Computer Network - Answers Interconnection of computers and other electronic devices for sharing
expensive peripherals and information.
LAN - Answers Network covering small geographical areas.
MAN - Answers Collection of LANs covering an area larger than a LAN.
WAN - Answers Collection of LANs and MANs covering a country or globe.
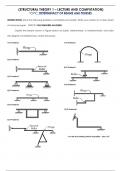
Bus Topology - Answers Network where computers are connected to a common cable forming a straight
line, using terminators and coaxial cable.
Star Topology - Answers Network where computers connect through a central point like a hub or switch
using UTP cable.
Ring Topology - Answers Network where computers are connected in a circular manner, using a special
token and having a circular flow of messages.
Physical Connection - Answers Actual physical contact of network devices using wired or wireless means.
Logical Connection - Answers Accessing network resources using a valid name and password.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) - Answers Network where each computer can act as a client and server, sharing
resources equally.
Client-Server - Answers Network where some computers request services (clients) and others respond
to requests (servers).
Transmission Media - Answers Enables computers to send and receive messages, not guaranteeing
message understanding.
Twisted Pair - Answers Copper cabling used in LANs, with categories like Cat 5e supporting up to 1Gbps.
Fiber Optics - Answers Consists of glass or plastic optical strands offering high bandwidth and improved
security.
Wireless - Answers Includes radio frequency, microwave, satellite, and infrared transmissions.
IP Address - Answers Unique number assigned to devices on a network, with IPv4 and IPv6 versions.
Subnet - Answers Smaller network connected to a larger one through a router, having its own address
system.
RTO - Answers Request Timeout in networking.
Straight-through cable - Answers Cable connecting dissimilar devices like PC to Router.