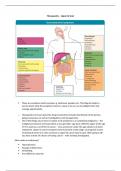
Calculating allele
frequency :
P Cdominant frequency) + & Crecessive
frequency) =
1
Hardy-Weinberg principle In a stable population with no disturbing factors the awdle
:
↳ frequency will remain constant and no evolution will
2
occur
p q2 1 p2 homozygous dominant 2pg : heterozygous Recessive
:
:
+
2pq + =
↳
g ... genotype frequency
2 =
Recessive =
p .
Factors
affecting evolution mutation , Sexual selection immigration B emigration
:
, ,
drift
genetic , natural selection
Density dependent factors competition predation parasitism communicable disease
:
, , ,
Density independent factors Climate change natural disasters Seasonal change human activity
:
, , ,
Population Bottleneck Great loss genetic variation after a catastrophic effect
in
:
Founder effect Colonies established by isolated individuals with small
gene pools
:
Directional Selection is
Environmental
change so the normal phenotype longer the best
:
no
Disruptive Selection
:
The extremes are are selected for instead of the norm .
Speciation of a new species through evolution
:
formation
Allopatric speciation Speciation due to physical barriers i e a river
:
. .
Sympatric speciation Speciation in the same habitat due to interspecies breeding
:
frequency :
P Cdominant frequency) + & Crecessive
frequency) =
1
Hardy-Weinberg principle In a stable population with no disturbing factors the awdle
:
↳ frequency will remain constant and no evolution will
2
occur
p q2 1 p2 homozygous dominant 2pg : heterozygous Recessive
:
:
+
2pq + =
↳
g ... genotype frequency
2 =
Recessive =
p .
Factors
affecting evolution mutation , Sexual selection immigration B emigration
:
, ,
drift
genetic , natural selection
Density dependent factors competition predation parasitism communicable disease
:
, , ,
Density independent factors Climate change natural disasters Seasonal change human activity
:
, , ,
Population Bottleneck Great loss genetic variation after a catastrophic effect
in
:
Founder effect Colonies established by isolated individuals with small
gene pools
:
Directional Selection is
Environmental
change so the normal phenotype longer the best
:
no
Disruptive Selection
:
The extremes are are selected for instead of the norm .
Speciation of a new species through evolution
:
formation
Allopatric speciation Speciation due to physical barriers i e a river
:
. .
Sympatric speciation Speciation in the same habitat due to interspecies breeding
: