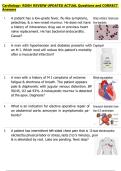
1. Wide P waves in lead II P-mitrale which is caused by left atrial enlargement.
and a deep negative de-
flection in lead V1 is due
to
2. Definition of persevera- the persistent repetition of words or concepts in the process of speak-
tion ing. This is often seen in cognitive disorders, schizophrenia, and other
mental illness.
3. Atrial myxoma Atrial myxoma most commonly presents with sudden onset of symp-
toms that are typically positional in nature due to the effect that gravity
has on the tumor. Myxomas are the most common type of primary
cardiac tumor in all age groups and are most commonly found in the
atria.
4. Methanol poisoning Tx Treatment: Ethanol, dialysis, fomepizole.
5. Which of the follow- exudative
ing types of pleural ef- Increased production of fluid due to inflammatory or malignant
fusion result from in- processes results in an exudative pleural effusion.
creased production of
fluid due to underly- Transudates result from increased hydrostatic or decreased oncotic
ing inflammatory condi- pressures across normal capillaries.
tions?
6. ideas of reference Ideas of reference are fixed beliefs that people are referring to you and
about you through media.
7. when is surgery indicat- Open reduction is indicated with angulation >40 degrees.
ed for boxers fracture
8. What is the treatment Ceftriaxone 1 g intramuscularly once, plus doxycycline 100 mg orally
for gonococcal conjunc- twice daily for 7 days if chlamydial infection has not been excluded.
, tivitis in adults and ado-
lescents?
9. When should hyperten- If the systolic is > 220 mm Hg, the diastolic is > 110 mm Hg, or if the
sion be treated in the patient has another condition that would benefit from blood pressure
setting of an acute is- control.
chemic stroke?
10. Dx foreign body aspira- Delayed diagnosis often presents with postobstructive pneumonia.
tion Chest radiographs may be normal if the foreign body is not radiopaque.
Decubitus or forced expiratory radiographs will detect air trapping as
the lung will remain hyperinflated on the affected side. Pulmonology
will need to be consulted for bronchoscopy.
11. what 2 findings suggest if patients have rhinorrhea or conjunctivitis with pharyngitis, they are
viral pharyngitis over more likely to have a viral etiology rather than a bacterial etiology
bacterial
12. The Ottawa ankle rules (1) tenderness at the posterior edge of the distal 6 cm or the tip of the
are a validated set of lateral malleolus, (2) tenderness at the posterior edge of the distal 6 cm
rules helpful in the de- or the tip of the medial malleolus, and (3) inability to bear weight for
termination of a need at least four steps both immediately after the injury and at the time of
for a radiograph in evaluation.
the setting of ankle in-
juries evaluated with-
in 48 hours of in-
jury. Imaging is re-
quired when any of the
following are present:
13. Cervical radiculopathy -Posterolateral disk herniation is most commonly seen
-C7 is the most commonly affected nerve root and results in pain that
radiates down the posterior arm to the dorsum of the forearm and third
, digit. weakness with forearm extension and pronation and a decreased
triceps reflex.
14. The main cause of acute obstruction of aqueous humor outflow, usually by the lens or the iris
angle-closure glauco- obstructing the trabecular meshwork
ma is -Patients usually present with eye pain, a fixed midposition pupil, con-
junctival injection, a hazy-appearing cornea, and elevated intraocular
pressures
15. Initial management aimed at rapidly decreasing intraocular pressure by blocking the pro-
of acute angle-closure duction of aqueous humor (topical beta-blocker, carbonic anhydrase
glaucoma is inhibitors), facilitating drainage of aqueous humor (topical alpha ago-
nist), and reducing the volume of vitreous humor (mannitol).
16. what antidepressant Bupropion
should be avoided in
patients with anorexia
or bulimia nervosa due
to the risk of seizures
17. ages RSV is found in primarily affects young children < 2 years of age
18. physical exam in bron- exam findings include nasal drainage, tachypnea, cough, intercostal
chiolitis and subcostal retractions, wheezing, and fine or coarse crackles
19. when to give K+ in Tx of Potassium should be administered with IV fluids when the potassium
DKA is d5.0 mEq/mL. In patients in which the initial potassium is low (< 3.3
mEq/L), levels could become life-threatening following the administra-
tion of insulin. Therefore, potassium should be vigorously repleted in
concentrations of 20-40 mEq/L prior to initiating insulin therapy.
20. caused by immune complex deposition in the kidney, causing local
damage and impaired filtration