Expert Solutions
Save
Terms in this set (30)
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is the use of a
cardiopulmonary bypass circuit for temporary life
ECMO Definition
support for patients with potentially reversible cardiac/
and or respiratory failure.
oxygenator is a piece of equipment that acts as the
Membrane oxygenation
lungs
Venous blood is taken from the patient, oxygenator
removes CO2 and adds O2, blood is heated to body
How does ECMO work?
temperature and then a pump returns oxygenated
blood back to the patient.
acts as the heart, pulls blood from the heart and pushes
Centerfuge
back to the aorta
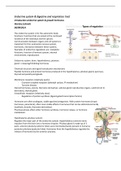
Types of ECMO VA or Veno-Arterial & VV or Veno-Venous
-Bypass the heart and lungs
VA or Veno-Arterial -Allows gas exchange and hemodynamic support while
blood is pumped from the venous to the arterial side.
-Bypass lungs
-Facilitates gas exchange; blood is removed from the
VV or Veno-Venous venous side and then pumped back into it, but does to
provide hemodynamic support. (Refer to slide 9 for
visual)
-higher PaO2 is achieved
- lower perfusion rates are needed
- bypass pulmonary circulation
VA ECMO notes
- decreases pulmonary artery pressures
- provided cardia support to assist systemic circulation
- requires arterial cannulation
, - lower PaO2 is achieved
- higher perfusion rates are needed
- maintains pulmonary blood flow
VV ECMO notes - elevates mixed venous PO2
- does not provide cardiac support to assist systemic
circulation
- requires only venous cannulation
- refractory cariogenic shock
- cardiopulmonary arrest
- failure to wean from cardiopulmonary bypass after
Indication for VA ECMO
cardiac surgery
- as a bridge to placement of a left ventricular assist
device (LVAD) or heart transplant.
- hypoxemia respiratory failure with a P/F rain <100
mmHg despite optimal ventilator settings (i.e. FiO2 of
100%, PEEP 12, ect.)
- hypercapnia respiratory failure with an arterial pH <
Indications for VV ECMO
7.20
- Pulmonary embolism not affecting cardiac function
- pneumonia
- murray score of 3 or greater
Any condition that precludes the use of anticoagulation
Absolute Contraindications
therapy (uncontrolled active bleeding)
- high-pressure ventilation (end-inspiratory pressure of
>30 cm H2O) for > 7 days
- high FiO2 requirements (>0.8) for > 7 days
- limited vascular access
Relative Contraindications
- any condition or organ dysfunction that would limit the
likelihood of overall benefit from ECMO, such as severe,
irreversible brain injury or untreatable mestatatic cancer
(stage IV)
> The purpose of ECMO therapy is to allow the lungs to
rest and heal, for children the initial therapy used is
"dead-space' ventilation (lungs act as trap for air). Adults
use a "lung protective" strategy is preferred with lower
Ventilation Strategy tidal volumes and increased PEE.
- Open lungs and keep them open with minimal stress
- Avoid complete de-recruitment (alveolar collapse)
- Avoid high FIO2 (reabsorption atelectasis)
- Ventilate at greatest compliance