TOPIC 18 Human Genetics
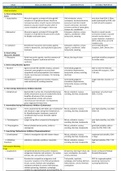
Mendelian Non Mendelian
Autosomal Recessive
gene codes functional protein
Diy 2n normal forhumans
heterozygous carrier Disjunction homologous chromosomes sisters
carriers codominant fail to separate
2 versionsofsame
geneare expressed Aneuploidy abnormal of aparticular chromosome
separately
difftraitsin TurnerSyndrome X
individuals onlypossible monosomy
normal cells hemoglobin shortthick webbedneck generallysterile
4 abnormal does not
Klinefelter syndrome XXY
tallistffenfipqetf.ggingdisabilities
Autosomal Dominant
just have to inherit 1 copy
start a age40 xxY Males
usually fertile
Tishmy 3 copiesof particular chromosome
DownSyndrome Trisomy 21
Moomy missing I copyofchromosome
Changes to Chromosome structure
Deletion segment deleted
Duplication segment appears twice gene overexpressed
Inversion segmentswitches flips problem producing protein
Translocation non homologs lineup exchange
Genomic imprinting
methyl tags deactivate 1 allele
during gamete formation gene is permanently chulated
I copy expressed I copy is not
Andelman Syndrome methylation ofchrom frommom distinct physical development characteristics
Prader Willi Syndrome methylation of chrom fromdad obesity type 2 diabetes
wretabolic endocrine
, Fetal Testing Newborn Screening
Amniocentesis cimhiotic PKU Phenylketonuria
fluid is inherited as 2 recessive
8 TFweeks removed alleles
tested
specialdiet nomeatfishdairy breadnuts
Chronic Villus tissue sample prick babyfoot
fromplacenta
TEY oweek Maternal PKU damages brain of fetus
Recessive Disorders Dominant Disorders
SickleCell Disease Achondroplasia
single as in hemoglobin
protein aminoacid
mutation in gene thatcodes
Me GÉfnt
for betachain
6ᵗʰ as GlutamicAcid valine Polydactl
6 fingers dominant
amino acid changed so protein 5 fingers recessive
won't make hemoglobin
Lethal Alleles
Albinism partial complete absence of Recessive passeddownfrom1 gen tonext
melanin homozygous recessive death
Dominant
Cystic Fibrosis I copy death before individual matures produce
late onset
Huntington Disease
gradual neural degeneration
age 40
childhas 50 chanceofinheritance
, TOPIC 19 Intro to Evolution
Pe Darwaniann
Darwinian ideas
Variation membersofpop vary intraits
Overproduction more offspring produced thancansurvive
Unequal Ability to survive reproduce
Nonrandom survival reproduction survival reproduction is based on phenotype
best added most offspring
Thomas Malthus natural resources LIMITED
organisms compete for resources
more ind than resources
Illustrations of Evolution
Artificialselection humandriven
Direct Observation antibioticresistance
Homology similarity resulting fromcommon ancestry
FossilRecord remains or traces inrock of previously
existing organisms
Mendelian Non Mendelian
Autosomal Recessive
gene codes functional protein
Diy 2n normal forhumans
heterozygous carrier Disjunction homologous chromosomes sisters
carriers codominant fail to separate
2 versionsofsame
geneare expressed Aneuploidy abnormal of aparticular chromosome
separately
difftraitsin TurnerSyndrome X
individuals onlypossible monosomy
normal cells hemoglobin shortthick webbedneck generallysterile
4 abnormal does not
Klinefelter syndrome XXY
tallistffenfipqetf.ggingdisabilities
Autosomal Dominant
just have to inherit 1 copy
start a age40 xxY Males
usually fertile
Tishmy 3 copiesof particular chromosome
DownSyndrome Trisomy 21
Moomy missing I copyofchromosome
Changes to Chromosome structure
Deletion segment deleted
Duplication segment appears twice gene overexpressed
Inversion segmentswitches flips problem producing protein
Translocation non homologs lineup exchange
Genomic imprinting
methyl tags deactivate 1 allele
during gamete formation gene is permanently chulated
I copy expressed I copy is not
Andelman Syndrome methylation ofchrom frommom distinct physical development characteristics
Prader Willi Syndrome methylation of chrom fromdad obesity type 2 diabetes
wretabolic endocrine
, Fetal Testing Newborn Screening
Amniocentesis cimhiotic PKU Phenylketonuria
fluid is inherited as 2 recessive
8 TFweeks removed alleles
tested
specialdiet nomeatfishdairy breadnuts
Chronic Villus tissue sample prick babyfoot
fromplacenta
TEY oweek Maternal PKU damages brain of fetus
Recessive Disorders Dominant Disorders
SickleCell Disease Achondroplasia
single as in hemoglobin
protein aminoacid
mutation in gene thatcodes
Me GÉfnt
for betachain
6ᵗʰ as GlutamicAcid valine Polydactl
6 fingers dominant
amino acid changed so protein 5 fingers recessive
won't make hemoglobin
Lethal Alleles
Albinism partial complete absence of Recessive passeddownfrom1 gen tonext
melanin homozygous recessive death
Dominant
Cystic Fibrosis I copy death before individual matures produce
late onset
Huntington Disease
gradual neural degeneration
age 40
childhas 50 chanceofinheritance
, TOPIC 19 Intro to Evolution
Pe Darwaniann
Darwinian ideas
Variation membersofpop vary intraits
Overproduction more offspring produced thancansurvive
Unequal Ability to survive reproduce
Nonrandom survival reproduction survival reproduction is based on phenotype
best added most offspring
Thomas Malthus natural resources LIMITED
organisms compete for resources
more ind than resources
Illustrations of Evolution
Artificialselection humandriven
Direct Observation antibioticresistance
Homology similarity resulting fromcommon ancestry
FossilRecord remains or traces inrock of previously
existing organisms