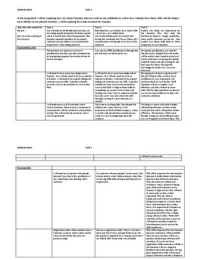
requires
thought
cognitive Associative Autonomous
Jerky, lack of less jerky, motor Kinaesthesis formed,
fluency, trial + programs start to little mistakes,
error, lots of form less mistakes experienced, fluent,
mistakes, uses practice stage motivated, corrects
consious thinking Feedback extrinsic own mistakes, intrinsic
relys on extrinsic and intrinsic starts motivation, successful
feedback- KOR, as kinaesthesis Intrinsic feedback-
praise, encouragement starts to form. KOP, enjoyment
Types of practice Examples Advantages Dis advantages
Fixed: involves mainly closed + repetitive practice - doesn't always prepare
skills which are pre-learned and • golf swing, tennis serve allows muscle memory performers for when things
promotes over learning. to activate. go wrong.
Varied: involve mainly open skills
as environment changes so practice • rugby tackle, netball + allows performers - can be difficult to
needs to differ so performer can practice drives/defense, Football to practice in situations replicate game situations.
the skill in different scenarios. tackles realistic to activity
Experiences are stored in long term
memory and the motor programmes
use this in future situations. + good for learning - Breaks too long leads
Distributed: Includes BREAKS • Performing a drill for most skills, time to to boredom, lack of
skill to be mastered. During the rest 10 mins then having a recover, good for motivation
athletes use mental rehearsal on other 5 min rest intervals. dangerous situations
activities not related to main drill.
Massed: No rest intervals. + good for grooving - can lead to fatigue =
skill to be mastered by repeating the • 30 mins of continuous skills + learning short injury potentially or
drill continuously. passing in netball discrete skills lack of motivation = boredom
methods Of Practice: Advantages Disadvantage mental Practice cognitive: thinking about
and strategies help improv
whole: skill is performed from start + quicker learning - unsuitable for complex mental rehearsal is used making.
to end. It cannot be broken down into performer can get a skills. as a form of visualisation neuromuscular: durin
sub-routines. Skill is high in organisation, feel of whole skill or imagery. Athletes rehearsal the muscle neuron
simple skills, discrete, short. visualise themselves in as if using the muscle.
Part: can be broken down into sub-routines + provides earlier - time consuming competition to improve confidence: improves co
as skill is low in organisation, serial + success + safer small groups/individual performance. Both mental as focus is on success and
complex. Each part is practiced separately can focus on certain learning. difficult to and physical practice is performance. Used in dan
then joined together at end. parts of skill put skill together to flow needed to enhance situations as a safe pract
whole-part-whole: performance. Physical is
thought
cognitive Associative Autonomous
Jerky, lack of less jerky, motor Kinaesthesis formed,
fluency, trial + programs start to little mistakes,
error, lots of form less mistakes experienced, fluent,
mistakes, uses practice stage motivated, corrects
consious thinking Feedback extrinsic own mistakes, intrinsic
relys on extrinsic and intrinsic starts motivation, successful
feedback- KOR, as kinaesthesis Intrinsic feedback-
praise, encouragement starts to form. KOP, enjoyment
Types of practice Examples Advantages Dis advantages
Fixed: involves mainly closed + repetitive practice - doesn't always prepare
skills which are pre-learned and • golf swing, tennis serve allows muscle memory performers for when things
promotes over learning. to activate. go wrong.
Varied: involve mainly open skills
as environment changes so practice • rugby tackle, netball + allows performers - can be difficult to
needs to differ so performer can practice drives/defense, Football to practice in situations replicate game situations.
the skill in different scenarios. tackles realistic to activity
Experiences are stored in long term
memory and the motor programmes
use this in future situations. + good for learning - Breaks too long leads
Distributed: Includes BREAKS • Performing a drill for most skills, time to to boredom, lack of
skill to be mastered. During the rest 10 mins then having a recover, good for motivation
athletes use mental rehearsal on other 5 min rest intervals. dangerous situations
activities not related to main drill.
Massed: No rest intervals. + good for grooving - can lead to fatigue =
skill to be mastered by repeating the • 30 mins of continuous skills + learning short injury potentially or
drill continuously. passing in netball discrete skills lack of motivation = boredom
methods Of Practice: Advantages Disadvantage mental Practice cognitive: thinking about
and strategies help improv
whole: skill is performed from start + quicker learning - unsuitable for complex mental rehearsal is used making.
to end. It cannot be broken down into performer can get a skills. as a form of visualisation neuromuscular: durin
sub-routines. Skill is high in organisation, feel of whole skill or imagery. Athletes rehearsal the muscle neuron
simple skills, discrete, short. visualise themselves in as if using the muscle.
Part: can be broken down into sub-routines + provides earlier - time consuming competition to improve confidence: improves co
as skill is low in organisation, serial + success + safer small groups/individual performance. Both mental as focus is on success and
complex. Each part is practiced separately can focus on certain learning. difficult to and physical practice is performance. Used in dan
then joined together at end. parts of skill put skill together to flow needed to enhance situations as a safe pract
whole-part-whole: performance. Physical is