Hypersensitivity
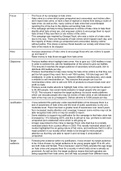
Hypersensitivity Mechanism Examples Treatment
Type I Allergen binds to IgE, leading to mast cell degranulation • Skin: eczema • General treatment methods:
and inflammatory mediator release such as: • Infection: helminths (IgE & eosinophil degranulation) Corticosteroids: suppress transcription of proinflammatory genes
Histamine, serotonin, prostaglandins, TNFα, leukotrienes • Systemic: peanut allergy Sodium cromoglicate: inhibits mast cell degranulation
Antihistamine
Severe symptoms: Montelukast: leukotriene receptor antagonist
Vasodilation + vasopermeability increase → BP decrease + ARDS Omalizumab - anti-IgE
Type II IgG autoAb binds to self cells, leading to activation of • HDN
complement or macrophage/neutrophil phagocytosis • Transplantation/transfusion reactions
• Streptococcal endocarditis
• Goodpasture's syndrome/anti-GBM (autoimmune) - autoAb targets collagen
IV & damages lung/kidney basement membrane
Type III IgG, IgM forms immune complexes → causes obstruction • SLE (autoimmune) - autoAb against self-DNA & chromatin molecules Corticosteroids (prednisolone) Contraind: hydralazine, isoniazid, procainamide
Macrophages/complement/neutrophils damage • Rheumatoid arthritis
endothelial cells whilst clearing the immune complex • Farmer's lung/pigeon fancier's disease
• Glomerulonephritis
Type IV T cells bind to peptide-MHC leading to macrophage • TB & granuloma
activation • Acute graft rejection (transplant)
• Coeliac disease (autoimmune) - response to gluten causing gut inflammation
• Hashimoto's thyroiditis (autoimmune) - T cells attacks thyroid gland -
hypothyroidism • Levothyroxine (replaces thyroxine as an analogue) - activates nuclear receptors
to increase thyroid hormone levels
Type V Stimulatory autoAb leads to cells functioning at higher • Graves' disease - agonistic Ab binds to TSHR* - leads to hyperthyroidism
rate by binding to hormone/neurotransmitter receptors • Myasthenia gravis - autoAb binds to ACh in muscle leading to muscle
weakness & fatigue
*anti-TSHR - autoAb produced for thyroid stimulating hormone receptor
I^MD Page 1
Hypersensitivity Mechanism Examples Treatment
Type I Allergen binds to IgE, leading to mast cell degranulation • Skin: eczema • General treatment methods:
and inflammatory mediator release such as: • Infection: helminths (IgE & eosinophil degranulation) Corticosteroids: suppress transcription of proinflammatory genes
Histamine, serotonin, prostaglandins, TNFα, leukotrienes • Systemic: peanut allergy Sodium cromoglicate: inhibits mast cell degranulation
Antihistamine
Severe symptoms: Montelukast: leukotriene receptor antagonist
Vasodilation + vasopermeability increase → BP decrease + ARDS Omalizumab - anti-IgE
Type II IgG autoAb binds to self cells, leading to activation of • HDN
complement or macrophage/neutrophil phagocytosis • Transplantation/transfusion reactions
• Streptococcal endocarditis
• Goodpasture's syndrome/anti-GBM (autoimmune) - autoAb targets collagen
IV & damages lung/kidney basement membrane
Type III IgG, IgM forms immune complexes → causes obstruction • SLE (autoimmune) - autoAb against self-DNA & chromatin molecules Corticosteroids (prednisolone) Contraind: hydralazine, isoniazid, procainamide
Macrophages/complement/neutrophils damage • Rheumatoid arthritis
endothelial cells whilst clearing the immune complex • Farmer's lung/pigeon fancier's disease
• Glomerulonephritis
Type IV T cells bind to peptide-MHC leading to macrophage • TB & granuloma
activation • Acute graft rejection (transplant)
• Coeliac disease (autoimmune) - response to gluten causing gut inflammation
• Hashimoto's thyroiditis (autoimmune) - T cells attacks thyroid gland -
hypothyroidism • Levothyroxine (replaces thyroxine as an analogue) - activates nuclear receptors
to increase thyroid hormone levels
Type V Stimulatory autoAb leads to cells functioning at higher • Graves' disease - agonistic Ab binds to TSHR* - leads to hyperthyroidism
rate by binding to hormone/neurotransmitter receptors • Myasthenia gravis - autoAb binds to ACh in muscle leading to muscle
weakness & fatigue
*anti-TSHR - autoAb produced for thyroid stimulating hormone receptor
I^MD Page 1