ELECTROLYSIS AND LASER BOARD
REVIEW EXAM GUIDE QUESTIONS
WITH COMPLETE ANSWERS
Polycystic ovaries - Answer-Most common cause of hirsutism and menstrual
irregularity in Excess hair that is not abnormal for persons age and sex but omen
less than 50 years of age.
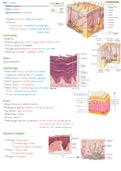
Contributors to skin color - Answer-Carotene, blood vessels and melanin
Melanin can be found - Answer-Hair, skin, eyes
stratum lucidum - Answer-Layer of the skin where electing is found
stratum spinosum - Answer-Prickle cell layer of the skin
True skin, cutis - Answer-Other names for dermis
Dark skin - Answer-Type of skin where melanocytes are larger and more active
Papillary layer - Answer-Made up of elastic collagenous and reticular fibers
Meissner - Answer-Type of corpuscle found in the papillary layer that is sensitive to
touch
Merkel - Answer-Only corpuscle in the epidermis and sensitive to light touch
Ruffini - Answer-Corpuscles that responds to heat
reticular layer - Answer-Layer of the skin composed of dense bundles of collagen
fibers
Krause - Answer-Corpuscles in the skin sensitive to cold
Pacinian - Answer-Corpuscle in the skin sensitive to pressure
Subcutis and subcutaneous - Answer-Layer at the base of the dermis composed of
fatty or adipose tissue
inner root sheath - Answer-Anchors and holds the hair in the follicle
Apocrine - Answer-Type of gland found mainly in the arm pits and groin area and
usually the smelly ones
Under arms - Answer-Body area where apocrine glands tend to be the largest
,Sebaceous gland - Answer-oil-secreting gland in the dermis that is associated with
hair follicles also vellus hair originates
Late anagen - Answer-Stage of hair growth easier for electrologist to epilate
Arrest or pili muscle - Answer-Appendage of the hair follicle attached between the
bulb and sebaceous gland. Goose bumps
Lanugo - Answer-fine, soft hair, especially that which covers the body and limbs of a
human fetus or newborn.
Functions of the skin include: - Answer-Protection, heat regulation, respiration,
absorption, secretion and elimination
Langerhans cells - Answer-First cells in the epidermis that fight infection or invading
microorganisms
Cortex - Answer-Layer of the hair that contains melanin
Layer of the hair from inside to out - Answer-Medulla, cortex and cuticle
Legs - Answer-Part of the body you find most red dots after electrolysis
Electrolysis - Answer-Only permanent hair removal procedure
Terminal to vellus - Answer-It will never turn back
Herpes I & II and warts - Answer-Contagious outbreaks that should be treated with
electrolysis
Verruca - Answer-Another name for wart
Herpes type I - Answer-cold sores or fever blisters from the waist up
herpes type 2 - Answer-Transmitted sexually and usually from the waist down
Isotretinoin - Answer-Another name for acutane
3 months - Answer-Wait for electrolysis treatment after dermabrasion
tetracycline antibiotic - Answer-Treats acne, Lyme disease and rosacea
Glad at top of kidney - Answer-Adrenal gland
Diabetes that's is auto immune and insulin dependent - Answer-Type 1 & juvenile
Diabetic client - legs - Answer-Worst area of the body for electrolysis due to slow
healing
Causes increased hair growth - Answer-Sun, stress, tweezing and aspirin
, Matrix - Answer-Where mitosis cells in the hair begin their growth activity
sudoriferous glands - Answer-NOT part of the pilosebaceous unit
Terminal hair on the face for women - Answer-Means an excess of androgens
Sub layers of the dermis - Answer-papillary and reticular
Handwashing - Answer-Most important before and after treatment
Bacteria can enter the body through - Answer-broken skin
Sterilizing unpackaged instruments - Answer-Autoclave a 250 F w 15-17 PSI for 15
minutes
Hair and follicle - Answer-Part of the epidermis and pilosebaceous unit
Personal service workers (PSWs) - Answer-Defined by CDC as person whose
occupation involves close personal contact with patients
Voltage - Answer-Electrical pressure that helps electrons flow
Concentration of circulating androgens - Answer-Male and female hair patterns differ
primarily because of differences.
Causes of hirsutism - Answer-Pituitary hypersecretion, adrenal tumors and ovarian
tumors
Electrons move - Answer-From negative to positive
Chemical decomposition - Answer-The galvanic modality effects permanent hair
removal by
The blend - Answer-Short wave and direct current
Desiccation - Answer-dehydration; the process of being rendered free from moisture
Client's history assessment record inlcudes - Answer-Accurate records of areas
treated, client's signature and verification of health history and electrologist treatment
plan
Causes of blanching - Answer-Over treatment of the skin and shallow insertion
Hepatitis A - Answer-Spread through fecal-oral and can live outside the body for
months
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) - Answer-virus that causes inflammation of the liver;
transmitted through any body fluid, including vaginal secretions, semen, and blood. It
can live outside the body for 7 days
REVIEW EXAM GUIDE QUESTIONS
WITH COMPLETE ANSWERS
Polycystic ovaries - Answer-Most common cause of hirsutism and menstrual
irregularity in Excess hair that is not abnormal for persons age and sex but omen
less than 50 years of age.
Contributors to skin color - Answer-Carotene, blood vessels and melanin
Melanin can be found - Answer-Hair, skin, eyes
stratum lucidum - Answer-Layer of the skin where electing is found
stratum spinosum - Answer-Prickle cell layer of the skin
True skin, cutis - Answer-Other names for dermis
Dark skin - Answer-Type of skin where melanocytes are larger and more active
Papillary layer - Answer-Made up of elastic collagenous and reticular fibers
Meissner - Answer-Type of corpuscle found in the papillary layer that is sensitive to
touch
Merkel - Answer-Only corpuscle in the epidermis and sensitive to light touch
Ruffini - Answer-Corpuscles that responds to heat
reticular layer - Answer-Layer of the skin composed of dense bundles of collagen
fibers
Krause - Answer-Corpuscles in the skin sensitive to cold
Pacinian - Answer-Corpuscle in the skin sensitive to pressure
Subcutis and subcutaneous - Answer-Layer at the base of the dermis composed of
fatty or adipose tissue
inner root sheath - Answer-Anchors and holds the hair in the follicle
Apocrine - Answer-Type of gland found mainly in the arm pits and groin area and
usually the smelly ones
Under arms - Answer-Body area where apocrine glands tend to be the largest
,Sebaceous gland - Answer-oil-secreting gland in the dermis that is associated with
hair follicles also vellus hair originates
Late anagen - Answer-Stage of hair growth easier for electrologist to epilate
Arrest or pili muscle - Answer-Appendage of the hair follicle attached between the
bulb and sebaceous gland. Goose bumps
Lanugo - Answer-fine, soft hair, especially that which covers the body and limbs of a
human fetus or newborn.
Functions of the skin include: - Answer-Protection, heat regulation, respiration,
absorption, secretion and elimination
Langerhans cells - Answer-First cells in the epidermis that fight infection or invading
microorganisms
Cortex - Answer-Layer of the hair that contains melanin
Layer of the hair from inside to out - Answer-Medulla, cortex and cuticle
Legs - Answer-Part of the body you find most red dots after electrolysis
Electrolysis - Answer-Only permanent hair removal procedure
Terminal to vellus - Answer-It will never turn back
Herpes I & II and warts - Answer-Contagious outbreaks that should be treated with
electrolysis
Verruca - Answer-Another name for wart
Herpes type I - Answer-cold sores or fever blisters from the waist up
herpes type 2 - Answer-Transmitted sexually and usually from the waist down
Isotretinoin - Answer-Another name for acutane
3 months - Answer-Wait for electrolysis treatment after dermabrasion
tetracycline antibiotic - Answer-Treats acne, Lyme disease and rosacea
Glad at top of kidney - Answer-Adrenal gland
Diabetes that's is auto immune and insulin dependent - Answer-Type 1 & juvenile
Diabetic client - legs - Answer-Worst area of the body for electrolysis due to slow
healing
Causes increased hair growth - Answer-Sun, stress, tweezing and aspirin
, Matrix - Answer-Where mitosis cells in the hair begin their growth activity
sudoriferous glands - Answer-NOT part of the pilosebaceous unit
Terminal hair on the face for women - Answer-Means an excess of androgens
Sub layers of the dermis - Answer-papillary and reticular
Handwashing - Answer-Most important before and after treatment
Bacteria can enter the body through - Answer-broken skin
Sterilizing unpackaged instruments - Answer-Autoclave a 250 F w 15-17 PSI for 15
minutes
Hair and follicle - Answer-Part of the epidermis and pilosebaceous unit
Personal service workers (PSWs) - Answer-Defined by CDC as person whose
occupation involves close personal contact with patients
Voltage - Answer-Electrical pressure that helps electrons flow
Concentration of circulating androgens - Answer-Male and female hair patterns differ
primarily because of differences.
Causes of hirsutism - Answer-Pituitary hypersecretion, adrenal tumors and ovarian
tumors
Electrons move - Answer-From negative to positive
Chemical decomposition - Answer-The galvanic modality effects permanent hair
removal by
The blend - Answer-Short wave and direct current
Desiccation - Answer-dehydration; the process of being rendered free from moisture
Client's history assessment record inlcudes - Answer-Accurate records of areas
treated, client's signature and verification of health history and electrologist treatment
plan
Causes of blanching - Answer-Over treatment of the skin and shallow insertion
Hepatitis A - Answer-Spread through fecal-oral and can live outside the body for
months
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) - Answer-virus that causes inflammation of the liver;
transmitted through any body fluid, including vaginal secretions, semen, and blood. It
can live outside the body for 7 days