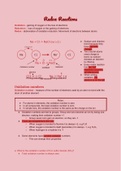
Organic I -335 Section 02
Chapter 3
Stereoisomerism and Chirality
A drawing by Dutch designer and artist 3.1 Chirality—The Handedness of Molecules
M. C Escher (Lizards; Symmetry Drawing 25) 3.2 Stereoisomerism
They are non-superposable mirror images HOW TO: Draw Chiral Molecules
illustrating 2D chirality in objects
3.3 Naming Chiral Centers—The R,S System
HOW TO: Assign R or S Configuration to a Chiral Center
3.4 Acyclic Molecules with Two or More Stereocenters
HOW TO: Quickly Draw and Recognize Enantiomers and Diastereomers
3.5 Cyclic Molecules with Two or More Chiral Centers
3.6 Tying All the Terminology Together
They are non- 3.7 Optical Activity—How Chirality Is Detected in the Laboratory
superposable 3.8 The Significance of Chirality in the Biological World
mirror images Connections to Biological Chemistry Chiral Drugs
illustrating 3D
MCAT Pract ice: Passa ge and Quest ions Amino Acid Stereochemistry
chirality in
molecules 3.9 Separation of Enantiomers—Resolution
1
,Isomerism
2
,3.1 Chirality—The Handedness of Molecules
3.2 Stereoisomerism
HOW TO: Draw Chiral Molecules
3.3 Naming Chiral Centers—The R,S System
HOW TO: Assign R or S Configuration to a Chiral Center
3.4 Acyclic Molecules with Two or More Stereocenters
HOW TO: Quickly Draw and Recognize Enantiomers and Diastereomers
3.5 Cyclic Molecules with Two or More Chiral Centers
3.6 Tying All the Terminology Together
3.7 Optical Activity—How Chirality Is Detected in the Laboratory
3.8 The Significance of Chirality in the Biological World
Connections to Biological Chemistry Chiral Drugs
MCAT Pract ice: Passa ge and Quest ions Amino Acid Stereochemistry
3.9 Separation of Enantiomers—Resolution
3
, …what is “chirality” ?
ancient Greek χείρ, hand
a chiral object (.. or molecule!) lacks :
• an internal plane of symmetry
• a center of symmetry
it cannot be superposed with its mirror- image
4
Chapter 3
Stereoisomerism and Chirality
A drawing by Dutch designer and artist 3.1 Chirality—The Handedness of Molecules
M. C Escher (Lizards; Symmetry Drawing 25) 3.2 Stereoisomerism
They are non-superposable mirror images HOW TO: Draw Chiral Molecules
illustrating 2D chirality in objects
3.3 Naming Chiral Centers—The R,S System
HOW TO: Assign R or S Configuration to a Chiral Center
3.4 Acyclic Molecules with Two or More Stereocenters
HOW TO: Quickly Draw and Recognize Enantiomers and Diastereomers
3.5 Cyclic Molecules with Two or More Chiral Centers
3.6 Tying All the Terminology Together
They are non- 3.7 Optical Activity—How Chirality Is Detected in the Laboratory
superposable 3.8 The Significance of Chirality in the Biological World
mirror images Connections to Biological Chemistry Chiral Drugs
illustrating 3D
MCAT Pract ice: Passa ge and Quest ions Amino Acid Stereochemistry
chirality in
molecules 3.9 Separation of Enantiomers—Resolution
1
,Isomerism
2
,3.1 Chirality—The Handedness of Molecules
3.2 Stereoisomerism
HOW TO: Draw Chiral Molecules
3.3 Naming Chiral Centers—The R,S System
HOW TO: Assign R or S Configuration to a Chiral Center
3.4 Acyclic Molecules with Two or More Stereocenters
HOW TO: Quickly Draw and Recognize Enantiomers and Diastereomers
3.5 Cyclic Molecules with Two or More Chiral Centers
3.6 Tying All the Terminology Together
3.7 Optical Activity—How Chirality Is Detected in the Laboratory
3.8 The Significance of Chirality in the Biological World
Connections to Biological Chemistry Chiral Drugs
MCAT Pract ice: Passa ge and Quest ions Amino Acid Stereochemistry
3.9 Separation of Enantiomers—Resolution
3
, …what is “chirality” ?
ancient Greek χείρ, hand
a chiral object (.. or molecule!) lacks :
• an internal plane of symmetry
• a center of symmetry
it cannot be superposed with its mirror- image
4