If a cell has flagella.. - Answer-it must be able to move, e.g. sperm cells
What is the process by which cells become specialised? - Answer-differentiation
What is meant by the term differentiation of cells? - Answer-- when cells start to divide
they are very similar
- as the tissues develop the cells change to form particular function
What is a tissue? - Answer-a group of similar cells that work together to carry out a
particular function
What sort of tissue can you find in mammals? - Answer-- Epithelial tissue: covers some
parts of the body, e.g. the inside and outside of the gut
- Muscular tissue: contracts to move whatever its attached to
- Glandular tissue: makes and secretes chemicals like hormones and enzymes
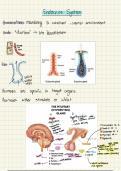
What is an organ? - Answer-a group of different tissues that work together to perform a
certain function, e.g. stomach
What tissues are the stomach made up of and what are their purposes? - Answer--
Epithelial tissue: covers the inside and outside of the stomach
- Muscular tissue: contracts the stomach wall to churn up the food
- Glandular tissue: produces digestive juices to digest food
What is an organ system? - Answer-a group of organs working together to perform a
particular function, e.g. the digestive system breaks down food
What organs does the digestive system include? - Answer-- glands
- the stomach
- the liver
- the small intestine
-the large intestine
What two glands produce digestive juices? - Answer-pancreas and salivary glands
what does both the stomach and small intestine do? - Answer-digest food
1|Page
,What does the liver do? - Answer-produces bile
What does the small intestine do? - Answer-absorbs soluble food molecules
In which type of cell would you find a cell wall, chloroplasts and a vacuole? - Answer-
plant cell
What does an animal cell have? - Answer-- cytoplasm
- nucleus
- ribosomes
- cell membrane
- mitochondria
What does the nucleus do? - Answer-contains genetic material that controls the
activities of the cell
What is the cytoplasm? - Answer-gel-like substance where most of the chemical
reactions happen. It contains enzymes which control these chemical reactions
What is the cell membrane - Answer-holds the cell together and controls what goes in
and out
What happens in the mitochondria? - Answer-these are where most of the reactions for
respiration take place. Respiration releases energy that the cell needs to work
What happens in the ribosomes? - Answer-these are where proteins are made in the
cell
What does a bacterial cell NOT have? - Answer-a nucleus- genetic material floats in the
cytoplasm
What is a yeast cell an example of? - Answer-a single cell organism
What does a yeast cell have? - Answer-- nucleus
- cytoplasm
- cell membrane
- surrounding cell wall
How is a leaf cell different from a yeast cell? - Answer-leaf cells have chloroplasts and a
cellulose cell wall. yeast cells have neither
What is the definition of diffusion? - Answer-the SPREADING OUT of PARTICLES from
an area of HIGH CONCENTRATION to an area of LOW CONCENTRATION
or
the NET MOVEMENT of PARTICLES down a CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
2|Page
, What substances can diffuse through cell membranes? - Answer-small molecules like
oxygen, glucose, amino acids and water
What substances can't diffuse through cell membranes? - Answer-big molecules like
starch and proteins
What are some examples of diffusion? - Answer-- the diffusion of oxygen into the cells
of the body from the bloodstream as the cells are respiring (and using up oxygen)
- the diffusion of carbon dioxide into actively photosynthesising plant cells
- the diffusion of simple sugars and amino acids for the gut through cell membranes
When, and in which direction, will diffusion take place in solutions and in gases? -
Answer-- if two solutions are separated by a cell membrane, particles will move from a
region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
- gases will also diffuse through the air from a region of high concentration to a region of
low concentration
How is a leaf cell adapted to carry out photosynthesis? - Answer-- the leaf has
mesophyll tissue
- the mesophyll cells contain chloroplasts which can photosynthesise
How are palisade cells adapted for photosynthesis? - Answer-- packed will chloroplasts
for photosynthesis
- tall shape means a lot of surface area exposed down the side for absorbing carbon
dioxide from the air in the leaf
- they are grouped together at the top of the leaf so that they can absorb more sunlight
How are red blood cells adapted to carry oxygen? - Answer-- concave shape gives a big
surface area for absorbing oxygen. it also helps them pass smoothly through capillaries
to reach body cells
- packed with haemoglobin which absorbs oxygen
- they have no nucleus to leave even more room for haemoglobin
How are sperm cells adapted for swimming to the egg? - Answer-- streamlined head
and flagella to help it swim to the egg
- there are a lot of mitochondria in the cell to provide the energy needed
- carry enzymes in their heads to digest through the egg cell membrane
If a cell has many mitochondria... - Answer-it must need a lot of energy, e.g. muscle cell,
sperm cell
If a cell has many ribosomes... - Answer-it is making a lot of protein, e.g. gland cells
which produce enzymes
3|Page