Exam Questions with 100% Correct
Answers
Which patient population would be most at risk for opportunistic infection? - Answer-
Immunocompromised patients are at high risk for opportunistic infections. Traditionally,
there are infections that arise from endogenous reactivation of latent infections, and
nosocomial transmission. Therefore, it is deemed likely that special infection control (IC)
interventions are required to prevent transmission in healthcare settings.
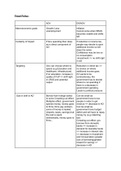
What immunoglobulin is associated with Type I hypersensitivity and action, examples? -
Answer-Type I hypersensitivity is also known as an immediate reaction and involves
immunoglobulin E (IgE) mediated release of antibodies against the soluble antigen. This
activity reviews the evaluation and management of type I hypersensitivity and reviews
the role of the interprofessional teams in managing patients with this condition.
What immunoglobulin is associated with Type II hypersensitivity and action, examples?
- Answer-Ige, IgM, Blood type responses, 5-8 HOURS
What immunoglobulin is associated with Type III hypersensitivity and action, examples?
- Answer-IgG, autoimmune disorders 2-8 HOURS. Type III hypersensitivity is also
known as immune complex reactions and involves IgG , IgM , and sometimes IgA
antibodies. The build-up of these immune complexes results in complement system
activation, which leads to polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) chemotaxis and
eventually causing tissue damage.
What immunoglobulin is associated with Type IV hypersensitivity and action, examples?
- Answer-celular, contact dermatitis, chrons disease 1-3 DAYS. A Type IV
hypersensitivity reaction is mediated by T cells that provoke an inflammatory reaction
against exogenous or endogenous antigens. In certain situations, other cells, such as
monocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils, can be involved. After antigen exposure, an
initial local immune and inflammatory response occurs that attracts leukocytes. The
antigen engulfed by the macrophages and monocytes is presented to T cells, which
then becomes sensitized and activated. These cells then release cytokines and
chemokines, which can cause tissue damage and may result in illnesses. Examples of
illnesses resulting from type IV hypersensitivity reactions include contact dermatitis and
drug hypersensitivity. Type IV reactions are further subdivided into type IVa, IVb, IVc,
and IVd based on the type of T cell (CD4 T-helper type 1 and type 2 cells) involved and
the cytokines/chemokines produced.
, What immunoglobulin is associated with Delayed hypersensitivity and action,
examples? - Answer-delayed hypersensitivity reaction (DHR), which takes more than 12
hours to develop. Typically the maximal reaction time occurs between 48 to 72 hours.
Antibodies do not mediate DHR; it is mediated by T cells that cause an inflammatory
reaction to either exogenous or autoantigens. This HR to exogenous antigens involves
T cells and also antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as macrophages and dendritic
cells, all produce cytokines that stimulate a local inflammatory response in a sensitized
individual. The DHR to autoantigens can be seen in type 1 diabetes mellitus, which is
an autoimmune disease that results from autoimmune cell-mediated destruction of
insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells. DHR cannot be transferred from an animal to
another by means of antibodies or serum. However, it can be transferred by T cells,
particularly CD4 Th1 cells, but it is progressively lost in individuals with HIV/AIDS.
Antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as Langerhans cells engulf process and present
antigens to antigen-specific T cells that become sensitized. Cytokines produced by
keratinocytes, APC, and T cells recruit antigen-nonspecific T cells and macrophages to
participate in a local inflammatory reaction. The activity describes the interprofessional
evaluation and management of patients with delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
What lab tests measure inflammation? - Answer-C-reactive protein (CRP), Erythrocyte
sedimentation rate (ESR), plasma viscosity (PV) blood tests are commonly used to
detect increase in protein in the blood. In this way they are used as markers of
inflammation.
the complications of stress - Answer-casues:
hypertension
tension headaches
insomnia
diabetes mellitus
infection
heart failure
peptic ulcer
fatigue
induces pre-existing diseases:
asthma
angina
GI issues
seizures
herpes
acne
rheumatoid arthritis
Examples of body's adaptive immune response - Answer-Vertebrates, too, depend on
such innate immune responses as a first line of defense (discussed in Chapter 25), but
they can also mount much more sophisticated defenses, called adaptive immune
responses.