OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Tenth Edition Student Solutions Manual
Chapter 29 – The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
Solutions to Problems
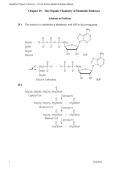
29.1 This reaction is a substitution at phosphorus, with ADP as the leaving group.
29.2
1 10/4/2023
, OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Tenth Edition Student Solutions Manual
29.3 A fatty acid with n carbons yields n/2 acetyl CoA molecules after (n/2 – 1) passages of
the β-oxidation pathway.
(a)
Seven passages of the β-oxidation pathway are needed.
(b)
Nine passages of the β-oxidation pathway are needed.
29.4 β-Hydroxybutyryl ACP resembles the β-hydroxy ketones that were described in Chapter
23 and that dehydrate readily by an E1cB mechanism.
29.5 A fatty acid synthesized from 13CH3CO2H has an alternating labeled and unlabeled
carbon chain. The carboxylic acid carbon is unlabeled.
C H3CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2 CO2 H
10/4/2023 2
, OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Tenth Edition Student Solutions Manual
29.6 The face in front of the plane of the page is the Re face. Since addition occurs from
behind the plane of the page, it occurs at the Si face.
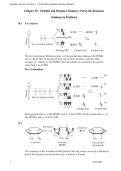
29.7 ATP is produced in step 7 (1,3-bisphosphoglycerate → 3-phosphoglycerate) and in step
10 (phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate). Refer to Figure 29.8.
29.8 Step 1 is a nucleophilic acyl substitution at phosphorus (phosphate transfer) by the
–OH group at C6 of glucose, with ADP as the leaving group.
Step 2 is an isomerization, in which the pyranose ring of glucose 6-phosphate opens,
tautomerism causes isomerization to fructose 6-phosphate, and a furanose ring is formed.
Step 3 is a substitution, similar to the one in step 1, involving the –OH group at C1 of
fructose 6-phosphate (phosphate transfer).
Step 4 is a retro-aldol reaction that cleaves fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to glyceraldehydes
3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Step 5 is an isomerization of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
that occurs by keto–enol tautomerization.
Step 6 begins with a nucleophilic addition reaction to the aldehyde group of
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by a thiol group of an enzyme to form a hemithioacetal,
which is oxidized by NAD+ to an acyl thioester. Nucleophilic acyl substitution by
phosphate yields the product 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Step 7 is a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction at phosphorus, in which ADP reacts
with 1,3-diphosphoglycerate, yielding ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate (phosphate transfer).
Step 8 is an isomerization of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate.
Step 9 is an E1cB elimination of H2O to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
Step 10 is a substitution reaction at phosphorus that forms ATP and enolpyruvate, which
tautomerizes to pyruvate (phosphate transfer).
3 10/4/2023
Chapter 29 – The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
Solutions to Problems
29.1 This reaction is a substitution at phosphorus, with ADP as the leaving group.
29.2
1 10/4/2023
, OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Tenth Edition Student Solutions Manual
29.3 A fatty acid with n carbons yields n/2 acetyl CoA molecules after (n/2 – 1) passages of
the β-oxidation pathway.
(a)
Seven passages of the β-oxidation pathway are needed.
(b)
Nine passages of the β-oxidation pathway are needed.
29.4 β-Hydroxybutyryl ACP resembles the β-hydroxy ketones that were described in Chapter
23 and that dehydrate readily by an E1cB mechanism.
29.5 A fatty acid synthesized from 13CH3CO2H has an alternating labeled and unlabeled
carbon chain. The carboxylic acid carbon is unlabeled.
C H3CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2CH 2 C H 2 CO2 H
10/4/2023 2
, OpenStax Organic Chemistry: A Tenth Edition Student Solutions Manual
29.6 The face in front of the plane of the page is the Re face. Since addition occurs from
behind the plane of the page, it occurs at the Si face.
29.7 ATP is produced in step 7 (1,3-bisphosphoglycerate → 3-phosphoglycerate) and in step
10 (phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate). Refer to Figure 29.8.
29.8 Step 1 is a nucleophilic acyl substitution at phosphorus (phosphate transfer) by the
–OH group at C6 of glucose, with ADP as the leaving group.
Step 2 is an isomerization, in which the pyranose ring of glucose 6-phosphate opens,
tautomerism causes isomerization to fructose 6-phosphate, and a furanose ring is formed.
Step 3 is a substitution, similar to the one in step 1, involving the –OH group at C1 of
fructose 6-phosphate (phosphate transfer).
Step 4 is a retro-aldol reaction that cleaves fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to glyceraldehydes
3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Step 5 is an isomerization of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
that occurs by keto–enol tautomerization.
Step 6 begins with a nucleophilic addition reaction to the aldehyde group of
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate by a thiol group of an enzyme to form a hemithioacetal,
which is oxidized by NAD+ to an acyl thioester. Nucleophilic acyl substitution by
phosphate yields the product 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Step 7 is a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction at phosphorus, in which ADP reacts
with 1,3-diphosphoglycerate, yielding ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate (phosphate transfer).
Step 8 is an isomerization of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate.
Step 9 is an E1cB elimination of H2O to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
Step 10 is a substitution reaction at phosphorus that forms ATP and enolpyruvate, which
tautomerizes to pyruvate (phosphate transfer).
3 10/4/2023