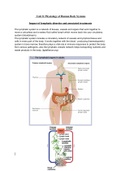
What is innate immunity?
Innate immunity, also called natural immunity, is the first line of defense. This
type of defense is in place before an infection takes place and can function
immediately. It is comprised of physical, chemical, cellular, and molecular
defenses.
How does the skin act as a physical barrier?
The skin’s design makes it a strong physical barrier. It has closely packed cells in
multiple layers that are continuously being shed. Keratin covers the skin, which
creates a salty, acidic environment inhospitable to microbes. It also contains
antimicrobial proteins and lysozymes that inhibit microorganisms and help to
destroy them.
What cells are involved in innate immunity?
The cells responsible for this response include neutrophils, macrophages,
dendritic cells (DC), natural killer (NK) cells, and intraepithelial lymphocytes.
Describe each type of leukocyte and explain their function:
- Neutrophils are the most abundant in the body and are an early
responder in innate immunity and use phagocytosis to kill microbes.
- Eosinophils are active in parasitic infections and allergic responses.
- Basophils release histamine and proteolytic enzymes.
- Monocytes are the largest in size and are released from the bone marrow
and mature into macrophages and dendritic cells where they engage in
the inflammatory response and phagocytize foreign substances and
cellular debris.
- Macrophages have a long life span, reside in the tissues, and are the first
phagocyte that organisms encounter. Neutrophils and macrophages work
together on behalf of the host’s initial defense system.
, -
Describe adaptive immunity:
Adaptive immunity, also called acquired immunity, is the second line of defense
and includes both humoral and cellular mechanisms that respond to cell-specific
substances known as antigens. Adaptive immunity is acquired through previous
exposure to infections and other foreign agents. It can not only distinguish self
from nonself but can recognize and destroy specific foreign agents based on
their different antigenic properties. This response takes more time but is
extremely effective.
What are antigens?
Antigens are present on the surface of pathogens or other foreign substances
that elicit the adaptive immune response.
What are the primary cells of adaptive immunity?
The primary cells of the adaptive immune system are the lymphocytes, APCs
(antigen presenting cells), and effector cells.
Describe B & T lymphocytes and discuss their role in immunity:
B lymphocytes produce the antibodies (humoral immunity) and T lymphocytes
provide the cell-mediated immunity. B and T lymphocytes have the unique
function as the only cells to recognize specific antigens present on the surface of
pathogens and to remember them in the future.