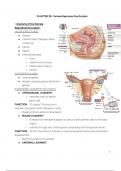
1. Anatomy of the Female
Reproductive system:
MAJOR STRUCTURES
● Ovaries
● Uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes
/ Oviducts)
● Uterus
● Vagina
● External Genitalia:
○ Vulva
○ Labia minora (minus)
○ Labia majora (majus)
○ Clitoris
ACCESSORY GLANDS
● Urethral glands
● Greater vestibular gland (Bartholin’s
glands)
SUSPENSORY LIGAMENTS OF UTERUS
● UTEROSACRAL LIGAMENT
○ Aaches overy to lateral
pelvic wall
FUNCTION: - To support the ovary and
maintain its position within the pelvic cavity
- Prevent inferior-anterior movements
● ROUND LIGAMENT
○ Extends from the lateral aspect of uterus (near uterine tube) to the labia
majora.
○ Extends through very small inguinal canal along with ilioinguinal nerves.
FUNCTION - Anchor the uterus in the pelvic cavity and prevents excessive movement /
displacement
- Restricts posterior movement
● CARDINAL LIGAMENT
1
, ○ Aaches to the cervix of the
uterus and to the lateral pelvic
walls.
FUNCTION - Provides support to the cervix and
helps maintain the position of the uterus within
the pelvis
- Prevents inferior movements
MESENTARIES OF THE UTERUS, OVARIES, AND
UTERINE TUBES
● MESOSALPINX A fold of peritoneum
that encloses the uterine tubes and aaches them to the lateral aspect of the
uterus
● MESOVARIUM Thickened fold of mesentary, supports and stabilizes the position
of each ovary
● BROAD LIGAMENT A broad fold of
peritoneum that encloses and
supports the uterus, fallopian tubes,
and ovaries.
2. Anatomy of the Ovaries:
● Small, almond-shaped organs near
lateral walls of the pelvic cavity
● Stabilized by a pair of ligaments:
○ The ovarian ligament
○ The suspensory (infundulopelvic) ligament
FUNCTIONS
● Produce immature female gametes (oocytes)
● Secrete female sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone)
● Secrete inhibin - involved in the feedback control of pituitary FHS production
LAYERS OF THE OVARIES
● VISCERAL PERITONEUM (Germinal Epithelium): covers the surface of each
ovary and has a layer of columnar epithelial cells that lays over the tunica
albuginea
● STROMA the interior tissues of the ovary - divided into layers
2
, ○ SUPERFICIAL CORTEX Gametes produced here
○ DEEPER MEDULLA
MESENTARY OF THE OVARY
● The mesovarium
ARTERIES THAT SUPPLY OVARIES
● Primarily supplied by the ovarian arteries
○ Ovarian arteries originate in the abdominal aorta and travel through the
suspensory ligament to the ovary
3. Anatomy of the Uterine Tube:
● Also called Fallopian tubes or
Oviducts
● Hollow, muscular tubes about 13 cm
long
● Has three regions:
○ Infundibulum: the end closest
to the ovary that forms an
expanded funnel with fimbriae
that extend into the pelvic cavity
■ Fimbriae drape over the
surface of the ovary but there is NO
PHYSICAL CONNECTION between the
two structures
■ Inner surface of infundibulum is lines with
cilia
○ Ampulla: the middle region of the Uterine tube
■ Thickness of smooth muscle layers
increase as the tube approaches the
uterus
○ Isthmus: the ampulla leads into the isthmus
■ Short region connected to the uterine wall
UTERINE TUBE HISTOLOGY
3