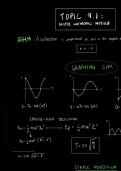
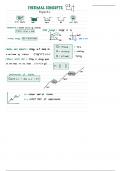
FLETC WRITTEN EXAM #1 EXAM
WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
Graham v. Connor (1989) -ANSRecognized that the right to make an arrest or
investigatory stop necessarily carries with it the right to use some degree of physical
coercion/threat to affect it.
In the course of an arrest or stop is properly analyzed by Fourth Amendment's 'objective
reasonableness' standard
Graham Factors -ANSSeverity of crime
Whether suspect poses an immediate threat
Whether suspect is actively resisting arrest
Attempting to evade arrest by flight
Additional factors considered when applying standard of Graham v. Connor that may
govern the reasonableness of using force -ANS# of suspects/# of officers
Size, age, condition of officer/suspect
Duration of action
Whether force applied resulted in injury
Previous violent history known to officer at time
Use of alcohol/drugs
Suspect's mental history known to officer at time
Presence of innocent bystanders
Availability of officer weapons
Range of Reasonableness -ANSOfficer responses range from:
Hesitation---------------Aggressive
Tennessee v. Garner (1985) -ANSSupreme Court stated it is not reasonable to shoot an
unarmed non-dangerous fleeing suspect.
Key Elements of Tennessee v. Garner -ANSProbable cause
Threat
Officer not obligated to wait until death or serious bodily harm is occurring
If based on totality of circumstance and the officer perceives a threat of such action, a
reasonable force option may be used
Pre-Assault Indicators -ANSVerbal aggression
Change in posture
Face becomes red, showing teeth, breathing faster
Individual ignores you or stares through you
,Aggression
Hands tighten
Individual becomes rigid
Chin tucked
Common Restrictions in Agency Use of Force Policy -ANSUse of warning shots
Use of maximum force
Moving vehicles
Exhausting lesser means of force first
Physiological Changes triggered when faced with a threat -ANSPounding heart
Muscle tension
Rapid, shallow breathing
Nausea
Dizziness
Dry mouth
Diminished sound
Tunnel vision
Slow motion time
Memory loss
Memory distortion
Tunnel Vision -ANSLoss of peripheral vision
Heightened Visual Clarity -ANSClear picture of details you ordinarily might not
notice/remember
Hearing Distortions -ANSTotal loss of hearing, to muffled or distant
Time Distortion -ANSThings seem to speed up or slow down
Cognitive/Behavioral Changes triggered when faced with a threat -ANSAutomatic
Behavior
Memory Gaps
Intrusive Thoughts
Methods of overcoming hesitation in use of force -ANSMental preparation
Proper Training
Belief in mission
Personal Appearance
Physical Fitness
Understanding the law
Reality Based Training
Continuous Positive Visualization
Understanding of agency policy
Commitment to family/friends
, Will to win
Fundamentals of Documenting Use of Force Incident -ANSOfficer Safety
Objective, not subjective
Training and Experience
Matched Description
Basis for Seizure
Terry Stop -ANSReasonable suspicion sufficient for investigation stop or detention; no
warrant needed
Two Main Parts of the Mind -ANSThe conscious and the subconscious
The Conscious Mind -ANSRational, analytical part of the mind. Home to will power and
short-term memory
The Subconscious Mind -ANSThe real boss, communicates through feelings and
emotions
Mistaken Assumptions of Perception -ANSEveryone sees what really occurs
Everyone sees everything that occurs
Everyone processes information the same way
Everyone remembers exactly what occurred during an incident
Memories stay the same, maintain accuracy, and remain consistent over time
People can replay experiences with accuracy and detail
Arousal -ANSDefined by physiology
Anxiety -ANSDefined by terms of emotional or cognitive impact of arousal
Situational Awareness -ANSA person's perception of the elements in the environment
within a volume of time and space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the
projection of their status in the near future
Effective Situational Awareness -ANSPerception of changing elements during dynamic
events and correctly reacting in a timely manner
Global Attention -ANSNot focused on one specific thing
Selective Attention -ANSFocus on one specific thing
Inattentional Blindness -ANSInattention to cues during dynamic events results in failure
to accurately interpret patterns and implications of the behavior leading to ineffective
decisions and poor performance
WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
Graham v. Connor (1989) -ANSRecognized that the right to make an arrest or
investigatory stop necessarily carries with it the right to use some degree of physical
coercion/threat to affect it.
In the course of an arrest or stop is properly analyzed by Fourth Amendment's 'objective
reasonableness' standard
Graham Factors -ANSSeverity of crime
Whether suspect poses an immediate threat
Whether suspect is actively resisting arrest
Attempting to evade arrest by flight
Additional factors considered when applying standard of Graham v. Connor that may
govern the reasonableness of using force -ANS# of suspects/# of officers
Size, age, condition of officer/suspect
Duration of action
Whether force applied resulted in injury
Previous violent history known to officer at time
Use of alcohol/drugs
Suspect's mental history known to officer at time
Presence of innocent bystanders
Availability of officer weapons
Range of Reasonableness -ANSOfficer responses range from:
Hesitation---------------Aggressive
Tennessee v. Garner (1985) -ANSSupreme Court stated it is not reasonable to shoot an
unarmed non-dangerous fleeing suspect.
Key Elements of Tennessee v. Garner -ANSProbable cause
Threat
Officer not obligated to wait until death or serious bodily harm is occurring
If based on totality of circumstance and the officer perceives a threat of such action, a
reasonable force option may be used
Pre-Assault Indicators -ANSVerbal aggression
Change in posture
Face becomes red, showing teeth, breathing faster
Individual ignores you or stares through you
,Aggression
Hands tighten
Individual becomes rigid
Chin tucked
Common Restrictions in Agency Use of Force Policy -ANSUse of warning shots
Use of maximum force
Moving vehicles
Exhausting lesser means of force first
Physiological Changes triggered when faced with a threat -ANSPounding heart
Muscle tension
Rapid, shallow breathing
Nausea
Dizziness
Dry mouth
Diminished sound
Tunnel vision
Slow motion time
Memory loss
Memory distortion
Tunnel Vision -ANSLoss of peripheral vision
Heightened Visual Clarity -ANSClear picture of details you ordinarily might not
notice/remember
Hearing Distortions -ANSTotal loss of hearing, to muffled or distant
Time Distortion -ANSThings seem to speed up or slow down
Cognitive/Behavioral Changes triggered when faced with a threat -ANSAutomatic
Behavior
Memory Gaps
Intrusive Thoughts
Methods of overcoming hesitation in use of force -ANSMental preparation
Proper Training
Belief in mission
Personal Appearance
Physical Fitness
Understanding the law
Reality Based Training
Continuous Positive Visualization
Understanding of agency policy
Commitment to family/friends
, Will to win
Fundamentals of Documenting Use of Force Incident -ANSOfficer Safety
Objective, not subjective
Training and Experience
Matched Description
Basis for Seizure
Terry Stop -ANSReasonable suspicion sufficient for investigation stop or detention; no
warrant needed
Two Main Parts of the Mind -ANSThe conscious and the subconscious
The Conscious Mind -ANSRational, analytical part of the mind. Home to will power and
short-term memory
The Subconscious Mind -ANSThe real boss, communicates through feelings and
emotions
Mistaken Assumptions of Perception -ANSEveryone sees what really occurs
Everyone sees everything that occurs
Everyone processes information the same way
Everyone remembers exactly what occurred during an incident
Memories stay the same, maintain accuracy, and remain consistent over time
People can replay experiences with accuracy and detail
Arousal -ANSDefined by physiology
Anxiety -ANSDefined by terms of emotional or cognitive impact of arousal
Situational Awareness -ANSA person's perception of the elements in the environment
within a volume of time and space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the
projection of their status in the near future
Effective Situational Awareness -ANSPerception of changing elements during dynamic
events and correctly reacting in a timely manner
Global Attention -ANSNot focused on one specific thing
Selective Attention -ANSFocus on one specific thing
Inattentional Blindness -ANSInattention to cues during dynamic events results in failure
to accurately interpret patterns and implications of the behavior leading to ineffective
decisions and poor performance