Stanford University - Coursera
Latest uploads at Stanford University - Coursera. Looking for notes at Stanford University - Coursera? We have lots of notes, study guides and study notes available for your school.
-
43
- 0
-
2
All courses for Stanford University - Coursera
Latest content Stanford University - Coursera
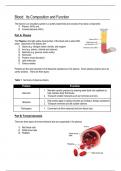
Blood: Its Composition and Function The blood in our circulatory system is a watery based fluid and consists of two basic components: 1) Plasma (55%) and, 2) Formed elements (45%) Part A: Plasma The Plasma is the light yellow liquid portion of the blood and is about 90% water. Dissolved in the plasma are: 1) Gases (e.g. nitrogen carbon dioxide, and oxygen) 2) Ions (e.g. sodium, chloride and calcium) 3) Nutrients (e.g. glucose, amino acids) 4) Hormones 5) Proteins (most ...
BLOOD TRANSFUSION Jared At the end of 30 minutes, the group should be able to: •Define Blood Transfusion •Identify purposes of the procedure •Cite situations in which blood transfusion is needed clinical •Enumerate the different transfusion reactions with its signs interventions and appropriate nursing •Classify and describe the different blood products and how it is being used BLOOD TRANSFUSION •It is a procedure in which a patient receives a blood...
preparation and staining of peripheral blood film
BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS CASE DISCUSSION Reference Ranges: PH (7.35 – 7.45), pCO2 (35 - 45) mmHg, pO2(80 – 100) mmHg , HCO3 (20 – 30) mmol/L, Base Excess (+3 to -3), Sodium (135 – 145) mmol/L, Chloride (90 – 110) mmol/L, Potassium (3.5 -5.5) mmol/L 1. A 24 year-old woman is found subconscious at Jevanjee Gardens by some bystanders. The medics are called and, upon arrival, find her with an oxygen saturation of 88% on room air. She is brought into the Kenyatta National Hospital (...
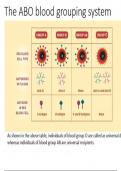
Blood is made up of cells, plasma and plasma proteins. Blood dyscrasias & diseases may be derived from abnormalities in the different components of blood. These include: I. Anaemia: Decrease in the number of RBCs/ Hb. II. Erythrocythemia: Increase in RBCs. Types of anaemia: May involve disorders that affect shape, size, number & level of Hb of the erythrocytes. These include: Iron deficiency anaemia Pernicious...
INTRODUCTION Blood products components prepared in a blood transfusion center (RBCs ,platelets , FFP, cryoprecipitate) or Plasma derivatives from pooled plasma donation (albumin, immunoglobulins, coagulation factors) Blood components: Derivatives from whole blood of a donor by phlebotomy. Prepared by centrifugation or apheresis. RBCs, WBCs, platelets and plasma Purpose of separation of components 1. Different components are useful for different patients 2...
EPIDEMIOLOGY 2-7 of every 1,000 births result in birth injuries despite advances in obstertic and intrapartum care Birth injuries account for 2%-3% of neonatal deaths ( 5-8 deaths per 100,000). Instrument deliveries ( vaacum or forcep) Very low birth weight or extreme prematurity Large babies – birth weight over about 4,000 grams Fetal anomalies PREDISPOSING FACTORS Prolonged or rapid delivery Cephalopelvic disproportion, small ma...
BACTERIAL IDENTIFICATION TESTS 11.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous chapter we have discussed various methods of isolation of bacteria. The bacteria thus isolated needs to be further identified to genus and species level. The identification is required so as to cure the illness or the infection caused due to the bacteria by using appropriate antibiotics. Identification also holds significance for epidemiological purposes. OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you will be able to ...
BASICS OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Public Health • The science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through organized community efforts Public health core functions • Assessment • The assessment & monitoring of the health of communities and populations at risk to identify health problems and priorities • Policy Development • The formulation of public policies designed to solve identified local and national health problems and priorities • ...