DAANCE- Module 3 study guide
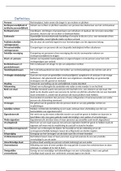
DAANCE- Module 3 study guide Nitrous oxide - This anesthetic was first introduced in 1840 by Horace Wells and William T. G. Morton Brevital (methohexital) - Introduced in 1960 and became the primary anesthetic agent until the beginning of 21st century Diazepam (generic) - Valium (brand) Meperidine (generic) - Demerol (brand) Midazolam (generic) - Versed (brand Propofol - Anesthetic introduced in 2002 when there was a shortage of brevital Analgesia - This effect makes someone feel no pain Examples: fentanyl, local anesthesia, ketamine Amnesia - This effect makes someone have no memory of surgery Examples: versed, valium Diazepam (generic) - Valium (brand) Five primary areas within the brain that anesthetics work - Centers for emotion, centers for wakefulness, the relay center, opioid receptors, vital centers Centers for emotion - One of the primary areas within the brain that anesthetics work Benzodiazepines exert their effects here and reduce anxiety Examples: diazepam (Valium), Midazolam (Versed) Centers for wakefulness - One of the primary areas within the brain that anesthetics work Radiations from the base of the brain to the cerebral cortex maintain this center of the brain Examples of meds that interrupt this are propofol and methohexital The relay center - One of the primary areas within the brain that anesthetics work Turning off this center allows that brain to not feel pain Examples are ketamine, resulting in a state of dissociative anesthesia Opioid Receptors - One of the primary areas within the brain that anesthetics work This system is disrupted by medications to provide relief of pain E
Written for
- Institution
- DAANCE
- Course
- DAANCE
Document information
- Uploaded on
- January 9, 2024
- Number of pages
- 5
- Written in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
-
daance module 3 study guide
Also available in package deal