Answer Key
,Answer Key for v v
Workbook for Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11e
v v v v v
Chapter 1 v
SECTION 1: ASSESSING YOUR UNDERSTANDING
v v v v
Activity A
v
1. Illness
2. Client
3. Healthcare delivery system v v
4. Health
5. Medicaid
Activity B
v
1. Holism
2. Healthcare team v
3. Medicare
4. Diagnosis-related groups v
5. Wellness
Activity C
v
1. C
2. D
3. E
,4. A
5. B
Activity D v
1. The major difference between illness and disease is that illness is highly individual and
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vpersonal, whereas disease is something more definitive and measurable. For example, a client
v v v v v v v v v v v v
vwith arthritis presents with distinct pathologic changes associated with the disease. A person,
v v v v v v v v v v v v
vhowever, may or may not be ill with arthritis. The degree of pain, suffering, and immobility
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vvaries from person to person.
v v v v
2. Health maintenance refers to protecting one’s current level of health by preventing illness or
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vdeterioration, such as by complying with medication regimens, being screened for diseases
v v v v v v v v v v v
vsuch as breast cancer or colon cancer, or practicing safe sex. Health promotion refers to
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vengaging in strategies to enhance health such as eating a diet high in grains and complex
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vcarbohydrates, exercising regularly, balancing work with leisure activities, and practicing
v v v v v v v v v
vstress-reduction techniques. v
3. Medicare covers individuals who are 65 years or older, permanently disabled workers of any
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vage with specific disabilities, and persons with end-stage renal disease.
v v v v v v v v v
4. The team includes physicians, nurses, psychologists, pharmacists, dietitians, social workers,
v v v v v v v v v
vrespiratory and physical therapists, occupational therapists, nursing assistants, technicians,
v v v v v v v v
, and insurance company staff. All members of this team collaborate on client issues (medical,
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vsocial, and financial) to achieve the best possible outcomes.
v v v v v v v v
5. Groups such as children, older adults, ethnic minorities, and the poor are most likely to be
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vunderserved by the healthcare system. v v v v
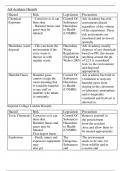
Activity E v
1. Point-of-service (POS) organizations involve a network of providers. Clients select a primary
v v v v v v v v v v v
vcare physician within the group who then serves as the gatekeeper for other healthcare
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vservices. Clients can use healthcare providers in or out of the provider group, but may pay
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vadditional fees, such as a higher deductible or copayment, for providers outside the group,
v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vunless the primary physician approves.
v v v v
2. Clients select a primary care physician within the group who then serves as the gatekeeper
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vfor other healthcare services. As with other types of managed care organizations, the focus is
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
von prevention as the best way to manage healthcare costs.
v v v v v v v v v
3. Benefits for the insurer include discounted services, reduced services, and elimination of
v v v v v v v v v v v
vunnecessary referrals (Chitty & Black, 2011). v v v v v
4. All are types of managed care networks. They provide a number of services within the
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vnetwork at a controlled cost. All provide incentive to stay within the network by providing
v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
vlower cost services. Seeking services outside each of the organizations would incur higher
v v v v v v v v v v v v