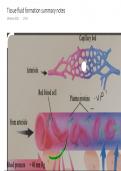
&ANSWERS(RATED A+)
What is another name for cell to cell communication?
a. signal transition
b. signal transduction
c. signal translation
d. signal transference
e. all of the above - ANSWERb. signal transduction
Paracrine signaling is when:
a. signal molecules pass through gap junctions to neighboring cells
b. signal molecules pass through the bloodstream to other cells
c. signal molecules cause two separate cells to fuse
d. signal molecules pass from one cell to a nearby cell
e. all of the above - ANSWERd. signal molecules pass from one cell to a nearby cell
If something is "hormonal" or "endocrine" signalling, this means:
a. the signalling molecule is hydrophobic
b. the signalling molecule binds to a cell surface receptor
c. the signalling molecule passes through the bloodstream
d. the signalling molecule is a small organic molecule
e. the signalling molecule is a protein or peptide - ANSWERc. the signalling molecule
passes through the bloodstream
In most signal transduction pathways, what actually passes through the membrane?
a. cyclic AMP
b. GTP
c. small peptides
d. transcription factors
e. nothing but information - ANSWERe. nothing but information
What are GPCRs ?
a. G-protein coupled receptors
b. transmembrane proteins
c. cell surface receptors
d. common drug binding targets
e. all of the above - ANSWERe. all of the above
The goal of most signal transduction pathways is:
a. to stimulate a hormone
b. to increase metabolism
c. to form tissues
d. to turn a gene on or off
e. to stimulate the immune system - ANSWERd. to turn a gene on or off
, What is the first thing an RTK (receptor tyrosine kinase) does after binding a
signaling molecule?
a. flip from one side of the membrane to the other
b. bind to a G-protein
c. form a dimer in the membrane
d. turn on a gene
e. release ATP - ANSWERc. form a dimer in the membrane
Some signaling molecules do not need to bind to a cell surface receptor, they bind
an internal protein and go all the way to the nucleus themselves. These are almost
always:
a. steroid hormones
b. hydrophobic
c. lipids
d. membrane permeable
e. all of the above - ANSWERe. all of the above
One of the following is NOT a secondary messenger, which one?
a. cyclic AMP
b. calcium
c. IP3 (inositol 3 phosphate)
d. insulin peptide
e. all of these are secondary messengers - ANSWERd. insulin peptide
A signal transduction pathway = reception + transduction + response. What is a
common process in the transduction?
a. release of proteins from the membrane
b. turning a gene on or off
c. internalization of the receptor
d. a series of phosphorylations
e. all of the above - ANSWERd. a series of phosphorylations
In a signal transduction pathway, what actually turns the genes on or off?
a. receptors
b. primary signal molecules
c. adenylate cyclase
d. GPCRs
e. transcription factors - ANSWERe. transcription factors
What is the main purpose of the phosphorylation cascade in transduction?
a. to amplify the signal
b. to increase the charge on the transduction proteins
c. to activate the receptor protein
d. to release GTP
e. all of the above - ANSWERa. to amplify the signal
In the phosphorylation cascade in a signal transduction pathway, phosphorylation of
an enzyme usually:
a. requires GTP
b. activates it