BIOD 151 A&P 1 Module 6: 6.1 Anatomy of the Endocrine System
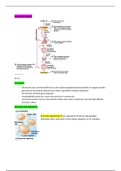
6.1 Anatomy of the Endocrine System Introduction to the Endocrine System ● Endocrine uses chemical messengers to coordinate various roles of body ● Chemical messengers, called hormones, use bloodstream to interact with cells ● Endocrine is slower than nervous system to react to external and internal stimuli ● Cells can react to hormone with specific receptors through lock-and-key method ● Certain cells can only respond to specific hormones and not others based on what receptors they have ● Hormone-organic chemical produced by one set of cell that affects a different set of cells ○ Influence metabolism of recipient cell ○ Many are proteins coded for by genes and synthesized within cytoplasm at the ribosomes ○ Hormones then packaged into vesicles at Golgi apparatus and secreted at plasma membranes ● 2 types of Hormones: Peptide and Steroid ● Peptide Hormones ○ Peptide hormones derived from proteins, peptides, or catecholamines ○ Activate existing enzymes in cell ○ Act quickly but temporarily ● Steroid Hormones ○ Derived from cholesterol ○ Act slower than peptide hormones since it takes time to synthesize new proteins than to activate enzymes that are already present in the cell ○ Stored in fat droplets in cytoplasm until released ○ Can enter nucleus and cell freely without needing to worry about membrane ○ Once in nucleus, steroid hormone binds to receptors=hormone-receptor-complex ■ Activates specific genes leading to protein synthesis ○ Sustained effect on metabolism of cell compared to peptide hormones since they can create new proteins for the cell ● Endocrine glands ○ Ductless, secrete contents directly into bloodstream for distribution throughout body ● Exocrine glands ○ Ducts that secrete contents into epithelial surface ○ Ex. salivary glands and they release salivary amylase into mouth Endocrine Organs ● Primary endocrine organs ○ Only job is to secrete hormones ○ Secrete hormones chemically regulating body functions ○ Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, and pancreas ○ Left and right adrenal glands ■ Located superiorly to each kidney
Written for
- Institution
- BIOD 151
- Course
- BIOD 151
Document information
- Uploaded on
- September 4, 2023
- Number of pages
- 10
- Written in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Other
- Person
- Unknown
Subjects
-
biod 151 ap 1 module 6 61 anatomy of the endocr
Document also available in package deal