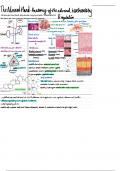
Biol 200 methods/techniques
With Accurate Answer
2024/2025
all proteins are negatively charged at _____?
high pHs
all proteins are positively charged at _____?
low pHs
Cells that do not take up the plasmid die. Why?
bc the plasmid has the ampicillin antibiotic and on ampicillin plates, cells without the plasmid
die
Centrifugation
Function - separates particles and molecules that differ in mass or density
process - rapid spinning generates centrifugal force, which acts on particles in a suspended
medium
-->if particles are denser than medium they go to the bottom of the tube
-->if particles are less dense, they will go to the top of the tube
-->if particles have the same density they will stay where they are
Chromatography
Function - separates proteins based on their different interactions with an immobile phase
cleavage by EcoR1 results in ___?
sticky ends, meaning that different pieces of DNA that don't come from the same source can be
stuck together
Detecting polymorphisms with probes
If there is a mutation that affect the EcoRI site, it doesn't cut so you end up with one combined
fragment, your probe will recognize the whole fragment
--Means that there is a polymorphism that changes the DNA so that the EcoRI site no longer
recognizes it, know that it's a different size band
, Does the fragmentation in MS-MS break every peptide bond in every molecule, reducing the
peptide to its individual amino acids?
NOO--the fragmentation is partial and random, on average only one or a few peptide bonds per
molecule is broken
EMSA (electrophoretic mobility shift assay)
Classic means to identify protein involved in regulating transcription, based on the idea that a
given protein or protein complex can interact w specific segment of DNA (regulatory sequence)
and in doing so form a protein DNA complex
Explain how primary and secondary antibodies work
primary antibodies, from species A are made against something foreign, like COVID antibodies.
Secondary antibodies are against human covid antibodies introduced into species B
Explain the annealing step in PCR?
temperature is decreased so oligonucleotide primers can base pair to complementary DNA
template
Explain the extension step in PCR?
polymerase extends primer to form nascent DNA strand, by adding free dNTPs
Explain the steps of a western blot
run SDS -PAGE on protein mixture of interest, blot the membrane with a with primary
antibody--against protein of interest then blot secondary antibody against primary antibody
How does antibody-affinity chromatography work?
antibodies specific for any protein can be covalently coupled to the solid phase, and when the
protein mixture flows through, only the protein the antibody binds to is retained. All the other
proteins can be washed then the target protein is released from antibody by lowering the pH
How does EcoR1 cut?
recognizes a site and makes staggered cuts at specific sequences
How does gel filtration chromatography separate proteins? How does this work?
With Accurate Answer
2024/2025
all proteins are negatively charged at _____?
high pHs
all proteins are positively charged at _____?
low pHs
Cells that do not take up the plasmid die. Why?
bc the plasmid has the ampicillin antibiotic and on ampicillin plates, cells without the plasmid
die
Centrifugation
Function - separates particles and molecules that differ in mass or density
process - rapid spinning generates centrifugal force, which acts on particles in a suspended
medium
-->if particles are denser than medium they go to the bottom of the tube
-->if particles are less dense, they will go to the top of the tube
-->if particles have the same density they will stay where they are
Chromatography
Function - separates proteins based on their different interactions with an immobile phase
cleavage by EcoR1 results in ___?
sticky ends, meaning that different pieces of DNA that don't come from the same source can be
stuck together
Detecting polymorphisms with probes
If there is a mutation that affect the EcoRI site, it doesn't cut so you end up with one combined
fragment, your probe will recognize the whole fragment
--Means that there is a polymorphism that changes the DNA so that the EcoRI site no longer
recognizes it, know that it's a different size band
, Does the fragmentation in MS-MS break every peptide bond in every molecule, reducing the
peptide to its individual amino acids?
NOO--the fragmentation is partial and random, on average only one or a few peptide bonds per
molecule is broken
EMSA (electrophoretic mobility shift assay)
Classic means to identify protein involved in regulating transcription, based on the idea that a
given protein or protein complex can interact w specific segment of DNA (regulatory sequence)
and in doing so form a protein DNA complex
Explain how primary and secondary antibodies work
primary antibodies, from species A are made against something foreign, like COVID antibodies.
Secondary antibodies are against human covid antibodies introduced into species B
Explain the annealing step in PCR?
temperature is decreased so oligonucleotide primers can base pair to complementary DNA
template
Explain the extension step in PCR?
polymerase extends primer to form nascent DNA strand, by adding free dNTPs
Explain the steps of a western blot
run SDS -PAGE on protein mixture of interest, blot the membrane with a with primary
antibody--against protein of interest then blot secondary antibody against primary antibody
How does antibody-affinity chromatography work?
antibodies specific for any protein can be covalently coupled to the solid phase, and when the
protein mixture flows through, only the protein the antibody binds to is retained. All the other
proteins can be washed then the target protein is released from antibody by lowering the pH
How does EcoR1 cut?
recognizes a site and makes staggered cuts at specific sequences
How does gel filtration chromatography separate proteins? How does this work?