Registered Nurse RN in-depth revision questions with
100% correct answers
1. A 65 year old male patient has experienced full-thickness electrical burns on the legs and
arms. As the nurse you know this patient is at risk for the following: Select all that apply:
A. Acute kidney injury
B. Dysrhythmia
C. Iceberg effect
D. Hypernatremia
E. Bone fractures
F. Fluid volume overload - Correct Answers-A. Acute kidney injury
B. Dysrhythmia
C. Iceberg effect
E. Bone fractures
The answers are A, B, C, and E. Electric burns are due to an electrical current passing through
the body that leads to damage to the skin but also the muscles and bones that are underneath
the skin. The patient is at risk for AKI (acute kidney injury) because when the muscles become
affected they release myoglobin and the red blood cells release hemoglobin in the blood, which
can collect in the kidneys leading to injury. In addition, the heart's electrical system can become
damaged leading to dysrhythmia. The iceberg effect can present as well because the extent of
damage is not clearly visible on the skin (there can be severe damage underneath). In addition,
if the electrical current is strong enough it can lead to bone fractures (specifically cervical spine
injuries) due to the severe contraction of the muscles involved.
True or False: A patient who experiences an alkali chemical burn is easier to treat because the
skin will neutralize the chemical rather than with an acidic chemical burn.
,True
False - Correct Answers-False:
Alkali burns are harder to treat than acidic chemical burns because the skin will neutralize the
acidic burn.
As the nurse providing care to a patient who experienced a full-thickness electrical burn you
know to monitor the patient's urine for:
A. Hemoglobin and myoglobin
B. Free iron and white blood cells
C. Protein and red blood cells
D. Potassium and Urea - Correct Answers-The answer is A.Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
Patients who've experienced a severe electrical burn or full-thickness burns are at risk for acute
kidney injury. This is because the muscles can experience damage from the electrical current
leading them to release myoglobin. In addition, the red blood cells will release hemoglobin.
These substances will collect in the kidneys leading to acute tubular necrosis (hence leading to
AKI). Therefore, the nurse should monitor the patient's urine for these substances.
Select the patient below who is at MOST risk for complications following a burn:
A. A 42 year old male with partial-thickness burns on the front of the right and left arms and
legs.
B. A 25 year old female with partial-thickness burns on the front of the head and neck and front
and back of the torso.
C. A 36 year old male with full-thickness burns on the front of the left arm.
D. A 10 year old with superficial burns on the right leg. - Correct Answers-B. A 25 year old
female with partial-thickness burns on the front of the head and neck and front and back of the
torso.
, The answer is B. When thinking about which patient will have the MOST complications following
a burn think about: percentage of the total body surface area that is burned (use the rule of
nine to calculate), depth of the burn, age, location of the burn, and patient's medical history.
The patient in option B has 40.5% TSBA burned (option A 27%, C: 4.5%, D: 9%). Remember that
the higher the total of the body surface area that is burned the higher the risk of complications
due to an increase in capillary permeability (swelling, hypovolemic shock etc.). In addition, the
location of the burn is a major issue with the patient in option B. The burns are on the head and
neck and front and back of the torso. Therefore, with head and neck burns always think about
respiratory issues because the airway can become compromised due to swelling or an
inhalation injury. And with torso burns that are on the front and back, the patient is at risk for
circumferential burns that can lead to further respiratory compromise. The other options have
burns that are isolated.
The _____________ layer of the skin helps regulate our body temperature.
A. Epidermis
B. Dermis
C. Hypodermis
D. Fascia - Correct Answers-C. Hypodermis
This layer contains fatty tissue, veins, arteries, nerves and helps insulate the muscles, bones,
organs and helps REGULATE our body temperature.
You receive a patient who has experienced a burn on the right leg. You note the burn contains
small blisters and is extremely pinkish red and shiny/moist. The patient reports severe pain. You
document this burn as:
A. 1st Degree (superficial)
B. 2nd Degree (partial-thickness)
C. 3rd Degree (full-thickness)
D. 4th Degree (deep full-thickness) - Correct Answers-B. 2nd Degree (partial-thickness)
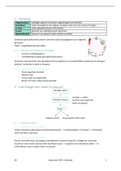
Based on the depth of the burn in figure 1 (picture is above), you would expect to find:
100% correct answers
1. A 65 year old male patient has experienced full-thickness electrical burns on the legs and
arms. As the nurse you know this patient is at risk for the following: Select all that apply:
A. Acute kidney injury
B. Dysrhythmia
C. Iceberg effect
D. Hypernatremia
E. Bone fractures
F. Fluid volume overload - Correct Answers-A. Acute kidney injury
B. Dysrhythmia
C. Iceberg effect
E. Bone fractures
The answers are A, B, C, and E. Electric burns are due to an electrical current passing through
the body that leads to damage to the skin but also the muscles and bones that are underneath
the skin. The patient is at risk for AKI (acute kidney injury) because when the muscles become
affected they release myoglobin and the red blood cells release hemoglobin in the blood, which
can collect in the kidneys leading to injury. In addition, the heart's electrical system can become
damaged leading to dysrhythmia. The iceberg effect can present as well because the extent of
damage is not clearly visible on the skin (there can be severe damage underneath). In addition,
if the electrical current is strong enough it can lead to bone fractures (specifically cervical spine
injuries) due to the severe contraction of the muscles involved.
True or False: A patient who experiences an alkali chemical burn is easier to treat because the
skin will neutralize the chemical rather than with an acidic chemical burn.
,True
False - Correct Answers-False:
Alkali burns are harder to treat than acidic chemical burns because the skin will neutralize the
acidic burn.
As the nurse providing care to a patient who experienced a full-thickness electrical burn you
know to monitor the patient's urine for:
A. Hemoglobin and myoglobin
B. Free iron and white blood cells
C. Protein and red blood cells
D. Potassium and Urea - Correct Answers-The answer is A.Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
Patients who've experienced a severe electrical burn or full-thickness burns are at risk for acute
kidney injury. This is because the muscles can experience damage from the electrical current
leading them to release myoglobin. In addition, the red blood cells will release hemoglobin.
These substances will collect in the kidneys leading to acute tubular necrosis (hence leading to
AKI). Therefore, the nurse should monitor the patient's urine for these substances.
Select the patient below who is at MOST risk for complications following a burn:
A. A 42 year old male with partial-thickness burns on the front of the right and left arms and
legs.
B. A 25 year old female with partial-thickness burns on the front of the head and neck and front
and back of the torso.
C. A 36 year old male with full-thickness burns on the front of the left arm.
D. A 10 year old with superficial burns on the right leg. - Correct Answers-B. A 25 year old
female with partial-thickness burns on the front of the head and neck and front and back of the
torso.
, The answer is B. When thinking about which patient will have the MOST complications following
a burn think about: percentage of the total body surface area that is burned (use the rule of
nine to calculate), depth of the burn, age, location of the burn, and patient's medical history.
The patient in option B has 40.5% TSBA burned (option A 27%, C: 4.5%, D: 9%). Remember that
the higher the total of the body surface area that is burned the higher the risk of complications
due to an increase in capillary permeability (swelling, hypovolemic shock etc.). In addition, the
location of the burn is a major issue with the patient in option B. The burns are on the head and
neck and front and back of the torso. Therefore, with head and neck burns always think about
respiratory issues because the airway can become compromised due to swelling or an
inhalation injury. And with torso burns that are on the front and back, the patient is at risk for
circumferential burns that can lead to further respiratory compromise. The other options have
burns that are isolated.
The _____________ layer of the skin helps regulate our body temperature.
A. Epidermis
B. Dermis
C. Hypodermis
D. Fascia - Correct Answers-C. Hypodermis
This layer contains fatty tissue, veins, arteries, nerves and helps insulate the muscles, bones,
organs and helps REGULATE our body temperature.
You receive a patient who has experienced a burn on the right leg. You note the burn contains
small blisters and is extremely pinkish red and shiny/moist. The patient reports severe pain. You
document this burn as:
A. 1st Degree (superficial)
B. 2nd Degree (partial-thickness)
C. 3rd Degree (full-thickness)
D. 4th Degree (deep full-thickness) - Correct Answers-B. 2nd Degree (partial-thickness)
Based on the depth of the burn in figure 1 (picture is above), you would expect to find: