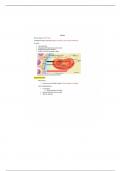
/. When does malrotation occur? - Answer-✅at about the 10th week of gestation
/.What is a malrotation? - Answer-✅a congenital abnormality that occurs during the
embryonic phase of development when the midgut retracts into the abdominal cavity.
The midgut rotates counterclockwise
/.When do infants typically become symptomatic with a malrotation? - Answer-✅at 3
weeks of life
/.What is the classic sign of a malrotation? - Answer-✅bilious vomitting
/.How is a malrotation diagnosed? - Answer-✅upper GI study
/.What are some radiologic findings that are indicative of a malrotation? - Answer-
✅corkscrew appearance with barium swallow; Signs of obstruction (air-fluid levels) may
be present, along with an abnormal gas pattern at the stomach and duodenum.
/.What is pyloric stenosis? - Answer-✅results from hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter
(muscle in the distal stomach), which leads to poor gastric emptying into the duodenum.
/.When does pyloric stenosis usually present? - Answer-✅At 2-4 weeks of age
/.What are the symptoms of pyloric stenosis? - Answer-✅vomiting that becomes
projectile; typically occurs immediately after feeding, is nonbilious, and the infant is
hungry after vomiting. The parents may also report constipation, excessive crying and
weight loss, or failure to gain weight
/.What can delay symptoms of pyloric stenosis? - Answer-✅breastfeeding
/.What is pyloric stenosis usually mistaken for? - Answer-✅reflux or formula intolerance
/.What is the hallmark finding of pyloric stenosis? - Answer-✅an olive-shaped mass in
RUQ
/.What are typical lab and radiologic findings of a baby with pyloric stenosis? - Answer-
✅hypochloremia, metabolic alkalosis, Hypokalemia. KUB imaging reveals a dilated
gastric silhouette. An ultrasound typically reveals a thickened and elongated pylorus,
measuring greater than 4 mm.
, /.What is intussusception? - Answer-✅involves the invagination of a section of the
intestine into itself. The most frequent site is at the terminal ileum.
/.What is often a predisposing factor of intussusception? - Answer-✅A recent viral
illness, mesenteric lymphadenitis, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, and cystic fibrosis
/.What is the typical age of onset of idiopathic intussusception? - Answer-✅6 to 18
months, with an average age of 7 to 8 months
/.If intussusception occurs beyond 36 mths, it is typically due to a physical abnormality
such as? - Answer-✅meckel's diverticulum or polyps
/.Is intussusception more common in girls or boys? - Answer-✅boys
/.What is the classic presentation of intussusception? - Answer-✅colicky abdominal
pain, recent viral illness with some vomiting and perhaps diarrhea. The child begins to
have episodes of colicky abdominal pain, draws up the knees or stiffens the legs for a
brief period, and then becomes quiet for several minutes. The series of events recurs,
typically every 15 to 20 minutes, and continues for several hours. The child may have
blood in his or her stools, prompting the "currant jelly" descriptor
/.What is typically present on palpation with intussusception? - Answer-✅A sausage
shaped mass typically in the right lower quad
/.What interventions should be considered when intussusception is suspected? -
Answer-✅consult a pediatric surgeon. Initiate intravenous hydration and order an air-
contrast enema. Consider an abdominal ultrasound as well
/.What will often diagnose and cure intussusception? - Answer-✅an air contrast enema
/.What are contraindication s to an air contrast enema? - Answer-✅perforation, shock,
and peritonitits
/.What is usually classic hx of appendicitis? - Answer-✅abd pain that starts in the
periumbilical area and migrates to the right lower quadrant, along with low-grade fever,
a small amount of emesis, and anorexia
/.What exacerbates the pain associated with appendicitis? - Answer-✅movement and
the child frequently walks stooped over
/.What does examination of a child with appendicitis usually reveal? - Answer-✅point
tenderness in the right lower quadrant with voluntary guarding, and perhaps some