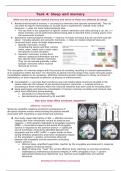
Important terms Law and Security
First Exam
International human rights law:
- It was progressively developed with the expectation to limit states’ coercive practices
against other human beings.
- It applies at all times; peace and war times
- Negative and positive obligation to seek the protection of rights that are inherent to
the human person.
- Might be suspended, except for non-derogable rights
- Includes regional treaties; such as
International Humanitarian Law:
- Regulates conduct in an armed conflict to limit the effects of armed conflicts and to
protect those who do not take part of hostilities
- IHL applies only in armed conflict
- A state cannot suspend IHL
- Based on Geneva and Hague conventions
State of emergency:
- An emergency is: a significant departure from a state of normalcy, triggered by an
extreme event that is highly disruptive or threatening to the established order. It gives
extraordinary powers to steer the state through the crisis/emergency.
Problems with emergencies: The challenges with emergencies are that they often lead to
actions that not only violate the basic legal requirements essential for the rule of law but also
go against the fundamental principles and values embedded in those legal requirements.
The 3 type of emergencies identified by Fatovic (2019)
1. Emergencies arising from violence
2. Natural disasters
3. Economic crises
Emergencies are always temporal; there is a clear beginning and end. The measures taken
are only for as long as necessary.
The essentials:
- Exceptional threat: the crisis must present a real, current or at least an imminent
danger to the community
- The parliament can launch ad hoc inquires and investigations on the use of
emergency powers during the state of emergency.
- The temporality: the state of emergency is temporal
- Declaration: the state of emergency must be announced publicly; this informs citizens
of legal situations.
- Communication: notification of the measurements taken must be made to other
states and relevant treaty-monitoring bodies.
- Proportionality: the measures taken to counter the crisis must be proportional to the
gravity of the emergency situation.
, - Delegation of powers
- Necessity
- No matter the crisis, the state always has to protect the principle of legality
- Intangibility: derogation of rights
Interpol:
- Worldwide and not EU based organization focused on police cooperation
- States have representatives within Interpol
- They focus on information exchange and have huge data sets that member states can
access
- Interpol does not have the authority or possibility to independently operate in a
specific country, they can only work through a member’s states police.
Europol:
- Focused on police cooperation only within the European Union
- Limited mandate, there is no real Europol police, so they can only deal with
transnational issues through the law enforcement of member states.
- They form JIT’s (Joint investigation teams) that consist of representatives of each
state, which makes handling specific security issues involving multiple states easier.
Eurojust:
- Similar to Europol, but this is about judicial cooperation
- Limited mandate, there is no EU prosecuter or EU trial
- Information sharing and assistance -> support mandate
- Helps identifying best place for prosecution
- Can also establish JIT’s
OLAF and EPPO
- European anti-fraud office (OLAF)
- Fraud against the EU budget
- Investigations
- Prosecution on national level
- Strong cooperation with OLAF
- Limited mandate
- An EU actor involved with the prosecution of EU crimes, so doesn’t only act through
national courts
- Investigates, prosecutes and brings to judgement crimes against the financial
interests of the EU
- The EPPO undertakes investigations, carries out acts of prosecutions and exercises
the functions of prosecutor in the competent courts of the participating member
states.
- Eurojust, Europol, and OLAF do not carry out such criminal investigations and
prosecutions.
First Exam
International human rights law:
- It was progressively developed with the expectation to limit states’ coercive practices
against other human beings.
- It applies at all times; peace and war times
- Negative and positive obligation to seek the protection of rights that are inherent to
the human person.
- Might be suspended, except for non-derogable rights
- Includes regional treaties; such as
International Humanitarian Law:
- Regulates conduct in an armed conflict to limit the effects of armed conflicts and to
protect those who do not take part of hostilities
- IHL applies only in armed conflict
- A state cannot suspend IHL
- Based on Geneva and Hague conventions
State of emergency:
- An emergency is: a significant departure from a state of normalcy, triggered by an
extreme event that is highly disruptive or threatening to the established order. It gives
extraordinary powers to steer the state through the crisis/emergency.
Problems with emergencies: The challenges with emergencies are that they often lead to
actions that not only violate the basic legal requirements essential for the rule of law but also
go against the fundamental principles and values embedded in those legal requirements.
The 3 type of emergencies identified by Fatovic (2019)
1. Emergencies arising from violence
2. Natural disasters
3. Economic crises
Emergencies are always temporal; there is a clear beginning and end. The measures taken
are only for as long as necessary.
The essentials:
- Exceptional threat: the crisis must present a real, current or at least an imminent
danger to the community
- The parliament can launch ad hoc inquires and investigations on the use of
emergency powers during the state of emergency.
- The temporality: the state of emergency is temporal
- Declaration: the state of emergency must be announced publicly; this informs citizens
of legal situations.
- Communication: notification of the measurements taken must be made to other
states and relevant treaty-monitoring bodies.
- Proportionality: the measures taken to counter the crisis must be proportional to the
gravity of the emergency situation.
, - Delegation of powers
- Necessity
- No matter the crisis, the state always has to protect the principle of legality
- Intangibility: derogation of rights
Interpol:
- Worldwide and not EU based organization focused on police cooperation
- States have representatives within Interpol
- They focus on information exchange and have huge data sets that member states can
access
- Interpol does not have the authority or possibility to independently operate in a
specific country, they can only work through a member’s states police.
Europol:
- Focused on police cooperation only within the European Union
- Limited mandate, there is no real Europol police, so they can only deal with
transnational issues through the law enforcement of member states.
- They form JIT’s (Joint investigation teams) that consist of representatives of each
state, which makes handling specific security issues involving multiple states easier.
Eurojust:
- Similar to Europol, but this is about judicial cooperation
- Limited mandate, there is no EU prosecuter or EU trial
- Information sharing and assistance -> support mandate
- Helps identifying best place for prosecution
- Can also establish JIT’s
OLAF and EPPO
- European anti-fraud office (OLAF)
- Fraud against the EU budget
- Investigations
- Prosecution on national level
- Strong cooperation with OLAF
- Limited mandate
- An EU actor involved with the prosecution of EU crimes, so doesn’t only act through
national courts
- Investigates, prosecutes and brings to judgement crimes against the financial
interests of the EU
- The EPPO undertakes investigations, carries out acts of prosecutions and exercises
the functions of prosecutor in the competent courts of the participating member
states.
- Eurojust, Europol, and OLAF do not carry out such criminal investigations and
prosecutions.