Tutorial 3 - Integration theories
Assignment 1
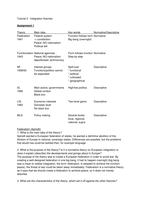
Theory Main idea Key words Normative/Descriptive
Federalism Federal system Function follows form Normative
1941 -> constitution Big bang (overnight)
Peace: NO nationalism
Political will
Functionalism National agencies Form follows function Normative
1943 Peace: NO nationalism Step-by-step
depoliticised, technocracy
NF Interest groups Spill-over Descriptive
1958/63 Functions/politics cannot * functional
be separated * political
* cultivated
* geographical
IG Main actors: governments High/low politics Descriptive
1966 Global context
Black box
LIG Economic interests Two-level game Descriptive
1993 Domestic level
No black box
MLG Policy making Several levels: Descriptive
local, regional,
national, supra
Federalism (Spinelli)
1. What is the main idea of the theory?
Spinelli wanted a European federation of states, he wanted a definitive abolition of the
division of Europe in national, sovereign states. Differences are possible, but the problems
that would rise could be tackled then, for example language.
2. What is the purpose of the theory? Is it a normative theory on European integration or
does it explain (describe) the developments and goings about in Europe?
The purpose of the theory was to create a European federation in order to avoid war. By
creating a well-designed federation in one big bang, it had to happen overnight (big bang
was a mean to realise integration, the form: federation, is adopted to achieve the function:
peace), the threat of war could be taken away immediately. Federalism is a normative theory
as it says that we should create a federation to achieve peace, so it does not merely
describe.
3. What are the characteristics of the theory, which set it off against the other theories?
Assignment 1
Theory Main idea Key words Normative/Descriptive
Federalism Federal system Function follows form Normative
1941 -> constitution Big bang (overnight)
Peace: NO nationalism
Political will
Functionalism National agencies Form follows function Normative
1943 Peace: NO nationalism Step-by-step
depoliticised, technocracy
NF Interest groups Spill-over Descriptive
1958/63 Functions/politics cannot * functional
be separated * political
* cultivated
* geographical
IG Main actors: governments High/low politics Descriptive
1966 Global context
Black box
LIG Economic interests Two-level game Descriptive
1993 Domestic level
No black box
MLG Policy making Several levels: Descriptive
local, regional,
national, supra
Federalism (Spinelli)
1. What is the main idea of the theory?
Spinelli wanted a European federation of states, he wanted a definitive abolition of the
division of Europe in national, sovereign states. Differences are possible, but the problems
that would rise could be tackled then, for example language.
2. What is the purpose of the theory? Is it a normative theory on European integration or
does it explain (describe) the developments and goings about in Europe?
The purpose of the theory was to create a European federation in order to avoid war. By
creating a well-designed federation in one big bang, it had to happen overnight (big bang
was a mean to realise integration, the form: federation, is adopted to achieve the function:
peace), the threat of war could be taken away immediately. Federalism is a normative theory
as it says that we should create a federation to achieve peace, so it does not merely
describe.
3. What are the characteristics of the theory, which set it off against the other theories?