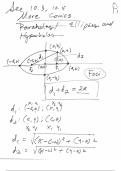
Embryology Practice Questions with Answers Graded A+
1.1. The part of the sperm containing proteolytic enzymes to digest the
zona pellucida is the:
A. capacitor
B. head
C. corona
D. acrosome
E. cumulus: D. is correct.
The acrosome is the part of the sperm containing proteolytic enzymes
to digest the zona pellucida. It is exposed by the process of
capacitation. Then, under the influence of substances released by
corona radiata cells, it releases its proteolytic enzymes and penetrates
the oocyte.
2.3. The seven-day blastocyst:
A. has a single layer of trophoblast at the embryonic pole
B. has an amniotic cavity
C. is attached to the endometrial epithelium
D. is surrounded by a degenerating zona pellucida
E. is called the hypoblast: C. is correct.
The decidual reaction of the endometrium creates a nourishing
environment for the conceptus a it buries itself by invasion of the
uterine endometrial wall. Progesterone produced by the corpus luteum
,stimulates glandular secretion in the endometrium during the secretory
phase of menstruation or early pregnancy.
3.5. The first week of human development is characterized by formation
of the:
A. inner cell mass
B. hypoblast
C. trophoblast
D. blastocyst
E. all of the above: E. is correct.
At four days, the blastocyst cavity of blastocele forms within the
morula. Trophoblast are outer cells of the blastocyst, while a knot of
cells appears, protruding into the blastocele. This is the inner cell mass.
Trophoblast becomes 2 layers: syncytiotro- phoblast and
cytotrophoblast. Inner cell mass becomes epiblast and hypoblast.
4.6. During implantation, the blastocyst:
A. implants in the endometrium
B. usually attaches to endometrial epithelium at its embryonic pole
C. usually implants in the posterior wall of the body of the uterus
D. causes change in the endometrial tissues
E. all of the above are correct: E. is correct.
Implantation occurs when the trophoblast cells at the embryonic pole
secrete prote- olytic enzymes that allow the blastocyst to penetrate the
wall of the uterus, usually the posterior wall. The endometrial lining
responds to implantation through the decidua reaction, by which it
, becomes more succulent for nourishing the blastocyst.
5.7. Capacitation of the sperm:
A. is caused by the zona pellucida
B. occurs in the male
C. prevents polyspermy
D. is essential for fertilization
E. removes the head of the sperm: D. is correct.
Capacitation involves removing the glycoprotein coat and seminal
plasma proteins from the head of the sperm, exposing the acrosome
and allowing the acrosome reaction to occur. Capacitation occurs within
the female genital tract, and without its occurrence, fertilization could
not occur.
6.8. The early stages of cleavage are characterized by:
A. formation of a hollow ball of cells
B. formation of the zona pellucida
C. increase in the size of the cells in the zygote
D. increase in the number of cells in the zygote
E. none of the above: D. is correct.
The earliest stages of cleavage are marked by a series of mitotic
divisions that increase the number of cells in the zygote without an
increase in size. As the cleavage continues the zygote becomes a
morula or a solid ball of 12-16 cels. A cavity forming within the morula
transforms it into a blasocyst, at about day 4.
7.9. The most common site for implantation in ectopic pregnancy is:
1.1. The part of the sperm containing proteolytic enzymes to digest the
zona pellucida is the:
A. capacitor
B. head
C. corona
D. acrosome
E. cumulus: D. is correct.
The acrosome is the part of the sperm containing proteolytic enzymes
to digest the zona pellucida. It is exposed by the process of
capacitation. Then, under the influence of substances released by
corona radiata cells, it releases its proteolytic enzymes and penetrates
the oocyte.
2.3. The seven-day blastocyst:
A. has a single layer of trophoblast at the embryonic pole
B. has an amniotic cavity
C. is attached to the endometrial epithelium
D. is surrounded by a degenerating zona pellucida
E. is called the hypoblast: C. is correct.
The decidual reaction of the endometrium creates a nourishing
environment for the conceptus a it buries itself by invasion of the
uterine endometrial wall. Progesterone produced by the corpus luteum
,stimulates glandular secretion in the endometrium during the secretory
phase of menstruation or early pregnancy.
3.5. The first week of human development is characterized by formation
of the:
A. inner cell mass
B. hypoblast
C. trophoblast
D. blastocyst
E. all of the above: E. is correct.
At four days, the blastocyst cavity of blastocele forms within the
morula. Trophoblast are outer cells of the blastocyst, while a knot of
cells appears, protruding into the blastocele. This is the inner cell mass.
Trophoblast becomes 2 layers: syncytiotro- phoblast and
cytotrophoblast. Inner cell mass becomes epiblast and hypoblast.
4.6. During implantation, the blastocyst:
A. implants in the endometrium
B. usually attaches to endometrial epithelium at its embryonic pole
C. usually implants in the posterior wall of the body of the uterus
D. causes change in the endometrial tissues
E. all of the above are correct: E. is correct.
Implantation occurs when the trophoblast cells at the embryonic pole
secrete prote- olytic enzymes that allow the blastocyst to penetrate the
wall of the uterus, usually the posterior wall. The endometrial lining
responds to implantation through the decidua reaction, by which it
, becomes more succulent for nourishing the blastocyst.
5.7. Capacitation of the sperm:
A. is caused by the zona pellucida
B. occurs in the male
C. prevents polyspermy
D. is essential for fertilization
E. removes the head of the sperm: D. is correct.
Capacitation involves removing the glycoprotein coat and seminal
plasma proteins from the head of the sperm, exposing the acrosome
and allowing the acrosome reaction to occur. Capacitation occurs within
the female genital tract, and without its occurrence, fertilization could
not occur.
6.8. The early stages of cleavage are characterized by:
A. formation of a hollow ball of cells
B. formation of the zona pellucida
C. increase in the size of the cells in the zygote
D. increase in the number of cells in the zygote
E. none of the above: D. is correct.
The earliest stages of cleavage are marked by a series of mitotic
divisions that increase the number of cells in the zygote without an
increase in size. As the cleavage continues the zygote becomes a
morula or a solid ball of 12-16 cels. A cavity forming within the morula
transforms it into a blasocyst, at about day 4.
7.9. The most common site for implantation in ectopic pregnancy is: