MGT 330 Final Exam 2025
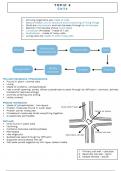
Human Resource Management (HRM) - -•System of organizational activities to attract,
develop, and motivate an effective and qualified workforce.
Value - -People create _____
Planning, Programming, Evaluating - -What are the 3 stages in Human Resources (HR)
planning
HR Planning - -HR Managers must know the company's business plans
HR Programming - -HR Managers implement specific activities
HR Evaluating - -HR Managers evaluate whether activities are producing results
needed to pursue business plans
Demand Forecasts - -Determine how many and what type of people are needed
Laboe Supply Forecasts - -Forecasting how many and what types of employees are
available
Include projecting workforce demographic trends
Reconciling Supply and Demand - -When managers need to hire, they use fair and
competitive compensation policies to attract talent
Job Analysis - -A tool for determining what is done on a given job and what should be
done on that job
Job description - -Describes the essential tasks, duties, and responsibilities involved in
performing the job
Job specification - -Describes the knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics
(KSAOs) needed to perform the job
Recruitment - -The development of a pool of applicants for jobs in an organization
Selection - -Choosing from among qualified applicants to hire into an organization
Unstructured/nondirective interview - -Interviewer asks different interviewees different
questions
MGT 330
,MGT 330
Structured Interview - -Interviewer asks all applicants the same questions and compares
their responses to a standardized set of answers
- Situational
- Behavioral
Reliability - -The consistency of test scores over a time and across alternative
measurements
Vaidity - -The degree to which a selection test predicts or correlates with job
performance
Layoffs - -May involve downsizing or restructuring
Outplacement - -______ helps dismissed people regain employment elsewhere
Termination - -_______ may involve poor performance or other reasons
Employment-at-will - -Legal concept that an employee may be terminated for any
reason
Termination interview - -The manager discusses a dismissal decision with the employee
Adverse impact - -One common reason employers are sued for discrimination is
___________; when a seemingly neutral employment practice has a disproportionately
negative effect on a protected group
Needs assessment - -Analysis identifying the jobs, people, and departments that need
training
Development - -Helping managers and professional employees learn the broad skills
needed for their present and future jobs
Orientation training - -Training designed to introduce new employees to the company
and familiarize them with policies, procedures, culture and the like
Team training - -Training that provides employees with the skills and perspectives they
need to collaborate with others
Diversity Training - -Programs that focus on identifying and reducing hidden biases
against people with differences and developing the skills needed to manage a
diversified workforce
Management Development Programs - -Training for new or experienced managers,
often focused on leadership and other "people skills."
MGT 330
, MGT 330
Performance Appraisal (PA) - -Assessment of an employee's job performance.
•Administrative
•Developmental
Management by objectives (MBO) - -involves a subordinate and a supervisor agreeing
in advance on specific performance goals (objectives).
360-degree appraisal - -process of using multiple sources of appraisal to gain a
comprehensive perspective on one's performance.
Cafeteria or Flexible Benefit Programs - -Employees choose from a menu of options to
create a benefit package tailored to their needs.
Employees are given credits to spend on benefits that fit their unique needs
The Equal Pay Act (E P A) of 19 63 - -prohibits unequal pay for men and women who
perform equal work
Labor Relations - -The system of relationships and interactions between workers and
management
Managing Diversity and Inclusion - -Managing a diverse workforce by recognizing the
characteristics common to groups while dealing with people as individuals and
supporting, nurturing, and using their differences to the organization's advantage
Glass ceiling - -A metaphor alluding to the invisible barriers that prevent minorities and
women from being promoted to top corporate positions
Affirmative action - -Special efforts to recruit and hire qualified members of groups that
were discriminated against in the past.
Sexual Harassment - -Conduct of a sexual nature that has negative consequences for
employment
Violate Title V I I of the Civil Rights Act of 19 64, regardless of the sex of the harasser
and the victim
Quid pro quo harassment - -form of sexual harassment in which sexual favors are
requested in return for job-related benefits
Hostile environment - -Occurs when unwelcome sexual conduct has the effect of
unreasonably interfering with job performance or creating an intimidating or hostile,
working environment
People with disabilities - -The largest unemployed minority in the US is _____
MGT 330