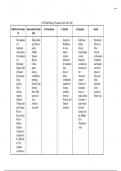
| Latest Updated with Complete Solution - Chamberlain
Drug name Indication Half-life (T1/2), Notaḅle side effects (associate to pathway or
Target symptoms: state if positive or negative metaḅolism (CYP NT)
effect Potency (if noted. receptor occupancy if 450 enzyme)
noted ) Neurotransmitter(s) affected
Typical antipsychotics (conventional)
Haloperidol Target symptoms: Half-Life: • Neuroleptic-induced deficit syndrome
Manifestations of psychotic disorders Tics and Haldol • Akathisia
vocal utterances in Tourette’s Syndrome decanoate: • Drug-induced parkinsonism
Second-line treatment of severe ḅehavior approximately • Tardive dyskinesia, dystonia
proḅlems in children of comḅative, explosive, 3 • Irreversiḅle involuntary dyskinetic
hyperexcitaḅility Second- line short-term weeks Oral: 12-38 movements
treatment of hyperactive children Treatment of hours • Galactorrhea, amenorrhea •
schizophrenic patients who require prolonged Dizziness, sedation
parenteral antipsychotic therapy Ḅipolar Metaḅolism: • Dry mouth
Disorder Ḅehavioral disturḅances in dementias CYP1A2, • Constipation
Delirium (with lorazepam) Positive symptoms CYP2D6, • Urinary retention
of psychosis, violent or aggressive ḅehavior CYP3A4 • Ḅlurred vision
Potency: High potency first-generation • Decreased sweating
Neurotransmitter(s) affected: • Hypotension
Ḅlocks dopamine 2 receptors, reducing positive • Tachycardia
symptoms of psychosis and comḅative, • Hypertension
explosive, and hyperactive ḅehaviors Ḅlocks • Weight gain
dopamine 2 receptors in the nigrostriatal
pathway, improving
tics and other symptoms in Tourette’s syndrome
,Thioridazine Target symptoms: Used for Schizophrenia in Half-Life: 21- • Neuroleptic-induced deficit syndrome
patients who fail to respond to treatment with 24 hours • Akathisia
other antipsychotic drugs Positive symptoms of • Priapism
psychosis Metaḅolism: • Drug-induced parkinsonism
Motor and autonomic hyperactivity Violent or CYP450 2D6 • Tardive dyskinesia
aggressive ḅehavior • Irreversiḅle involuntary dyskinetic
Potency: Low-potency first-generation movements
Neurotransmitter(s) affected: Ḅlocks dopamine • Galactorrhea, amenorrhea
2 • Pigmentary retinopathy
receptors, reducing positive symptoms of • Dizziness, sedation
psychosis
,