Summary BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN BODY
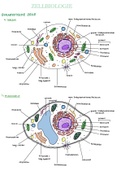
BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN BODY 1.0 INTRODUCTION You have gone through the basic biology course where you learnt that all living things share basic characteristics, some of which include the followings: Responsiveness Growth and differentiation Reproduction Metabolism and excretion That basic biology that you already know includes sub specialties. Examples of these sub-specialties are anatomy and physiology. They are biological subjects with slightly different perspectives. 2.0 OBJECTIVES At the end of this unit, you should be able to: Define what Anatomy is: Define what physiology is: Describe the various specialties of each discipline Explain the relationship between anatomy & physiology 3.0 MAIN CONTENT 3.1 Definition of anatomy and physiology HEM 704 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN BODY 2 The word ‘anatomy; has Greek origin. A literal translation would be “a cutting open” Anatomy is the study of internal and external structures of the body and the physical relationships among body parts for example studying how a particular muscle attaches to the skeleton while physiology which also has Greek origin, is the study of how organisms perform their vital functions. An example is the study of how a muscle contract or what kind of forces contracting muscles exert on the skeleton? 3.2 Relationship between anatomy and physiology Anatomy and physiology are closely integrated both theoretically and practically Anatomical information provides clues about probable functions and physiological mechanisms can be explained only in terms of the underlying anatomy. This observation leads to a very important concept: All specific functions are performed by specific structures. Anatomists and physiologists approach the relationship between structure and function from different perspectives. Please be attentive as we consider a simple non-biological analogy. Assume that this class is made up of Anatomists and physiologists and we are asked to consider an electric bulb. The anatomists may begin by describing and measuring the shape of the bulb and if possible, take it apart (“dissect it”) and put it back together. The physiologist could then explain its key structural relationships.
Written for
- Institution
- BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN BODY
- Course
- BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HUMAN BODY
Document information
- Uploaded on
- May 18, 2023
- Number of pages
- 111
- Written in
- 2022/2023
- Type
- Summary
Subjects
-
basic anatomy and physiology of human body