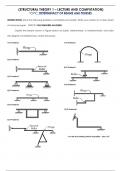
AIS - Chapter 2: Introduction
to Transaction Processing
fully solved & updated
Access Method - answer is the technique used to locate records and
to navigate through the database or file
accounting records - answer Documents, Journals, and Ledgers
alphabetic codes - answer are used for many of the same purposes
as numeric codes
alphanumeric codes - answer numeric codes where pure alphabetic
codes or alphabetic characters are embedded with
archive file - answer contains records of past transactions that are
retained for future reference.
audit trail - answer a path that allows a transaction to be traced
through a data processing system from point of origin to output or
backward from output to point of origin
batch - answer is a group of similar transactions (such as sales
orders) that are accumulated over time and then processed
together
batch systems - answer assemble transactions into groups for
processing
, block code - answer is a variation on sequential coding that partly
remedies the disadvantages just
described.
cardinality - answer is the numeric mapping between entity
instances and is a degree of the relationship between two entities
chart of accounts - answer the basis for the general ledger and is
thus
critical to a firm's financial and management reporting systems.
conversion cycle - answer is composed of two major subsystems:
the production system and the cost accounting system
data flow diagram (DFD) - answer uses symbols to represent the
entities, processes, data flows, and data stores that pertain to a
system.
data model - answer is the blueprint for what ultimately will become
the physical database.
data structures - answer constitute the physical and logical
arrangement of data in files and databases.
direct access files - answer random access files
direct access structures - answer store data at a unique location,
known as an address, on a hard disk or floppy
disk.
to Transaction Processing
fully solved & updated
Access Method - answer is the technique used to locate records and
to navigate through the database or file
accounting records - answer Documents, Journals, and Ledgers
alphabetic codes - answer are used for many of the same purposes
as numeric codes
alphanumeric codes - answer numeric codes where pure alphabetic
codes or alphabetic characters are embedded with
archive file - answer contains records of past transactions that are
retained for future reference.
audit trail - answer a path that allows a transaction to be traced
through a data processing system from point of origin to output or
backward from output to point of origin
batch - answer is a group of similar transactions (such as sales
orders) that are accumulated over time and then processed
together
batch systems - answer assemble transactions into groups for
processing
, block code - answer is a variation on sequential coding that partly
remedies the disadvantages just
described.
cardinality - answer is the numeric mapping between entity
instances and is a degree of the relationship between two entities
chart of accounts - answer the basis for the general ledger and is
thus
critical to a firm's financial and management reporting systems.
conversion cycle - answer is composed of two major subsystems:
the production system and the cost accounting system
data flow diagram (DFD) - answer uses symbols to represent the
entities, processes, data flows, and data stores that pertain to a
system.
data model - answer is the blueprint for what ultimately will become
the physical database.
data structures - answer constitute the physical and logical
arrangement of data in files and databases.
direct access files - answer random access files
direct access structures - answer store data at a unique location,
known as an address, on a hard disk or floppy
disk.