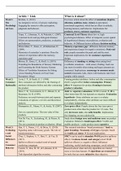
astrophysics
lenses:
(we assume that lenses are
i.
thin so light rays can pass
convex: concave: straight through the
centre)
images can be:
-real or virtual
-inverted or upright
-enlarged or diminished
the type of image formed depends on the position of the object and the focal length:
beyond 2f = real, inverted, diminished
at 2f = real, inverted, same size
between 2f and f = real, inverted, enlarged
at f = real, inverted, at infinity
less than f = virtual, upright, magnified
a
refracting telescope:
consists of 2 lenses:
objective lens - real diminished image of the object
eyepiece lens - acts as a magnifying glass eyepiece lens
normal adjustment is when the distance between the
objective lens and the eyepiece lens is the sum of objective lens
their focal lengths (the principal focus is in the same
place)
dispersion - lens causes white light to separate into its component colours
chromatic aberration - objective lens focuses the different colours over a range of focal
lengths
spherical aberration - spherical curvature results in light rays from the edge being deviated
more than necessary and having a shorter focal length
achromatic doublet - objective lens is made up of one convex lens (crown glass) and one
concave lens (flint glass) cemented together, the different dispersion and shapes help to
minimise any aberration focal length
angular of objective
magnification lens
f
M = fo
efocal length of
eyepiece lens
, reflecting telescope: collecting power a
lobjective diameter)
concave mirror P, d,2 ccd2 resolvable
Si
=
P2 dz
convex mirror
angle of diffraction wavelength
eyepiece
-
G
objective diameter
T
rayleigh criterion: two point objects can be resolved if their angular separation is at least 0D
=
atmospheric opacity: a measure of the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the
atmosphere, as a function of wavelength
radio telescopes infrared telescopes
-measures one wavelength at a time, builds up a -similar to reflecting optical telescopes, but
contour map of the intensity of each their detectors must be kept very cold
wavelength -lower resolving power than optical
-can be ground-based because the atmosphere telescopes
doesn't block most radio wavelengths -mirrors can have more impurities than is
-dish can be built of wire mesh (easy, cheap, required for radio telescopes
lighter) -can be much smaller than radio telescopes
-focus radio energy using a parabolic 'objective' with the same resolving power
dish antenna -mostly from space-based observatories or
-large diameter dish antenna to get a good high altitudes to avoid absorption by the
angular resolution atmosphere
-need large structures to support + steer them -some infrared windows (wavelength
-can operate during the day + night ranges) for which infrared observations
-must be away from artificial sources of radio from the ground are possible with minimal
interference atmospheric absorption
ultraviolet telescopes x-ray telescopes
-can detect objects not -much smaller than radio telescopes for same resolution
visible at other -must be placed in orbit
wavelengths -several metres long due to long focal length
-higher resolving power -lower collecting powers than other types of telescope
than optical telescopes
-smaller than radio gamma-ray telescopes
telescopes for the same
resolution -smaller than other telescopes as they don't need to focus
-must be in orbit to light
make observations -some observations can be made from earth's surface
-mirrors must be -cannot focus gamma rays into images with the same
smoother than optical clarity as other telescopes
telescopes -many have to be placed in orbit
-satellites need to shield or account for rays coming in from
other directions
lenses:
(we assume that lenses are
i.
thin so light rays can pass
convex: concave: straight through the
centre)
images can be:
-real or virtual
-inverted or upright
-enlarged or diminished
the type of image formed depends on the position of the object and the focal length:
beyond 2f = real, inverted, diminished
at 2f = real, inverted, same size
between 2f and f = real, inverted, enlarged
at f = real, inverted, at infinity
less than f = virtual, upright, magnified
a
refracting telescope:
consists of 2 lenses:
objective lens - real diminished image of the object
eyepiece lens - acts as a magnifying glass eyepiece lens
normal adjustment is when the distance between the
objective lens and the eyepiece lens is the sum of objective lens
their focal lengths (the principal focus is in the same
place)
dispersion - lens causes white light to separate into its component colours
chromatic aberration - objective lens focuses the different colours over a range of focal
lengths
spherical aberration - spherical curvature results in light rays from the edge being deviated
more than necessary and having a shorter focal length
achromatic doublet - objective lens is made up of one convex lens (crown glass) and one
concave lens (flint glass) cemented together, the different dispersion and shapes help to
minimise any aberration focal length
angular of objective
magnification lens
f
M = fo
efocal length of
eyepiece lens
, reflecting telescope: collecting power a
lobjective diameter)
concave mirror P, d,2 ccd2 resolvable
Si
=
P2 dz
convex mirror
angle of diffraction wavelength
eyepiece
-
G
objective diameter
T
rayleigh criterion: two point objects can be resolved if their angular separation is at least 0D
=
atmospheric opacity: a measure of the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the
atmosphere, as a function of wavelength
radio telescopes infrared telescopes
-measures one wavelength at a time, builds up a -similar to reflecting optical telescopes, but
contour map of the intensity of each their detectors must be kept very cold
wavelength -lower resolving power than optical
-can be ground-based because the atmosphere telescopes
doesn't block most radio wavelengths -mirrors can have more impurities than is
-dish can be built of wire mesh (easy, cheap, required for radio telescopes
lighter) -can be much smaller than radio telescopes
-focus radio energy using a parabolic 'objective' with the same resolving power
dish antenna -mostly from space-based observatories or
-large diameter dish antenna to get a good high altitudes to avoid absorption by the
angular resolution atmosphere
-need large structures to support + steer them -some infrared windows (wavelength
-can operate during the day + night ranges) for which infrared observations
-must be away from artificial sources of radio from the ground are possible with minimal
interference atmospheric absorption
ultraviolet telescopes x-ray telescopes
-can detect objects not -much smaller than radio telescopes for same resolution
visible at other -must be placed in orbit
wavelengths -several metres long due to long focal length
-higher resolving power -lower collecting powers than other types of telescope
than optical telescopes
-smaller than radio gamma-ray telescopes
telescopes for the same
resolution -smaller than other telescopes as they don't need to focus
-must be in orbit to light
make observations -some observations can be made from earth's surface
-mirrors must be -cannot focus gamma rays into images with the same
smoother than optical clarity as other telescopes
telescopes -many have to be placed in orbit
-satellites need to shield or account for rays coming in from
other directions