drug rather
than other molecules
affinity
measure of the tightness with which a drug binds to the receptor
partial agonists
bind to and partially stimulate receptors
right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time, (right
documentation)
what are the 5 rights of drug administration?
Nurse is the last line of defense for patient. They need to know
what medications are appropriate for the patient, what drugs are
contraindicated for the patient, the probable consequences of the
interactions between drug & patient.
Discuss the nurse's role in applying pharmacological principles
to patient care in the following aspects:
Date time order was written
name of medication *
dosage *
route *
frequency *
signature of prescriber
, What is needed for a medication order?
What are the bare minimum infos needed,
1.collect the baseline data needed to evaluate therapeutic and
adverse(undesired) responses: medical/surgical history, chronic
conditions, physical assessment findings
2.Identfying high-risk patients: diagnostic test results,
medications they are currently taking, allergies
3.Assessing the patients capacity for self-care: finnical, patterns
of health care, social/ physiological history, level of education,
social support
what do you do in the Pre-administration Assessment (before
you give meds)?
- Read the medication order carefully
- Verify the identity of the patient
- Read the medication label careful
- Verify dosage calculations
- Implement any special handling that the drug may require
- Do not administer any drug you do not understand the reason
for its use (safety check)
Certain drugs have more than one indication (the reason we are
giving a medication) and the dosage may differ depending on
the indication for which the drug is being used. Many drugs can
be administered by more than one route. What does a nurse have
to do for Dosage and Administration?
RN must know the expected THERAPEUTIC EFFECT (what is
it that we are trying to achieve with this medication)
promoting patient adherence also know as compliance or