,Before PFT's how long should a patient refrain from smoking? Using an inhaler? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-smoking: 6-8 h
inhaler: 4-6 h
What test must you do before performing an arterial puncture? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-Allen's test; patency of the ulnar artery- if blood returns to hand in 15s, then
the radial artery can be used for the puncture
How long should one apply pressure after an arterial puncture? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-5 minutes (20 min if the patient is on anticoagulant therapy)
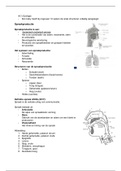
What are the normal ranges for ABG's?
(pH, PAO2, PACO2, HCO3, and SAO2) - CORRECT ANSWERS-pH: 7.35-7.45
PAO2: 80-100 mm Hg
PACO2: 35-45 mm Hg
HCO3: 21-28 mEq/L
SAO2: 95-100%
In what position should you place a patient if air embolism is expected? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-left side in trendelenburg
How long must a patient be NPO before a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT ANSWERS-4-8
hr
What types of medications might one administer prior to a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-anxiolytics
atropine (to treat bradycardia)
viscous lidocaine
local anesthetic throat spray
What should you be monitoring a patient for after a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-significant fever (mild is ok up to 24 hrs after the procedure), productive
cough, significant blood in sputum (small amounts are to be expected), hypoxemia,
laryngspasm
Prior to a thoracentesis what diagnostic procedure must be done? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-CXR
What position should the patient be in for a thoracentesis? - CORRECT ANSWERS-
sitting up over the bedside table
What are possible complications of a thoracentesis? How do we tell patients to identify
pneumothorax? - CORRECT ANSWERS-mediastinal shifts
,pneumothorax (deviated trachea, pain at the end of inhalation or exhalation, affected
side not moving with breath, increased HR, shallow respirations, nagging cough, air
hunger)
In what chest tube chamber (ONLY) should you see bubbling? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-suction
What is excessive drainage from a chest tube? - CORRECT ANSWERS-more than 70
ml/hr
How should the nurse document for care following a chest tube? How often? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-color and amount of drainage qh for 24h after insertion, then
q8h
mark date, hour, and drainage level on the container at the end of each shift
What supplies should be kept at the side of a bed for a patient with a chest tube? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-2 enclosed hemostats, sterile water, occlusive dressing
What should the nurse instruct the patient to do during chest tube removal? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-valsalva maneuver
What should the nurse do in the case that a chest tube is disconnected? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-1. have the client exhale as much as they can to remove air from the pleural
space
2. immerse the end of the chest tube in sterile water to restore the water seal
3. apply dry sterile gauze
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a nasal cannula? at what rate do we need to
administer humidification? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-44%
1-6 L/min
humidification at 4 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a simple face mask? - CORRECT ANSWERS-40-
60%
5-8 L/min (less than this causes the patient to rebreathe CO2)
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a partial rebreather mask? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-40-75%
6-11 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a non-rebreather? - CORRECT ANSWERS-80-
95%
10-15 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a venturi mask? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-50%
4-10 L/min
, What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a aerosol face mask, face tent, t-piece, and trach
collar? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-100%
10 L/min at least
*** Humidification requires frequent monitoring
What does hypercarbia look like? - CORRECT ANSWERS-restlessness, hypertension,
HA
What does oxygen toxicity look like? - CORRECT ANSWERS-non-productive cough,
substernal pain, nasal stuffiness, n/v, fatigue, HA, sore throat, hypoventillation
How does assist control (AC) work related to respiratory support? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-overtakes breathing for an intubated client
How does synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) work related to
respiratory support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-used in weaning; increases the work of
breathing
ventilator and patient work together
How does assist inverse ratio ventillation (IVR) work related to respiratory support? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-prolongs the inspiration phase to maximize oxygenation
HIGH RISK FOR VOLUTRAUMA
How does airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) work related to respiratory
support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-patient and ventilator work together
breath expelled by the lung's own natural recoil
How does independent lung ventilation work related to respiratory support? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-lungs are ventilated separately
need: 2 ventilators, sedation, neuromuscular blocking agents
How does PEEP work related to respiratory support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-preset
pressure on expiration
added to treat persistent hypoxemia
How does pressure support ventilation (PSV) work r/t respiratory support? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-greater oxygenation, makes the work of breathing easier, prevents alveolar
collapse
How do you document the placement of a tube for mechanical ventilation? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-in cm at the client's teeth or lips
What do the three ventilator alarms indicate? (volume, pressure, and apnea alarms) -
CORRECT ANSWERS-volume (low pressure): low exhaled volume due to a
disconnection, cuff leak, or tube displacement
CORRECT ANSWERS-smoking: 6-8 h
inhaler: 4-6 h
What test must you do before performing an arterial puncture? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-Allen's test; patency of the ulnar artery- if blood returns to hand in 15s, then
the radial artery can be used for the puncture
How long should one apply pressure after an arterial puncture? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-5 minutes (20 min if the patient is on anticoagulant therapy)
What are the normal ranges for ABG's?
(pH, PAO2, PACO2, HCO3, and SAO2) - CORRECT ANSWERS-pH: 7.35-7.45
PAO2: 80-100 mm Hg
PACO2: 35-45 mm Hg
HCO3: 21-28 mEq/L
SAO2: 95-100%
In what position should you place a patient if air embolism is expected? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-left side in trendelenburg
How long must a patient be NPO before a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT ANSWERS-4-8
hr
What types of medications might one administer prior to a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-anxiolytics
atropine (to treat bradycardia)
viscous lidocaine
local anesthetic throat spray
What should you be monitoring a patient for after a bronchoscopy? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-significant fever (mild is ok up to 24 hrs after the procedure), productive
cough, significant blood in sputum (small amounts are to be expected), hypoxemia,
laryngspasm
Prior to a thoracentesis what diagnostic procedure must be done? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-CXR
What position should the patient be in for a thoracentesis? - CORRECT ANSWERS-
sitting up over the bedside table
What are possible complications of a thoracentesis? How do we tell patients to identify
pneumothorax? - CORRECT ANSWERS-mediastinal shifts
,pneumothorax (deviated trachea, pain at the end of inhalation or exhalation, affected
side not moving with breath, increased HR, shallow respirations, nagging cough, air
hunger)
In what chest tube chamber (ONLY) should you see bubbling? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-suction
What is excessive drainage from a chest tube? - CORRECT ANSWERS-more than 70
ml/hr
How should the nurse document for care following a chest tube? How often? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-color and amount of drainage qh for 24h after insertion, then
q8h
mark date, hour, and drainage level on the container at the end of each shift
What supplies should be kept at the side of a bed for a patient with a chest tube? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-2 enclosed hemostats, sterile water, occlusive dressing
What should the nurse instruct the patient to do during chest tube removal? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-valsalva maneuver
What should the nurse do in the case that a chest tube is disconnected? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-1. have the client exhale as much as they can to remove air from the pleural
space
2. immerse the end of the chest tube in sterile water to restore the water seal
3. apply dry sterile gauze
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a nasal cannula? at what rate do we need to
administer humidification? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-44%
1-6 L/min
humidification at 4 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a simple face mask? - CORRECT ANSWERS-40-
60%
5-8 L/min (less than this causes the patient to rebreathe CO2)
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a partial rebreather mask? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-40-75%
6-11 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a non-rebreather? - CORRECT ANSWERS-80-
95%
10-15 L/min
What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a venturi mask? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-50%
4-10 L/min
, What is the FiO2 and the flow rate for a aerosol face mask, face tent, t-piece, and trach
collar? - CORRECT ANSWERS-24-100%
10 L/min at least
*** Humidification requires frequent monitoring
What does hypercarbia look like? - CORRECT ANSWERS-restlessness, hypertension,
HA
What does oxygen toxicity look like? - CORRECT ANSWERS-non-productive cough,
substernal pain, nasal stuffiness, n/v, fatigue, HA, sore throat, hypoventillation
How does assist control (AC) work related to respiratory support? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-overtakes breathing for an intubated client
How does synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) work related to
respiratory support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-used in weaning; increases the work of
breathing
ventilator and patient work together
How does assist inverse ratio ventillation (IVR) work related to respiratory support? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-prolongs the inspiration phase to maximize oxygenation
HIGH RISK FOR VOLUTRAUMA
How does airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) work related to respiratory
support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-patient and ventilator work together
breath expelled by the lung's own natural recoil
How does independent lung ventilation work related to respiratory support? -
CORRECT ANSWERS-lungs are ventilated separately
need: 2 ventilators, sedation, neuromuscular blocking agents
How does PEEP work related to respiratory support? - CORRECT ANSWERS-preset
pressure on expiration
added to treat persistent hypoxemia
How does pressure support ventilation (PSV) work r/t respiratory support? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-greater oxygenation, makes the work of breathing easier, prevents alveolar
collapse
How do you document the placement of a tube for mechanical ventilation? - CORRECT
ANSWERS-in cm at the client's teeth or lips
What do the three ventilator alarms indicate? (volume, pressure, and apnea alarms) -
CORRECT ANSWERS-volume (low pressure): low exhaled volume due to a
disconnection, cuff leak, or tube displacement