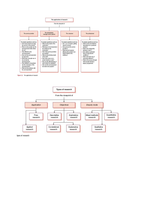
Classical Capitalism vs. Modern Capitalism
Three dimensions
(0) Private Property
(1) Firms
(2) Workers
(3) Markets
Classical Capitalism (Adam Smith)
(1) Firms → size, number in a market, who owned?
- Numerous small firms in a market
- Individual or family owned
- Owners had unlimited liabilities in the event of bankruptcy
(2) Wage Workers
- Workers are supervised and commanded by an individual capitalist or an entrepreneur
family → a very simple hierarchy
- No regulations on children and women’s labor conditions
- Long labor hours
(3) Markets
- Competitive
- Single or few firms cannot change market prices
Similarities Between Classical & Today’s Capitalism
What are the common constituting elements both in Adam Smith’s capitalism and
in today’s capitalism?
Capitalism = an economic system as a specific combination of private property,
markets, and firms
(1) Private ownership of capital goods
(2) Purchasing the labor power of wage workers through the market
(3) Market exchanges of the output of production for monetary profit
(4) Profit-seeking of the firm as its business objective
, Classical Capitalism vs. Modern Capitalism
(1) Evolution of Firms
- a. Single individual or family owned→ Corporations are owned by a multitude of
individuals who hold shares (cronies→ shareholders)
- b. Numerous small-scale firms→ Large corporations
- c. Owners operated their firms by themselves→ Separation of the ownership of the
enterprise and control of its operations
- d. Owners had unlimited liabilities if bankrupted→ Now shareholders have only limited
liabilities
(2) Workers
a. Homogeneous workers commanded by few capitalists → emergence of various
salaried managers and trade union
b. No regulation on children and women's labor → Strong regulation on children and
women + dominance of male workers in workplace
c. Long working hours & low wage → efficiency wage (pay higher wages to skilled
workers to hold them longer)
(3) Markets
a. Activities of numerous small firms were subject to market and price mechanisms.
Market competition was intense, and market had a pricing power over firms → Markets
are populated by large firms & market price is substantially affected by few firms
b. Localized markets with a limited range of manufactured goods → National & global
markets with a various range of goods and services
Three dimensions
(0) Private Property
(1) Firms
(2) Workers
(3) Markets
Classical Capitalism (Adam Smith)
(1) Firms → size, number in a market, who owned?
- Numerous small firms in a market
- Individual or family owned
- Owners had unlimited liabilities in the event of bankruptcy
(2) Wage Workers
- Workers are supervised and commanded by an individual capitalist or an entrepreneur
family → a very simple hierarchy
- No regulations on children and women’s labor conditions
- Long labor hours
(3) Markets
- Competitive
- Single or few firms cannot change market prices
Similarities Between Classical & Today’s Capitalism
What are the common constituting elements both in Adam Smith’s capitalism and
in today’s capitalism?
Capitalism = an economic system as a specific combination of private property,
markets, and firms
(1) Private ownership of capital goods
(2) Purchasing the labor power of wage workers through the market
(3) Market exchanges of the output of production for monetary profit
(4) Profit-seeking of the firm as its business objective
, Classical Capitalism vs. Modern Capitalism
(1) Evolution of Firms
- a. Single individual or family owned→ Corporations are owned by a multitude of
individuals who hold shares (cronies→ shareholders)
- b. Numerous small-scale firms→ Large corporations
- c. Owners operated their firms by themselves→ Separation of the ownership of the
enterprise and control of its operations
- d. Owners had unlimited liabilities if bankrupted→ Now shareholders have only limited
liabilities
(2) Workers
a. Homogeneous workers commanded by few capitalists → emergence of various
salaried managers and trade union
b. No regulation on children and women's labor → Strong regulation on children and
women + dominance of male workers in workplace
c. Long working hours & low wage → efficiency wage (pay higher wages to skilled
workers to hold them longer)
(3) Markets
a. Activities of numerous small firms were subject to market and price mechanisms.
Market competition was intense, and market had a pricing power over firms → Markets
are populated by large firms & market price is substantially affected by few firms
b. Localized markets with a limited range of manufactured goods → National & global
markets with a various range of goods and services