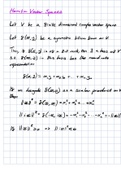SOLUTIONS
, CONTENTS
Preface …………………………………………...……………………………………….. 1
Chapter 2 Mathematical Concepts in Kinematics ……………………………………….. 2
Chapter 3 Fundamental Concepts in Kinematics ……………………………………….. 8
Chapter 4 Kinematic Analysis of Planar Mechanisms..................................................................19
Chapter 5 Dimensional Synthesis .................................................................................................81
Chapter 6 Static Force Analysis of Planar Mechanisms .............................................................159
Chapter 7 Dynamic Force Analysis of Planar Mechanisms ........................................................210
Chapter 8 Design & Kinematic Analysis of Gears .....................................................................288
Chapter 9 Design & Kinematic Analysis of Disk Cams .............................................................327
Chapter 10 Kinematic Analysis of Spatial Mechanisms ..............................................................364
Chapter 11 Introduction to Robotic Manipulators .......................................................................409
@
@SSeeisismmicicisisoolalatitoionn
, CHAPTER 2
Problem 2.1 Statement:
Formulate an equation for the vector loop illustrated in Figure P.2.1. Consider that vector V j
always lies along the real axis.
Figure P.2.1 Vector loop (3 vectors where V j changes length) in 2-D complex space
Problem 2.1 Solution:
Taking the clockwise sum of the vector loop in Figure P.2.1 produces the equation
V1ei1 +V2 ei2 − Vj = 0 .
When expanded and separated into real and imaginary terms, the vector loop equation becomes
V1 cos1 +V2 cos2 − Vj = 0
.
V1 sin 1 +V2 sin 2 = 0
Problem 2.2 Statement:
Formulate an equation for the vector loop illustrated in Figure P.2.2. Consider that vector V j
always lies along the real axis and vector V3 is always perpendicular to the real axis.
@Seismi2cisolation
@Seismicisolation
, Figure fP.2.2 fVector floop f(4 fvectors fwhere changes flength) fin f2-D fcomplex fspace
f Vfj
Problem f2.2 fSolution:
Taking fthe fclockwise fsum fof fthe fvector floop fin fFigure fP.2.2 fproduces fthe fequation
V fei11 f +V fe2 i2 f − fV3 f − fVj f = f0 f.
When fexpanded fand fseparated finto freal fand fimaginary fterms, fthe fvector floop fequation fbecomes
V1 f cos1 f +V2 f cos2 f − fVj f = f0
.
V1 fsin f1 f +V2 f sin f2 f − fV3 f = f0
Problem f2.3 fStatement:
Calculate fthe ffirst fderivative fof fthe fvector floop fequation fsolution ffrom fProblem f2.2. f Consider
only fangles f 1 f, and fvector from fProblem f2 fto fbe ftime-dependent.
f 2 f Vfj
Problem f2.3 fSolution:
Differentiating fthe fvector floop fequation fsolution ffrom fProblem f2.2 fproduces fthe fequation
i1V1ei1 + i2V2ei2 − V j = 0.
When fexpanded fand fseparated finto freal fand fimaginary fterms, fthe fvector floop fequation fbecomes
−1V1 sin 1 − 2V2 sin 2 − V j = 0
.
1V1 cos 1 + 2V2 cos 2 = 0
@Seismi 3cisolation
@Seismicisolation