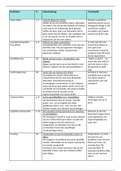
Fertilization -->2nd week
Primordial germ cells
Development begins with fertilization (egg + sperm)
Gametes are derived from Primordial germ cells
2nd week
Formation of PGCs from epiblast
3rd week
Move to the wall of yolk sac
4th week
PGC might from yolk sac to genital ridge along gut tube and dorsal mesentery (developing
during migration)
6th week
Invade the developing gonad (developing after invade)
7th week
Sex determined
Epithelium of genital ridge proliferate into mesenchyme--> primitive sex cord (indifferent
gonad)
Y chromosome (SRY gene)--> (primitive sex cord differentiate)medullary /testis cord-->
testis
XX chromosome (no SRY gene)-->(primitive cord degenerate) cortical cords
Meiosis and gametes production
Germ cell development
Male
Spermatogenesis (Sertoli cells and testis cords)
Mitotic arrest (spermatogonia) until after birth
First meiotic division at puberty
Second meiotic division through out life
Female
Oogenesis (oocytes)
Early stages of meiosis (meiotic recombination)
First meiotic division arrest at diplotene prophase I at birth and complete at puberty
Prophase I
Genetic recombination
Leptotene (condensation), zygotene (pairing of homologous
chromosomes), pachytene (crossing over), diplotene (separation)
Second meiotic division finish upon fertilization
2 major functions
Meiotic recombination
Reduction of number of chromosomes to haloid complement
Stages
1. Pre-meiotic DNA replication
2. Prophase I stage of Meiosis for genetic exchange
3. 2 rounds of chromosome segregation (meiosis I and II)
Meiosis : PGC-->gamete
Mitosis
Primordial germ cells
Development begins with fertilization (egg + sperm)
Gametes are derived from Primordial germ cells
2nd week
Formation of PGCs from epiblast
3rd week
Move to the wall of yolk sac
4th week
PGC might from yolk sac to genital ridge along gut tube and dorsal mesentery (developing
during migration)
6th week
Invade the developing gonad (developing after invade)
7th week
Sex determined
Epithelium of genital ridge proliferate into mesenchyme--> primitive sex cord (indifferent
gonad)
Y chromosome (SRY gene)--> (primitive sex cord differentiate)medullary /testis cord-->
testis
XX chromosome (no SRY gene)-->(primitive cord degenerate) cortical cords
Meiosis and gametes production
Germ cell development
Male
Spermatogenesis (Sertoli cells and testis cords)
Mitotic arrest (spermatogonia) until after birth
First meiotic division at puberty
Second meiotic division through out life
Female
Oogenesis (oocytes)
Early stages of meiosis (meiotic recombination)
First meiotic division arrest at diplotene prophase I at birth and complete at puberty
Prophase I
Genetic recombination
Leptotene (condensation), zygotene (pairing of homologous
chromosomes), pachytene (crossing over), diplotene (separation)
Second meiotic division finish upon fertilization
2 major functions
Meiotic recombination
Reduction of number of chromosomes to haloid complement
Stages
1. Pre-meiotic DNA replication
2. Prophase I stage of Meiosis for genetic exchange
3. 2 rounds of chromosome segregation (meiosis I and II)
Meiosis : PGC-->gamete
Mitosis