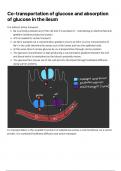
Co-transportation of glucose and absorption
of glucose in the ileum
It is indirect active transport.
Na is actively pumped out of the cell and K is pumped in - maintaining an electrochemical
gradient (sodium production pump)
ATP is needed for active transport
As Na is pumped out a concentration gradient occurs as there is a low concentration of
Na+ in the cells therefore Na moves out of the lumen and into the epithelial cells.
At the same time it carries glucose by co-transportation through carrier proteins
The glucose concentration is high producing a concentration gradient between the cell
and blood which is maintained as the blood constantly moves.
The glucose then moves out of the cell and into the blood through facilitated diffusion
using carrier proteins.
Co-transportation is the coupled movement of substances across a cell membrane via a carrier
protein. It is combined facilitated diffusion and active transport.
of glucose in the ileum
It is indirect active transport.
Na is actively pumped out of the cell and K is pumped in - maintaining an electrochemical
gradient (sodium production pump)
ATP is needed for active transport
As Na is pumped out a concentration gradient occurs as there is a low concentration of
Na+ in the cells therefore Na moves out of the lumen and into the epithelial cells.
At the same time it carries glucose by co-transportation through carrier proteins
The glucose concentration is high producing a concentration gradient between the cell
and blood which is maintained as the blood constantly moves.
The glucose then moves out of the cell and into the blood through facilitated diffusion
using carrier proteins.
Co-transportation is the coupled movement of substances across a cell membrane via a carrier
protein. It is combined facilitated diffusion and active transport.