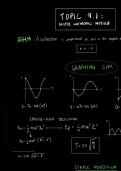
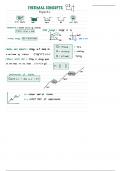
Evolution by Natural Selection
Introduction
Key Terminology
Biological evolution ● Any genetic changes in a population that’s inherited over
several generations
Biological species ● Group of organisms with similar characteristics that interbreed
with each other to produce fertile offspring
Population ● Group of individuals of same specied by occupying a certain
habitat
Punctuated equilibrium ● Evolution characterised by long periods of little/no change,
followed by short periods of rapid change
Natural selection ● Mechanism of evolution - organisms survive if they have
characteristics that make them suited to the environment
Artificial selection ● Human-driven selection force, eg. breeding of plants + animals
to produce desirable traits
Inbreeding ● Mating of individuals that are closely related
Outbreeding ● Mating of individuals that are not closely related
Speciation ● Formation of a new species
Geographic speciation ● Formation of a new species when parent population separated
by geographical barrier
Reproductive isolation ● Mechanism that prevents 2 species from mating with each
other + making fertile hybrids
Origin of ideas about origins:
● Theory of evolution = considered as a scientific theory since different hypotheses relating to
evolution has been tested + verified over time
● Theory: explanation of something that’s been observed in nature that can be supported by
facts, generalisations, tested hypotheses, models and laws
● Hypothesis: possible solution to a problem
● Evolution means change over time = process where organisms develop over time from
previous forms
● Biological evolution: any genetic change in a population that’s inherited + becomes a
characteristic of that population over several generations
, Evidence for Evolution:
Fossils ● Different fossils = found in different rock layers with oldest fossils in
oldest rock layer with transitional fossils present
● This systematic change through time = descent with modification
● Evidence shows characteristics that make organisms similar to each other
regularly from study of fossils
Biogeography ● Biogeography = study of where species are found and why they are
found there
● There are different collections of plants + animals in regions of same line
of latitude with similar climates + conditions suggesting those organisms
have a shared ancestor
Genetics ● Species that’re closely related have a greater genetic similarity to each
other than distant species so they share a more recent common ancestor
Other evidence ● Not studied in school: embryology, vestigial organs, comparative
anatomy
Genetic Evidence & Variation:
● Genetic evidence that organisms = closely related + likely to have a common ancestor
includes:
○ Identical DNA structure
○ Similar sequence of genes
○ Similar portions of DNA with no functions
○ Similar mutations (mitochondrial DNA)
● Species that’re closely related have a greater similarity to each other than more distantly
related species
● There’s a degree of variation between individuals of same species in a population
● Variation can be cause by:
○ Crossing over during Prophase 1 of meiosis involves exchange of genetic material,
leading to new combos of maternal + paternal genetic materials in each new
cell/gamete resulting in meiosis, making them different
○ Random arrangement of maternal + paternal chromosomes at equator during
metaphase allows different combos of chromosomes/chromatids to go into new
cell/gamete, resulting from meiosis, making them different
○ Random fertilisation between different egg cells + different sperm cells formed by
meiosis result in offspring that’re different from each other
○ Random mating between organisms in a species leads to a different set of offspring
from each mating pair
○ Mutation changes structure of gene/chromosome + the organism’s genotype
■ Since genotype influences phenotype, it creates organisms with new, different
characteristics from 1 generation to the next
Introduction
Key Terminology
Biological evolution ● Any genetic changes in a population that’s inherited over
several generations
Biological species ● Group of organisms with similar characteristics that interbreed
with each other to produce fertile offspring
Population ● Group of individuals of same specied by occupying a certain
habitat
Punctuated equilibrium ● Evolution characterised by long periods of little/no change,
followed by short periods of rapid change
Natural selection ● Mechanism of evolution - organisms survive if they have
characteristics that make them suited to the environment
Artificial selection ● Human-driven selection force, eg. breeding of plants + animals
to produce desirable traits
Inbreeding ● Mating of individuals that are closely related
Outbreeding ● Mating of individuals that are not closely related
Speciation ● Formation of a new species
Geographic speciation ● Formation of a new species when parent population separated
by geographical barrier
Reproductive isolation ● Mechanism that prevents 2 species from mating with each
other + making fertile hybrids
Origin of ideas about origins:
● Theory of evolution = considered as a scientific theory since different hypotheses relating to
evolution has been tested + verified over time
● Theory: explanation of something that’s been observed in nature that can be supported by
facts, generalisations, tested hypotheses, models and laws
● Hypothesis: possible solution to a problem
● Evolution means change over time = process where organisms develop over time from
previous forms
● Biological evolution: any genetic change in a population that’s inherited + becomes a
characteristic of that population over several generations
, Evidence for Evolution:
Fossils ● Different fossils = found in different rock layers with oldest fossils in
oldest rock layer with transitional fossils present
● This systematic change through time = descent with modification
● Evidence shows characteristics that make organisms similar to each other
regularly from study of fossils
Biogeography ● Biogeography = study of where species are found and why they are
found there
● There are different collections of plants + animals in regions of same line
of latitude with similar climates + conditions suggesting those organisms
have a shared ancestor
Genetics ● Species that’re closely related have a greater genetic similarity to each
other than distant species so they share a more recent common ancestor
Other evidence ● Not studied in school: embryology, vestigial organs, comparative
anatomy
Genetic Evidence & Variation:
● Genetic evidence that organisms = closely related + likely to have a common ancestor
includes:
○ Identical DNA structure
○ Similar sequence of genes
○ Similar portions of DNA with no functions
○ Similar mutations (mitochondrial DNA)
● Species that’re closely related have a greater similarity to each other than more distantly
related species
● There’s a degree of variation between individuals of same species in a population
● Variation can be cause by:
○ Crossing over during Prophase 1 of meiosis involves exchange of genetic material,
leading to new combos of maternal + paternal genetic materials in each new
cell/gamete resulting in meiosis, making them different
○ Random arrangement of maternal + paternal chromosomes at equator during
metaphase allows different combos of chromosomes/chromatids to go into new
cell/gamete, resulting from meiosis, making them different
○ Random fertilisation between different egg cells + different sperm cells formed by
meiosis result in offspring that’re different from each other
○ Random mating between organisms in a species leads to a different set of offspring
from each mating pair
○ Mutation changes structure of gene/chromosome + the organism’s genotype
■ Since genotype influences phenotype, it creates organisms with new, different
characteristics from 1 generation to the next