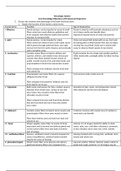
Growth, Development and Nutrition
1) Grown Development-Maturation
a) Directional pattern
i) Cephalocaudal = head to toe
ii) Proximodistal = inner to outer
b) Height
i) Family trait
ii) Linear due to skeletal growth
c) Weight- composed of high percentage of water
i) Birth weight double by 6 months
ii) Birth weight triples by 12 months
iii) After 1 year, weight gain is 4-6 lbs per year until puberty
2) Metabolic rate = higher in children than adults
3) Sleep patterns = may altered by culture
a) Some cultures value sleep more than others
i) Include naps are part of daily routine
b) Can reflect shift parent works
4) Growth Standards
a) Allow child to be compared to others and himself
b) Denver II Screening - tests if child is developing appropriately
i) Anything to left of line, child should be doing by that age.
c) CDC Growth line – measures/plots the percentile of chid
height/weight chart
i) One for boys and girls
ii) They should follow their growth curve on the graph
5) Influencing Factors of Uniqueness
a) Hereditary traits
i) Eye
ii) Hair color
iii) Physical resemblance
b) Nationality and race
c) Gender
d) Environment
e) Ordinal position in the family
i) Birth order
6) Families
a) Traditional = two parents and their children
b) Nuclear family = basic unit of American society
, i) Mother, father and their children
ii) 25% of households
c) Extended families = multiple generations living together under
one roof
i) 3 generations
d) One parent family = single parent households
e) Blended Families
i) Mom with children remarry a dad with children and them
they have their own family
ii) Family success requires:
(1)Problem solving
(2)Communication
(3)Flexibility
f) Homeless families = modern day problem
7) Freud (think sexual)
a) Infancy = orality
i) Exploring the world by mouth; babies put things in their
mouth
b) Early childhood (toddler) = anality
i) Learning to give and take
c) Late childhood (preschool/school age) = phallic/oedipal
i) Becoming aware of self as sexual being/sexuality
ii) School age = latency
iii) Focusing on peer relations
iv) Learning to live in groups and gaining more knowledge
d) Adolescence = genitality
i) Moral principles
ii) Having more perception on the world
iii) Accepting right and wrong
iv) Having personal conscious
v) Empathy
8) Erikson
a) Infancy = trust vs. Mistrust
i) Babies need to trust someone is going to meet their needs
ii) Babies recognize mom more distinctly
b) Early childhood (toddler) = autonomy vs shame and doubt
i) Accepting reality vs pleasure
ii) Figuring out themselves and how to talk
c) Late childhood (preschool) = initiative vs. Guilt
i) Exploring body and environment
, ii) Realize there is a difference between boys and girls
d) School age = industry vs. Inferiority
i) Learning to win recognition by producing things
ii) Exploring
iii) Collecting
iv) Relating to people of their own sex
e) Adolescence = identity vs. Role confusion
i) Selecting vocation
ii) Separating from family
iii) Integrating personality
iv) Accepting right vs wrong
v) Empathy
9) Piaget
a) Infancy = self-centered
b) Childhood
i) 2-7 years = preoperational (egocentric and think all see
the world as the child does)
(1)Preconceptual (2-4 years) - child not capable of
reason
(2)Perceptual (4-7 years) - some reason but only able to
concentrate on one thing at a time.
c) School age (7-11 years) = concrete operational
i) Reasoning is logical but limited to own experience/what
they know
d) Adolescence (11-16 years) = formal operational
i) Develops abstract concepts and problem solving
10) Moral Development- Kohlberg
a) Preconventional (4-7 years)- children try to be obedient for fear
of punishment
b) Conventional (7-11 years) - children show conformity & loyalty &
focus on obeying rules
c) Postconventional (12+)- moral values are developed to solve
complex problems with emphasis on individual conscience within
the society.
11) Nutrition
a) Child’s nutritional heritage
i) Factors influencing feeding children:
(1)Misinformation
(2)Income
(3)Folklore