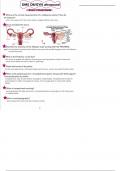
Some oxidation reduction Galvanic/voltaic cell
concepts and terms
- know the design of a
- oil rig galvanic cell
- oxidation is loss (of - anode: where oxidation
electrons) occurs
- reduction is gain (of - anode is where positive
electrons) electrode is
- redox rxns involves transfer - cathode: where reduction
of electrons takes places
- the element that gets oxidized - cathode is where
is the reducing agent negative electrode is
- element that gets reduced is - ions flow from anode to
oxidizing agent cathode
- oxidation and reduction - salt bridge: u-shaped tube
always occur together with solution of an inert
• oxidizing agent are strongest electrolyte (like kno3)
on top left of table, decrease - maintains electrical
in strength as you go down neutrality by flow of
• reducing Agent strongest on electrons
bottom right, decrease as you - keeps solution around
go up each electrode neutral
Cell potentials and - without, there would be
standard cell potentials buildup of charge and
- cell potential: driving force the rxn would come to
that causes e- to flow from halt
anode to cathode - anion goes to anode
- also called e cell
·
- cation goes to cathode
- units: volts (v) or (j/c)
- standard cell potential: the
cell potential that is
obtained when cell is
operated under standard
state
concepts and terms
- know the design of a
- oil rig galvanic cell
- oxidation is loss (of - anode: where oxidation
electrons) occurs
- reduction is gain (of - anode is where positive
electrons) electrode is
- redox rxns involves transfer - cathode: where reduction
of electrons takes places
- the element that gets oxidized - cathode is where
is the reducing agent negative electrode is
- element that gets reduced is - ions flow from anode to
oxidizing agent cathode
- oxidation and reduction - salt bridge: u-shaped tube
always occur together with solution of an inert
• oxidizing agent are strongest electrolyte (like kno3)
on top left of table, decrease - maintains electrical
in strength as you go down neutrality by flow of
• reducing Agent strongest on electrons
bottom right, decrease as you - keeps solution around
go up each electrode neutral
Cell potentials and - without, there would be
standard cell potentials buildup of charge and
- cell potential: driving force the rxn would come to
that causes e- to flow from halt
anode to cathode - anion goes to anode
- also called e cell
·
- cation goes to cathode
- units: volts (v) or (j/c)
- standard cell potential: the
cell potential that is
obtained when cell is
operated under standard
state