Introduction to Renal Physiology and Mass Balance
describe the stry of the
kidney
to
-
allow these main process
KIDNEYS OTHER FUNCTIONS
O
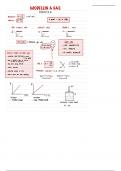
R A. Overview of main kidney structure-function including 3 basic renal processes. R 11. On an electron mic
structures of the glome
·
excretion of metabolic waste products and toxins ·
the Kidneys are vital
organs responsible for maintaining homeostasis
by filtering
blood and
regulating glomerular capillary ne
juxtaglomerular appara
Regulation of and
electrolyte balances
. The
Kidneys 200 under
hypoxic conditions.
·
water
water and electrolyte balance are also responsible for making glomerular filtration ba
·
Regulation of
body fluid osmolarity and
electrolytes
RBCs to
and the basement mem
Toa the # of :
↑O carrying capacity
.
Regulation of arterial blood pressure
·
· The three basic processes are filtration reabsorption , and secretion . Also excretion
,
! ·
The renal
corpuscle
=
glomerular t
of Aid-Base balance
Regulation
·
4 Glomerular Tuft Tuft ofC apillarie
=
selective membrane DIRECTION : BLOOD -BOWMAN'S CAPSULE
·
Regulation of
oxygen carrying capacity Filtration :
filtering of blood over a ,
Secretion Metabolism E xcretion of hormones.
and and specific GFR
and small solutes. Includes :
glomerula
occurs btwn
glomerular capillaries &
· ·
, ,
glomenius a .
·
Gluconeogenesis size +
charge
.
endothelium- fenestrated item
Reabsorption
·
:
occurs btorn the tubules . DIRECTION
and interstitium Filtrate blood (peritubular) podicalyxin Ca polyanisc sur f
Terminology
·
: ->
proximal convoluted Secretion :
Bowman's Double-walle
tubule
capsule
·
PCT = ↳ :
limb occurs between the tubules and interstitium
. DIRECTION blood (peritubular) Filtrate LAYERS
descending
·
-
TKDL
·
:
thick
·
=
A) Parietal couter) :
simple
TNDC limb excreted
things filtered t secreted but ot reabsorbed !
thin
descending Excretion stuff that are that
·
=
: The are are
3) Visceral (inner) :
pod
·
TNAL =
thin ascending limb excretion =
fitration +
secretion-reabsorption
&
TRA) thick
ascending
limb R 9. Describe in sequence the tubular segments through which ultrafiltrate flows after it is
·
=
formed at Bowman's capsule to when it enters the renal pelvis. Identify each structure as
·
DCT =
distal convoluted tubule .
being located in the renal cortex or renal medulla. Based on the glomerulus location and the ~
↳
cs
length of the loop of Henle, distinguish between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons.
collecting segment
·
=
BONMAN'S CAPULE- PET
-
-
LOH- ALT-COLLECTING DUCT -
RENAL PELVIS
-
,
duct
collecting
·
CD =
PATH OF ULTRAFILTRATE medulla
cortex medulla cor tex
component facilitates tubuloglomerular
proxima
vascular
Henle
↑ >
distal AA +
feedback
EA +
-
COH-loop of
-
region
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus extraglomerular mesangial
·
:
·
[Nats
L
macula densa cells detect
component tubular
·
·
macula densa
if low release factors thu Lacis
·
AA =
afferent arteriole (extraglomular mesengial cells)
>
-
the JG
-
activity regis
renin to PCT : &NRA &
A A to release energy
>
cells@ the
:
-
.
REABSORPTO mesen
initiate RAAS &BP
Key job
- .
· :
+ cat Po
EA efferent arteviole Proximal Tubule (PCT , TKDL)
,
g
·
= .
a a
. of
glucose ,
·
H2o , organic solute , Portion
chemic
injury Rxtoxicity by podo
+
prone to is
TKDL fr than in PCT
> : NKA activity
·
key job
.
= SECRETION organic anions + R 17. Identify the filt
cations some medication
TNDL
,
:
Permable to H20 , impermeable
of H20, Na, inulin, al
to ions
·
Rey job
:H2 REABSORBTION
·
Thin limb of LOH(TNDL TNAL) passive ; due to osmolarity
·
Filtration Barrier
,
TNAL : impermeable to H20,
to i s
> permeable
·
TKAL : REY JOB =
ACTIVE NaCl
OF
SUBSTANCE SIZE/C
KEY JOD MAINTAINANCE
·
:
TRANSPORTFROM LUMENE INTERSTITUM small
OSMOTIC GRADI ENT
·
,
interstitium medulla)
results in
hypertonic medullary (cortex + WATER
+ dilute tubular flid .
·
small
,
DCTMNAactivitrelativeimpermeable a cotransporter Nat
·
-
· small
,
fluid INULIN
CS
many nephrons
· =
connects + takes to CD
.
.
·
REY JOB :
K
+
secretion (reg'd by
aldosterone + Cas t reabsorption
(NatCa't exchangers Ca2 + Atpase)
ALBUMIN large , n
·
·
CD =
There are three
segments of the .
CD
of (LIGHT DARK)
In the presence 2 cell
Cortical CD :
types large
·
·
> ,
ADH all seg ments
of
KEY JOB :
SECRETION OF KT RB C
the CD become CLIGHT , PARK)
OuterMeduaMLIYP TRINEAUDIFICATION ; REABSORBTION OF 14
>
permeable to Hzu
LENGTH OF LOOP OF HENLE by AQP2 translocatio
.
CD REABSORBTION Nat C kt
Inner
MedullaryCURINE
KEY JOB Urea H2o
: :
> ,
, ,
mol ecu
H + SECRETION ALIDIFICATION) .
depending whether we're
the
length of the Lot vary on
viewing a cortical or
juxtamedullary nephron their
:
differences are
physiologically relevant
CORTICAL NEPHRONS JUXTAMEPULLARY NEPURONS
LOCATION RENAL CORTEX EXTEND INTO BOTH CORTEX +
MEDULLA
ROLE IN URINE Involved in reabsorption contribute to establishing /gradient
CONCENTRATION + .
contribute to turine] + producing highly [I'd urine
.
EFFIENCY IN URINE Limited
efficiency in More efficient in
producing CLINICAL CORRELATION :
MI
CONCENTRATION producing highly highly <I'd urine.
[J' urine ·
OCCURS WHEN :
There is a
OSMOTIC GRABIENT contributes to the maintenance plays major a role in
establishing membrane
Causing
maintaining
the
.
·
MAINTENANCE of Osm .
gradient and osm .
gradient.
in the medulla
.
R 7. Identify the site of
Well-adaptedfor Consewing specialized to conservation in
ADAPTATION TO WATER for
CONSERVATION
challenging environments (ex and : stimulus for erythropoi
erythropoietin action.
COUNTERCURRENT Involved in countercurrent critical for
maximizingHzo
EXCHANGE
exchange for salt+H20 reabsorption and [urine] .
·
Erythropoietin (EPO) is produced
MECHANISM
reabsorption
.
Stimulation
Adequate via
hy
·
ENVIRONMENTAL Suited for environments suited for environments
tissue Bode marr
Target
·
:
ADADTATION where Hzo conservation
relatively abundant u/
H20 is crucial
R B. Understand the rela
, Renal clearance
R 13. Explain the clearance principle. Use the clearance equation and an R 15. Given the plasm
appropriate compound to estimate the glomerular filtration rate, renal rate, calculate the filt
plasma flow, and renal blood flow. clearance of inulin, cr
CLEARANCE and penicillin. Predic
secretion will affect r
clearance ((x) the to the volume of plasma from which substance is
completely removed
=
a
·
FILTERED LOAD
by the kidney/time . NOTE
:
reabsorption and secretion can affect clearance
.
·
concept
:
·
(x =
clearance
·
Filtered Load i
reabsorbed its clearance rate will
REABSORPTION :
If
something is
readily be
·
low because i t isn't found in the urine
easily.
·
(x UX V substance filtered the
Ux urine [X] by
S . = ↳ As result this leads to a fractional excretion (FE)
.
= a Low FEC1 O.
Cabsorption)
PY excreted then more of it
Rain the
SECRETION a substance is easily is
represents
:I f
v I the initial step
·
=
affected
glomerular filtration rate urine flow rate
.
by urine
FE > 1 0 .
and its
Secretion/excretion
REABSORPTION RATEi s
.
LOW and SECRETION ,
GFR RPF =F
Px of the amount su
plasma [X]
· = measure
afferent vasoconstriction ↓ ↓ -
·
efferent vasoconstriction ↑ ↓ ↑
↳ GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR) normal GER
- 180L/day.
=
·
oncotic pressure
[X]
=
aplasma ↓ ↓ FLx
R 14. Distinguish between the use of inulin and creatinine clearances as measures of the
In
·
ureteral constriction ↓ ↓
a
glomerular filtration rate.
dehydration ↓
·
ideal compound neither reabsorbed nor secreted the tubules
an is inulin , a substance
by
·
aldosterone & M
-
a
·
angiotensin I ↑ ↓ ↑
for becausemoneisseei raune
TUBULAR TRANSPO
Cinulin
·
·
-
invin the =
GFR overestimate GFR
, -makes us
- GFR
·
creatinine Can also be used to estimate GFR however some @ f the PT (10 % )
creatinine is secreted
↑
·
fubular
transport :
the
Creatinine If we're GFR the
Kidneys. The
FF which means the
higher. making approximation
*
=
is the that creatinine
ren
RPF
then that would mean that we're overestimating GFR by 10 %. Thus for creatinine clearance formation where vari
,
a correction factor is ·
needed to maintain the
body
GFR = Creatinine x
(Ucreatininex) ;
where K =
to secretion of
the tubules
.
a constant relateda
creatinine
TT =
FL -
by
·
The rate of clearance of some substances can be used renal
to measure function.
↳ If [x > GFR net secretion of X
,
4) If (x < GFR net reabsorption of X
.
,
Fractional Excretion EXCRETION RATE (ER
·
Fractional excretion rate (FE) :
the proportion of filtered load of a substance that is excreted in the urine Lie ·
excretion rate :
th
cleared from the plasma
.
thru var
·
FE = tractional excretion · FEC1 O .
excretion rate
reabsorption HIGH
Low
; the
body
1 %: much more is
eX :
Fina
(x
=
clearance X
·
reabsorbed
kidneys
=
FE CX = CX excretion HIGH the or ot
rate
;
=
FE)1 .
0
(in =
clearance inulin
·
reabsorption LOW
Cin GFR is
ex :
Finulin 100 % much more
of
=
GFR the amount
·
excreted .
a
RENAL PLASMA FLOW (RPF) and RENAL BLOOD FLOW in
understanding th
blood that is
- I
both the blood that is entering and the leaving .
renal
kidneys in given/time
ava
blood flow
= ·
Renal Blood Flow volume of blood that passes : thre the a
RBF thm the
capillaries
Kidneys. BP , hormones Cx
Reflects perfusion of the It is influence by sympathetic NS
. ER
.
=
,
It
· Renal Plasma Flow :
volume of plasma that passes the the
kidneys/time .
represents the
portion of total cardial output directed to the
kidneys HOW DO CHANGES IN FILTRA
·
for filtration , reabsorption , and secretion
. ↳ FILTRATION : & filtrat
↳
estimated
by using substances like para-amino hippunt acd (PAH) which is ↑ filtration wh
·
a
,
cleared from RP F inulin 100 % filter
plasma
.
CPAH
= · =
·
RBF is RPF due to hematocrit difference btwn PAH RPF = ↑
20 %
higher than
·
=
approv
·
.
and whole .
blood ↳
REABSORPTION : &
r
·
RBF =
Renal Blood Flow (mL/min)
RPF =
RBF .
(1-hematocrit) RPF
processing + excretio
·
= Renal Plasma Flor
·
·
nematocrit reabsorption ,
R A. Distinguish between solute clearance versus free water clearance.
=
reabsorb
glucose
·
↳
SECRETION : ↑ Sec
·
The volume of plasma cleared of solute per unit time .
solute clearance ((X) It's
primarily focused on the removal of solutes and it processing + excret
secretion
·
UX V reflects the from
eliminating a solute ,
CX
efficiency of the
.
=
PX
creatinine
freely
=
bloodstream
. EX : creatinine clearance
.
penicilin actively
· =
Expressed as mL/min or
1/day
The volume of water cleared from solute-free water
per
·
unit time
. Foccuses on the removal of water from solute-free
describe the stry of the
kidney
to
-
allow these main process
KIDNEYS OTHER FUNCTIONS
O
R A. Overview of main kidney structure-function including 3 basic renal processes. R 11. On an electron mic
structures of the glome
·
excretion of metabolic waste products and toxins ·
the Kidneys are vital
organs responsible for maintaining homeostasis
by filtering
blood and
regulating glomerular capillary ne
juxtaglomerular appara
Regulation of and
electrolyte balances
. The
Kidneys 200 under
hypoxic conditions.
·
water
water and electrolyte balance are also responsible for making glomerular filtration ba
·
Regulation of
body fluid osmolarity and
electrolytes
RBCs to
and the basement mem
Toa the # of :
↑O carrying capacity
.
Regulation of arterial blood pressure
·
· The three basic processes are filtration reabsorption , and secretion . Also excretion
,
! ·
The renal
corpuscle
=
glomerular t
of Aid-Base balance
Regulation
·
4 Glomerular Tuft Tuft ofC apillarie
=
selective membrane DIRECTION : BLOOD -BOWMAN'S CAPSULE
·
Regulation of
oxygen carrying capacity Filtration :
filtering of blood over a ,
Secretion Metabolism E xcretion of hormones.
and and specific GFR
and small solutes. Includes :
glomerula
occurs btwn
glomerular capillaries &
· ·
, ,
glomenius a .
·
Gluconeogenesis size +
charge
.
endothelium- fenestrated item
Reabsorption
·
:
occurs btorn the tubules . DIRECTION
and interstitium Filtrate blood (peritubular) podicalyxin Ca polyanisc sur f
Terminology
·
: ->
proximal convoluted Secretion :
Bowman's Double-walle
tubule
capsule
·
PCT = ↳ :
limb occurs between the tubules and interstitium
. DIRECTION blood (peritubular) Filtrate LAYERS
descending
·
-
TKDL
·
:
thick
·
=
A) Parietal couter) :
simple
TNDC limb excreted
things filtered t secreted but ot reabsorbed !
thin
descending Excretion stuff that are that
·
=
: The are are
3) Visceral (inner) :
pod
·
TNAL =
thin ascending limb excretion =
fitration +
secretion-reabsorption
&
TRA) thick
ascending
limb R 9. Describe in sequence the tubular segments through which ultrafiltrate flows after it is
·
=
formed at Bowman's capsule to when it enters the renal pelvis. Identify each structure as
·
DCT =
distal convoluted tubule .
being located in the renal cortex or renal medulla. Based on the glomerulus location and the ~
↳
cs
length of the loop of Henle, distinguish between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons.
collecting segment
·
=
BONMAN'S CAPULE- PET
-
-
LOH- ALT-COLLECTING DUCT -
RENAL PELVIS
-
,
duct
collecting
·
CD =
PATH OF ULTRAFILTRATE medulla
cortex medulla cor tex
component facilitates tubuloglomerular
proxima
vascular
Henle
↑ >
distal AA +
feedback
EA +
-
COH-loop of
-
region
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus extraglomerular mesangial
·
:
·
[Nats
L
macula densa cells detect
component tubular
·
·
macula densa
if low release factors thu Lacis
·
AA =
afferent arteriole (extraglomular mesengial cells)
>
-
the JG
-
activity regis
renin to PCT : &NRA &
A A to release energy
>
cells@ the
:
-
.
REABSORPTO mesen
initiate RAAS &BP
Key job
- .
· :
+ cat Po
EA efferent arteviole Proximal Tubule (PCT , TKDL)
,
g
·
= .
a a
. of
glucose ,
·
H2o , organic solute , Portion
chemic
injury Rxtoxicity by podo
+
prone to is
TKDL fr than in PCT
> : NKA activity
·
key job
.
= SECRETION organic anions + R 17. Identify the filt
cations some medication
TNDL
,
:
Permable to H20 , impermeable
of H20, Na, inulin, al
to ions
·
Rey job
:H2 REABSORBTION
·
Thin limb of LOH(TNDL TNAL) passive ; due to osmolarity
·
Filtration Barrier
,
TNAL : impermeable to H20,
to i s
> permeable
·
TKAL : REY JOB =
ACTIVE NaCl
OF
SUBSTANCE SIZE/C
KEY JOD MAINTAINANCE
·
:
TRANSPORTFROM LUMENE INTERSTITUM small
OSMOTIC GRADI ENT
·
,
interstitium medulla)
results in
hypertonic medullary (cortex + WATER
+ dilute tubular flid .
·
small
,
DCTMNAactivitrelativeimpermeable a cotransporter Nat
·
-
· small
,
fluid INULIN
CS
many nephrons
· =
connects + takes to CD
.
.
·
REY JOB :
K
+
secretion (reg'd by
aldosterone + Cas t reabsorption
(NatCa't exchangers Ca2 + Atpase)
ALBUMIN large , n
·
·
CD =
There are three
segments of the .
CD
of (LIGHT DARK)
In the presence 2 cell
Cortical CD :
types large
·
·
> ,
ADH all seg ments
of
KEY JOB :
SECRETION OF KT RB C
the CD become CLIGHT , PARK)
OuterMeduaMLIYP TRINEAUDIFICATION ; REABSORBTION OF 14
>
permeable to Hzu
LENGTH OF LOOP OF HENLE by AQP2 translocatio
.
CD REABSORBTION Nat C kt
Inner
MedullaryCURINE
KEY JOB Urea H2o
: :
> ,
, ,
mol ecu
H + SECRETION ALIDIFICATION) .
depending whether we're
the
length of the Lot vary on
viewing a cortical or
juxtamedullary nephron their
:
differences are
physiologically relevant
CORTICAL NEPHRONS JUXTAMEPULLARY NEPURONS
LOCATION RENAL CORTEX EXTEND INTO BOTH CORTEX +
MEDULLA
ROLE IN URINE Involved in reabsorption contribute to establishing /gradient
CONCENTRATION + .
contribute to turine] + producing highly [I'd urine
.
EFFIENCY IN URINE Limited
efficiency in More efficient in
producing CLINICAL CORRELATION :
MI
CONCENTRATION producing highly highly <I'd urine.
[J' urine ·
OCCURS WHEN :
There is a
OSMOTIC GRABIENT contributes to the maintenance plays major a role in
establishing membrane
Causing
maintaining
the
.
·
MAINTENANCE of Osm .
gradient and osm .
gradient.
in the medulla
.
R 7. Identify the site of
Well-adaptedfor Consewing specialized to conservation in
ADAPTATION TO WATER for
CONSERVATION
challenging environments (ex and : stimulus for erythropoi
erythropoietin action.
COUNTERCURRENT Involved in countercurrent critical for
maximizingHzo
EXCHANGE
exchange for salt+H20 reabsorption and [urine] .
·
Erythropoietin (EPO) is produced
MECHANISM
reabsorption
.
Stimulation
Adequate via
hy
·
ENVIRONMENTAL Suited for environments suited for environments
tissue Bode marr
Target
·
:
ADADTATION where Hzo conservation
relatively abundant u/
H20 is crucial
R B. Understand the rela
, Renal clearance
R 13. Explain the clearance principle. Use the clearance equation and an R 15. Given the plasm
appropriate compound to estimate the glomerular filtration rate, renal rate, calculate the filt
plasma flow, and renal blood flow. clearance of inulin, cr
CLEARANCE and penicillin. Predic
secretion will affect r
clearance ((x) the to the volume of plasma from which substance is
completely removed
=
a
·
FILTERED LOAD
by the kidney/time . NOTE
:
reabsorption and secretion can affect clearance
.
·
concept
:
·
(x =
clearance
·
Filtered Load i
reabsorbed its clearance rate will
REABSORPTION :
If
something is
readily be
·
low because i t isn't found in the urine
easily.
·
(x UX V substance filtered the
Ux urine [X] by
S . = ↳ As result this leads to a fractional excretion (FE)
.
= a Low FEC1 O.
Cabsorption)
PY excreted then more of it
Rain the
SECRETION a substance is easily is
represents
:I f
v I the initial step
·
=
affected
glomerular filtration rate urine flow rate
.
by urine
FE > 1 0 .
and its
Secretion/excretion
REABSORPTION RATEi s
.
LOW and SECRETION ,
GFR RPF =F
Px of the amount su
plasma [X]
· = measure
afferent vasoconstriction ↓ ↓ -
·
efferent vasoconstriction ↑ ↓ ↑
↳ GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR) normal GER
- 180L/day.
=
·
oncotic pressure
[X]
=
aplasma ↓ ↓ FLx
R 14. Distinguish between the use of inulin and creatinine clearances as measures of the
In
·
ureteral constriction ↓ ↓
a
glomerular filtration rate.
dehydration ↓
·
ideal compound neither reabsorbed nor secreted the tubules
an is inulin , a substance
by
·
aldosterone & M
-
a
·
angiotensin I ↑ ↓ ↑
for becausemoneisseei raune
TUBULAR TRANSPO
Cinulin
·
·
-
invin the =
GFR overestimate GFR
, -makes us
- GFR
·
creatinine Can also be used to estimate GFR however some @ f the PT (10 % )
creatinine is secreted
↑
·
fubular
transport :
the
Creatinine If we're GFR the
Kidneys. The
FF which means the
higher. making approximation
*
=
is the that creatinine
ren
RPF
then that would mean that we're overestimating GFR by 10 %. Thus for creatinine clearance formation where vari
,
a correction factor is ·
needed to maintain the
body
GFR = Creatinine x
(Ucreatininex) ;
where K =
to secretion of
the tubules
.
a constant relateda
creatinine
TT =
FL -
by
·
The rate of clearance of some substances can be used renal
to measure function.
↳ If [x > GFR net secretion of X
,
4) If (x < GFR net reabsorption of X
.
,
Fractional Excretion EXCRETION RATE (ER
·
Fractional excretion rate (FE) :
the proportion of filtered load of a substance that is excreted in the urine Lie ·
excretion rate :
th
cleared from the plasma
.
thru var
·
FE = tractional excretion · FEC1 O .
excretion rate
reabsorption HIGH
Low
; the
body
1 %: much more is
eX :
Fina
(x
=
clearance X
·
reabsorbed
kidneys
=
FE CX = CX excretion HIGH the or ot
rate
;
=
FE)1 .
0
(in =
clearance inulin
·
reabsorption LOW
Cin GFR is
ex :
Finulin 100 % much more
of
=
GFR the amount
·
excreted .
a
RENAL PLASMA FLOW (RPF) and RENAL BLOOD FLOW in
understanding th
blood that is
- I
both the blood that is entering and the leaving .
renal
kidneys in given/time
ava
blood flow
= ·
Renal Blood Flow volume of blood that passes : thre the a
RBF thm the
capillaries
Kidneys. BP , hormones Cx
Reflects perfusion of the It is influence by sympathetic NS
. ER
.
=
,
It
· Renal Plasma Flow :
volume of plasma that passes the the
kidneys/time .
represents the
portion of total cardial output directed to the
kidneys HOW DO CHANGES IN FILTRA
·
for filtration , reabsorption , and secretion
. ↳ FILTRATION : & filtrat
↳
estimated
by using substances like para-amino hippunt acd (PAH) which is ↑ filtration wh
·
a
,
cleared from RP F inulin 100 % filter
plasma
.
CPAH
= · =
·
RBF is RPF due to hematocrit difference btwn PAH RPF = ↑
20 %
higher than
·
=
approv
·
.
and whole .
blood ↳
REABSORPTION : &
r
·
RBF =
Renal Blood Flow (mL/min)
RPF =
RBF .
(1-hematocrit) RPF
processing + excretio
·
= Renal Plasma Flor
·
·
nematocrit reabsorption ,
R A. Distinguish between solute clearance versus free water clearance.
=
reabsorb
glucose
·
↳
SECRETION : ↑ Sec
·
The volume of plasma cleared of solute per unit time .
solute clearance ((X) It's
primarily focused on the removal of solutes and it processing + excret
secretion
·
UX V reflects the from
eliminating a solute ,
CX
efficiency of the
.
=
PX
creatinine
freely
=
bloodstream
. EX : creatinine clearance
.
penicilin actively
· =
Expressed as mL/min or
1/day
The volume of water cleared from solute-free water
per
·
unit time
. Foccuses on the removal of water from solute-free